
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans which encode cell-surface proteins responsible for regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) found in many animals.

HLA-DR is an MHC class II cell surface receptor encoded by the human leukocyte antigen complex on chromosome 6 region 6p21.31. The complex of HLA-DR and peptide, generally between 9 and 30 amino acids in length, constitutes a ligand for the T-cell receptor (TCR). HLA were originally defined as cell surface antigens that mediate graft-versus-host disease. Identification of these antigens has led to greater success and longevity in organ transplant.

HLA-DQ (DQ) is a cell surface receptor protein found on antigen-presenting cells. It is an αβ heterodimer of type MHC class II. The α and β chains are encoded by two loci, HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DQB1, that are adjacent to each other on chromosome band 6p21.3. Both α-chain and β-chain vary greatly. A person often produces two α-chain and two β-chain variants and thus 4 isoforms of DQ. The DQ loci are in close genetic linkage to HLA-DR, and less closely linked to HLA-DP, HLA-A, HLA-B and HLA-C.

HLA-DQ8 (DQ8) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within the HLA-DQ (DQ) serotype group. DQ8 is a split antigen of the DQ3 broad antigen. DQ8 is determined by the antibody recognition of β8 and this generally detects the gene product of DQB1*0302.
HLA-DQ2 (DQ2) is a serotype group within HLA-DQ (DQ) serotyping system. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of β2 subset of DQ β-chains. The β-chain of DQ is encoded by HLA-DQB1 locus and DQ2 are encoded by the HLA-DQB1*02 allele group. This group currently contains two common alleles, DQB1*0201 and DQB1*0202. HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQB1*02 are almost synonymous in meaning. DQ2 β-chains combine with α-chains, encoded by genetically linked HLA-DQA1 alleles, to form the cis-haplotype isoforms. These isoforms, nicknamed DQ2.2 and DQ2.5, are also encoded by the DQA1*0201 and DQA1*0501 genes, respectively.

HLA-DQ4 (DQ4) is a serotype subgroup within HLA-DQ(DQ) serotypes. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of β4 subset of DQ β-chains. The β-chain of DQ is encoded by HLA-DQB1 locus and DQ4 are encoded by the HLA-DQB1*04 allele group. This group currently contains 2 common alleles, DQB1*0401 and DQB1*0402. HLA-DQ4 and HLA-DQB1*04 are almost synonymous in meaning. DQ4 β-chains combine with α-chains, encoded by genetically linked HLA-DQA1 alleles, to form the cis-haplotype isoforms. These isoforms, nicknamed DQ4.3 and DQ4.4, are also encoded by the DQA1*0303 and DQA1*0401 genes, respectively.

HLA-DQ6 (DQ6) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-DQ (DQ) serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of β6 subset of DQ β-chains. The β-chain of DQ isoforms are encoded by HLA-DQB1 locus and DQ6 are encoded by the HLA-DQB1*06 allele group. This group currently contains many common alleles, DQB1*0602 is the most common. HLA-DQ6 and DQB1*06 are almost synonymous in meaning. DQ6 β-chains combine with α-chains, encoded by genetically linked HLA-DQA1 alleles, to form the cis-haplotype isoforms. For DQ6, however, cis-isoform pairing only occurs with DQ1 α-chains. There are many haplotypes of DQ6.

HLA-DQ9 (DQ9) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within the HLA-DQ (DQ) serotype group. DQ9 is a split antigen of the DQ3 broad antigen. DQ9 is determined by the antibody recognition of β9 and this generally detects the gene product of DQB1*0303.

HLA-DQ7 (DQ7) is an HLA-DQ serotype that recognizes the common HLA DQB1*0301 and the less common HLA DQB1*0304 gene products. DQ7 is a form of 'split antigen' of the broad antigen group DQ3 which also contains DQ8 and DQ9.

