The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following the cephalic phase in which the sight and smell of food and the act of chewing are stimuli. In the stomach a chemical breakdown of food takes place by means of secreted digestive enzymes and gastric acid.

Peptic ulcer disease is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with upper abdominal pain, and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or poor appetite. About a third of older people with peptic ulcers have no symptoms. Complications may include bleeding, perforation, and blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases.
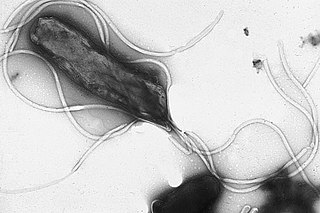
Helicobacter pylori, previously known as Campylobacter pylori, is a gram-negative, flagellated, helical bacterium. Mutants can have a rod or curved rod shape that exhibits less virulence. Its helical body is thought to have evolved to penetrate the mucous lining of the stomach, helped by its flagella, and thereby establish infection. The bacterium was first identified as the causal agent of gastric ulcers in 1983 by Australian physician-scientists Barry Marshall and Robin Warren. In 2005, they were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery.

Intrinsic factor (IF), cobalamin binding intrinsic factor, also known as gastric intrinsic factor (GIF), is a glycoprotein produced by the parietal cells (in humans) or chief cells (in rodents) of the stomach. It is necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12 later on in the distal ileum of the small intestine. In humans, the gastric intrinsic factor protein is encoded by the CBLIF gene. Haptocorrin (transcobalamin I) is another glycoprotein secreted by the salivary glands which binds to vitamin B12. Vitamin B12 is acid-sensitive and in binding to haptocorrin it can safely pass through the acidic stomach to the duodenum.

Pernicious anemia is a disease where not enough red blood cells are produced due to a deficiency of vitamin B12. Those affected often have a gradual onset. The most common initial symptoms are feeling tired and weak. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, feeling faint, a smooth red tongue, pale skin, chest pain, nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, heartburn, numbness in the hands and feet, difficulty walking, memory loss, muscle weakness, poor reflexes, blurred vision, clumsiness, depression, and confusion. Without treatment, some of these problems may become permanent.

Gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid (HCl) by the parietal cells of the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by G cells in the pyloric antrum of the stomach, duodenum, and the pancreas.

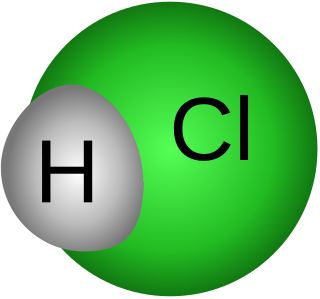
Gastric acid or stomach acid is the acidic component – hydrochloric acid of gastric juice, produced by parietal cells in the gastric glands of the stomach lining. With a pH of between one and three, gastric acid plays a key role in the digestion of proteins by activating digestive enzymes, which together break down the long chains of amino acids of proteins. Gastric acid is regulated in feedback systems to increase production when needed, such as after a meal. Other cells in the stomach produce bicarbonate, a base, to buffer the fluid, ensuring a regulated pH. These cells also produce mucus – a viscous barrier to prevent gastric acid from damaging the stomach. The pancreas further produces large amounts of bicarbonate and secretes bicarbonate through the pancreatic duct to the duodenum to neutralize gastric acid passing into the digestive tract.
Parietal cells (also known as oxyntic cells) are epithelial cells in the stomach that secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor. These cells are located in the gastric glands found in the lining of the fundus and body regions of the stomach. They contain an extensive secretory network of canaliculi from which the HCl is secreted by active transport into the stomach. The enzyme hydrogen potassium ATPase (H+/K+ ATPase) is unique to the parietal cells and transports the H+ against a concentration gradient of about 3 million to 1, which is the steepest ion gradient formed in the human body. Parietal cells are primarily regulated via histamine, acetylcholine and gastrin signalling from both central and local modulators.

A gastrectomy is a partial or total surgical removal of the stomach.

