
Esophageal achalasia, often referred to simply as achalasia, is a failure of smooth muscle fibers to relax, which can cause the lower esophageal sphincter to remain closed. Without a modifier, "achalasia" usually refers to achalasia of the esophagus. Achalasia can happen at various points along the gastrointestinal tract; achalasia of the rectum, for instance, may occur in Hirschsprung's disease. The lower esophageal sphincter is a muscle between the esophagus and stomach that opens when food comes in. It closes to avoid stomach acids from coming back up. A fully understood cause to the disease is unknown, as are factors that increase the risk of its appearance. Suggestions of a genetically transmittable form of achalasia exist, but this is neither fully understood, nor agreed upon.
Heartburn, also known as pyrosis, cardialgia or acid indigestion, is a burning sensation in the central chest or upper central abdomen. Heartburn is usually due to regurgitation of gastric acid into the esophagus. It is the major symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).

Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
An esophageal motility disorder (EMD) is any medical disorder resulting from dysfunction of the coordinated movement of esophagus, which causes dysphagia.
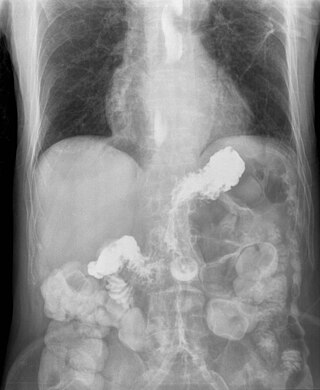
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic upper gastrointestinal disease in which stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or complications. Symptoms include dental corrosion, dysphagia, heartburn, odynophagia, regurgitation, non-cardiac chest pain, extraesophageal symptoms such as chronic cough, hoarseness, reflux-induced laryngitis, or asthma. In the long term, and when not treated, complications such as esophagitis, esophageal stricture, and Barrett's esophagus may arise.
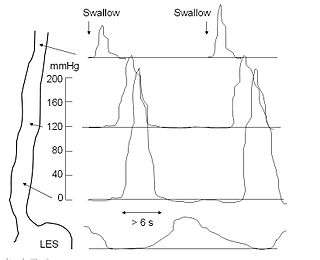
An esophageal motility study (EMS) or esophageal manometry is a test to assess motor function of the upper esophageal sphincter (UES), esophageal body and lower esophageal sphincter (LES).

Esophagitis, also spelled oesophagitis, is a disease characterized by inflammation of the esophagus. The esophagus is a tube composed of a mucosal lining, and longitudinal and circular smooth muscle fibers. It connects the pharynx to the stomach; swallowed food and liquids normally pass through it.
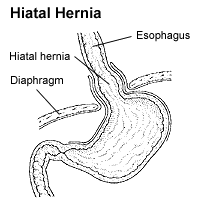
A hiatal hernia or hiatus hernia is a type of hernia in which abdominal organs slip through the diaphragm into the middle compartment of the chest. This may result in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) with symptoms such as a taste of acid in the back of the mouth or heartburn. Other symptoms may include trouble swallowing and chest pains. Complications may include iron deficiency anemia, volvulus, or bowel obstruction.
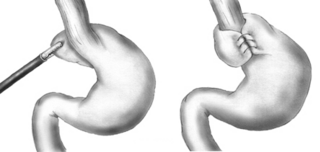
A Nissen fundoplication, or laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication when performed via laparoscopic surgery, is a surgical procedure to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and hiatal hernia. In GERD, it is usually performed when medical therapy has failed; but, with a Type II (paraesophageal) hiatus hernia, it is the first-line procedure. The Nissen fundoplication is total (360°), but partial fundoplications known as Thal, Belsey, Dor, Lind, and Toupet fundoplications are alternative procedures with somewhat different indications and outcomes.
Esophageal dysphagia is a form of dysphagia where the underlying cause arises from the body of the esophagus, lower esophageal sphincter, or cardia of the stomach, usually due to mechanical causes or motility problems.

A Schatzki ring or Schatzki–Gary ring is a narrowing of the lower esophagus that can cause difficulty swallowing (dysphagia). The narrowing is caused by a ring of mucosal tissue or muscular tissue. A Schatzki ring is a specific type of "esophageal ring", and Schatzki rings are further subdivided into those above the esophagus/stomach junction, and those found at the squamocolumnar junction in the lower esophagus.
Esophageal spasm is a disorder of motility of the esophagus.
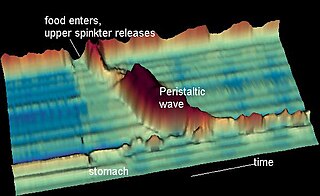
Nutcracker esophagus, jackhammer esophagus, or hypercontractile peristalsis, is a disorder of the movement of the esophagus characterized by contractions in the smooth muscle of the esophagus in a normal sequence but at an excessive amplitude or duration. Nutcracker esophagus is one of several motility disorders of the esophagus, including achalasia and diffuse esophageal spasm. It causes difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) with both solid and liquid foods, and can cause significant chest pain; it may also be asymptomatic. Nutcracker esophagus can affect people of any age but is more common in the sixth and seventh decades of life.

A benign esophageal stricture, or peptic stricture, is a narrowing or tightening of the esophagus that causes swallowing difficulties.

An esophageal food bolus obstruction is a medical emergency caused by the obstruction of the esophagus by an ingested foreign body.

Esophageal diseases can derive from congenital conditions, or they can be acquired later in life.
Cricopharyngeal spasms occur in the cricopharyngeus muscle of the pharynx. Cricopharyngeal spasm is an uncomfortable but harmless and temporary disorder.

Esophageal intramucosal pseudodiverticulosis (EIPD) is a rare condition wherein the esophagus wall develops numerous small outpouchings (pseudodiverticulae). Individuals with the condition typically develop difficulty swallowing. The outpouchings represent the ducts of the submucosal glands of the esophagus. It typically affects individuals in their sixth and seventh decades of life. While it is associated with certain chronic conditions, particularly alcoholism, diabetes and gastroesophageal reflux disease, the cause of the condition is unknown. Treatment involves medications to treat concomitant conditions such as reflux esophageal spasm, and dilation of strictures in the esophagus.
Esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction (EGJOO) is an esophageal motility disorder characterized by increased pressure where the esophagus connects to the stomach at the lower esophageal sphincter. EGJOO is diagnosed by esophageal manometry. However, EGJOO has a variety of etiologies; evaluating the cause of obstruction with additional testing, such as upper endoscopy, computed tomography, or endoscopic ultrasound may be necessary. When possible, treatment of EGJOO should be directed at the cause of obstruction. When no cause for obstruction is found, observation alone may be considered if symptoms are minimal. Functional EGJOO with significant or refractory symptoms may be treated with pneumatic dilation, per-oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM), or botulinum toxin injection.
Esophageal inlet patch or heterotopic gastric mucosa of the upper esophagus or gastric inlet patch is one or more areas of tissue resembling stomach tissue which is found in the upper portion of the esophagus.