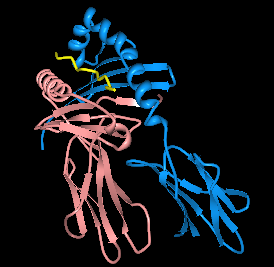
HLA-DQ1 is a serotype that covers a broad range of HLA-DQ haplotypes. Historically it was identified as a DR-like alpha chain called DC1; later, it was among 3 types DQw1, DQw2 and DQw3. Of these three serotyping specificities only DQw1 recognized DQ alpha chain. The serotype is positive in individuals who bear the DQA1*01 alleles. The most frequently found within this group are: DQA1*0101, *0102, *0103, and *0104. In the illustration on the right, DQ1 serotyping antibodies recognizes the DQ α (magenta), where antibodies to DQA1* gene products bind variable regions close to the peptide binding pocket.

HLA-DR52 is an HLA-DR serotype that recognizes gene products of HLA-DRB3 locus. Three allele groups can produce 35 isoforms.

HLA-DR17 (DR17) is an HLA-DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*0301 and *0304 gene products. DR17 is found at high frequency in Western Europe. DR17 is part of the broader antigen group HLA-DR3 and is very similar to the group HLA-DR18.

HLA-DR16(DR16) is a HLA-DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*1601, *1602 and *1604 gene products. DR16 is found in the Mediterranean at modest frequencies. DR16 is part of the older HLA-DR2 serotype group which also contains the similar HLA-DR15 antigens.

HLA-DR15 (DR15) is a HLA-DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*1501 to *1505 and *1507 gene products. DR15 is found at high levels from Ireland to Central Asia. DR15 is part of the older HLA-DR2 serotype group which also contains the similar HLA-DR16 antigens.

HLA-DR13(DR13) is a HLA-DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*1301 to *13082, *1310 and some other *13 gene products. DR13 serotype is a split antigen of the older HLA-DR6 serotype group which also contains the similar HLA-DR14 antigens.

HLA-DR14(DR14) is a HLA-DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*1401 to *1408, *1410 to *1418, and other *14 gene products. DR14 serotype is a split antigen of the older HLA-DR6 serotype group which also contains the similar HLA-DR13 antigens.

HLA-DR3 is composed of the HLA-DR17 and HLA-DR18 split 'antigens' serotypes. DR3 is a component gene-allele of the AH8.1 haplotype in Northern and Western Europeans. Genes between B8 and DR3 on this haplotype are frequently associated with autoimmune disease. Type 1 diabetes mellitus is associated with HLA-DR3 or HLA-DR4. Nearly half the US population has either DR3 or DR4, yet only a small percentage of these individuals will develop type 1 diabetes.
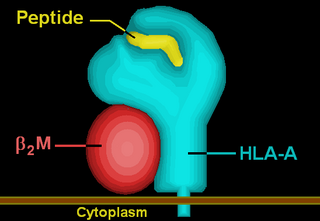
HLA-A3 (A3) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-A serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of α3 subset of HLA-A α-chains. For A3, the alpha, "A", chain are encoded by the HLA-A*03 allele group and the β-chain are encoded by B2M locus. This group currently is dominated by A*03:01. A3 and A*03 are almost synonymous in meaning. A3 is more common in Europe, it is part of the longest known multigene haplotype, A3~B7~DR15~DQ6.
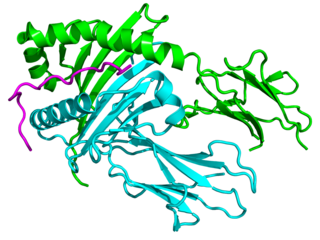
Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ alpha 1, also known as HLA-DQA1, is a human gene present on short arm of chromosome 6 (6p21.3) and also denotes the genetic locus which contains this gene. The protein encoded by this gene is one of two proteins that are required to form the DQ heterodimer, a cell surface receptor essential to the function of the immune system.
HLA B7-DR15-DQ6 is a multigene haplotype that covers a majority of the human major histocompatibility complex on chromosome 6. A multigene haplotype is set of inherited alleles covering several genes, or gene-alleles, common multigene haplotypes are generally the result of descent by common ancestry. Chromosomal recombination fragments multigene haplotypes as the distance to that ancestor increases in number of generations.