Gastritis is the inflammation of the lining of the stomach. It may occur as a short episode or may be of a long duration. There may be no symptoms but, when symptoms are present, the most common is upper abdominal pain. Other possible symptoms include nausea and vomiting, bloating, loss of appetite and heartburn. Complications may include stomach bleeding, stomach ulcers, and stomach tumors. When due to autoimmune problems, low red blood cells due to not enough vitamin B12 may occur, a condition known as pernicious anemia.
Achlorhydria and hypochlorhydria refer to states where the production of hydrochloric acid in gastric secretions of the stomach and other digestive organs is absent or low, respectively. It is associated with various other medical problems.
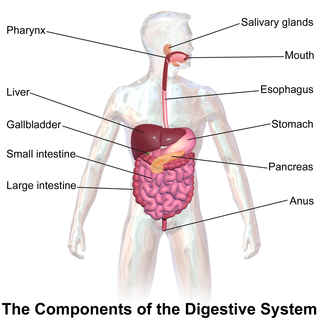
Gastrointestinal diseases refer to diseases involving the gastrointestinal tract, namely the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum; and the accessory organs of digestion, the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
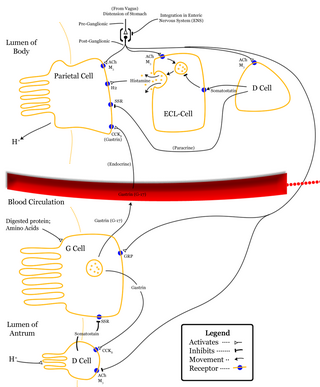
A G cell or gastrin cell is a type of cell in the stomach and duodenum that secretes gastrin. It works in conjunction with gastric chief cells and parietal cells. G cells are found deep within the pyloric glands of the stomach antrum, and occasionally in the pancreas and duodenum. The vagus nerve innervates the G cells. Gastrin-releasing peptide is released by the post-ganglionic fibers of the vagus nerve onto G cells during parasympathetic stimulation. The peptide hormone bombesin also stimulates gastrin from G cells. Gastrin-releasing peptide, as well as the presence of amino acids in the stomach, stimulates the release of gastrin from the G cells. Gastrin stimulates enterochromaffin-like cells to secrete histamine. Gastrin also targets parietal cells by increasing the amount of histamine and the direct stimulation by gastrin, causing the parietal cells to increase HCl secretion in the stomach. G-cells frequently express PD-L1 during homeostasis which protects them from Helicobacter pylori-induced immune destruction
MALT lymphoma is a form of lymphoma involving the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), frequently of the stomach, but virtually any mucosal site can be affected. It is a cancer originating from B cells in the marginal zone of the MALT.

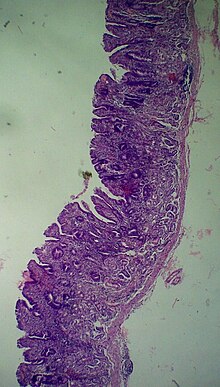
Gastric glands are glands in the lining of the stomach that play an essential role in the process of digestion. Their secretions make up the digestive gastric juice. The gastric glands open into gastric pits in the mucosa. The gastric mucosa is covered in surface mucous cells that produce the mucus necessary to protect the stomach's epithelial lining from gastric acid secreted by parietal cells in the glands, and from pepsin, a secreted digestive enzyme. Surface mucous cells follow the indentations and partly line the gastric pits. Other mucus secreting cells are found in the necks of the glands. These are mucous neck cells that produce a different kind of mucus.
Gastric hydrogen potassium ATPase, also known as H+/K+ ATPase, is an enzyme which functions to acidify the stomach. It is a member of the P-type ATPases, also known as E1-E2 ATPases due to its two states.
Ménétrier disease is a rare, acquired, premalignant disease of the stomach characterized by massive gastric folds, excessive mucus production with resultant protein loss, and little or no acid production (achlorhydria). The disorder is associated with excessive secretion of transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-α). It is named after French physician Pierre Eugène Ménétrier (1859–1935).

This is a timeline of the events relating to the discovery that peptic ulcer disease and some cancers are caused by H. pylori. In 2005, Barry Marshall and Robin Warren were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery that peptic ulcer disease (PUD) was primarily caused by Helicobacter pylori, a bacterium with affinity for acidic environments, such as the stomach. As a result, PUD that is associated with H. pylori is currently treated with antibiotics used to eradicate the infection. For decades prior to their discovery, it was widely believed that PUD was caused by excess acid in the stomach. During this time, acid control was the primary method of treatment for PUD, to only partial success. Among other effects, it is now known that acid suppression alters the stomach milieu to make it less amenable to H. pylori infection.

The gastric mucosa is the mucous membrane layer of the stomach, which contains the gastric pits, to which the gastric glands empty. In humans, it is about one mm thick, and its surface is smooth, soft, and velvety. It consists of simple secretory columnar epithelium, an underlying supportive layer of loose connective tissue called the lamina propria, and the muscularis mucosae, a thin layer of muscle that separates the mucosa from the underlying submucosa.

Stomach diseases include gastritis, gastroparesis, Crohn's disease and various cancers.