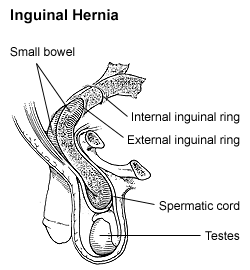
A hernia is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. The term is also used for the normal development of the intestinal tract, referring to the retraction of the intestine from the extra-embryonal navel coelom into the abdomen in the healthy embryo at about 7½ weeks. Various types of hernias can occur, most commonly involving the abdomen, and specifically the groin. Groin hernias are most commonly of the inguinal type but may also be femoral. Other types of hernias include hiatus, incisional, and umbilical hernias. Symptoms are present in about 66% of people with groin hernias. This may include pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, especially with coughing, exercise, or urinating or defecating. Often, it gets worse throughout the day and improves when lying down. A bulge may appear at the site of hernia, that becomes larger when bending down. Groin hernias occur more often on the right than left side. The main concern is bowel strangulation, where the blood supply to part of the bowel is blocked. This usually produces severe pain and tenderness in the area. Hiatus, or hiatal hernias often result in heartburn but may also cause chest pain or pain while eating.
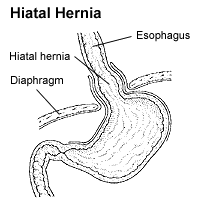
A hiatal hernia or hiatus hernia is a type of hernia in which abdominal organs slip through the diaphragm into the middle compartment of the chest. This may result in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) with symptoms such as a taste of acid in the back of the mouth or heartburn. Other symptoms may include trouble swallowing and chest pains. Complications may include iron deficiency anemia, volvulus, or bowel obstruction.
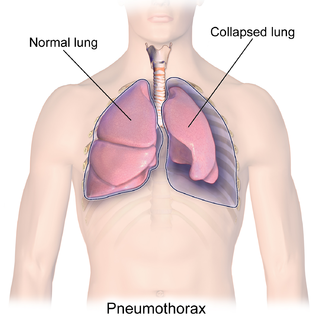
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve is formed by an area of damaged tissue, and the amount of air in the space between chest wall and lungs increases; this is called a tension pneumothorax. This can cause a steadily worsening oxygen shortage and low blood pressure. This leads to a type of shock called obstructive shock, which can be fatal unless reversed. Very rarely, both lungs may be affected by a pneumothorax. It is often called a "collapsed lung", although that term may also refer to atelectasis.

The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm, is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle.

Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) is a birth defect of the diaphragm. The most common type of CDH is a Bochdalek hernia; other types include Morgagni hernia, diaphragm eventration and central tendon defects of the diaphragm. Malformation of the diaphragm allows the abdominal organs to push into the chest cavity, hindering proper lung formation.

A hemothorax is an accumulation of blood within the pleural cavity. The symptoms of a hemothorax may include chest pain and difficulty breathing, while the clinical signs may include reduced breath sounds on the affected side and a rapid heart rate. Hemothoraces are usually caused by an injury, but they may occur spontaneously due to cancer invading the pleural cavity, as a result of a blood clotting disorder, as an unusual manifestation of endometriosis, in response to Pneumothorax, or rarely in association with other conditions.

An umbilical hernia is a health condition where the abdominal wall behind the navel is damaged. It may cause the navel to bulge outwards—the bulge consisting of abdominal fat from the greater omentum or occasionally parts of the small intestine. The bulge can often be pressed back through the hole in the abdominal wall, and may "pop out" when coughing or otherwise acting to increase intra-abdominal pressure. Treatment is surgical, and surgery may be performed for cosmetic as well as health-related reasons.

Pelvic exenteration is a radical surgical treatment that removes all organs from a person's pelvic cavity. It is used to treat certain advanced or recurrent cancers. The urinary bladder, urethra, rectum, and anus are removed. In women, the vagina, cervix, uterus, Fallopian tubes, ovaries and, in some cases, the vulva are removed. In men, the prostate is removed. The procedure leaves the person with a permanent colostomy and urinary diversion.

Fetal surgery also known as antenatal surgery, prenatal surgery, is a growing branch of maternal-fetal medicine that covers any of a broad range of surgical techniques that are used to treat congenital abnormalities in fetuses who are still in the pregnant uterus. There are three main types: open fetal surgery, which involves completely opening the uterus to operate on the fetus; minimally invasive fetoscopic surgery, which uses small incisions and is guided by fetoscopy and sonography; and percutaneous fetal therapy, which involves placing a catheter under continuous ultrasound guidance.

The EXIT procedure, or ex utero intrapartum treatment procedure, is a specialized surgical delivery procedure used to deliver babies who have airway compression. Causes of airway compression in newborn babies result from a number of rare congenital disorders, including bronchopulmonary sequestration, congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation, mouth or neck tumor such as teratoma, and lung or pleural tumor such as pleuropulmonary blastoma. Airway compression discovered at birth is a medical emergency. In many cases, however, the airway compression is discovered during prenatal ultrasound exams, permitting time to plan a safe delivery using the EXIT procedure or other means.

Perineal hernia is a hernia involving the perineum. The hernia may contain fluid, fat, any part of the intestine, the rectum, or the bladder. It is known to occur in humans, dogs, and other mammals, and often appears as a sudden swelling to one side of the anus.
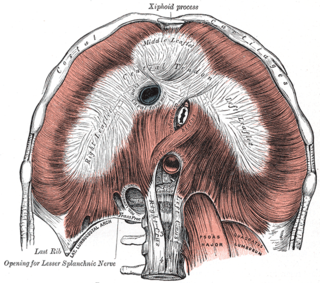
The central tendon of the diaphragm is a thin but strong aponeurosis situated slightly anterior to the vault formed by the muscle, resulting in longer posterior muscle fibers.
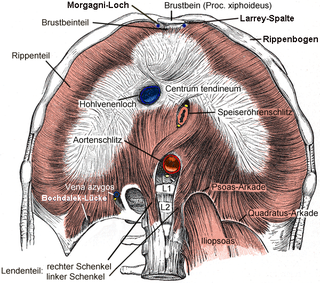
Bochdalek hernia is one of two forms of a congenital diaphragmatic hernia, the other form being Morgagni hernia. A Bochdalek hernia is a congenital abnormality in which an opening exists in the infant's diaphragm, allowing normally intra-abdominal organs to enter into the thoracic cavity. In the majority of people, the affected lung will be deformed, and the resulting lung compression can be life-threatening. Bochdalek hernias occur more commonly on the posterior left side.

Diaphragmatic rupture is a tear of the diaphragm, the muscle across the bottom of the ribcage that plays a crucial role in breathing. Most commonly, acquired diaphragmatic tears result from physical trauma. Diaphragmatic rupture can result from blunt or penetrating trauma and occurs in about 0.5% of all people with trauma.

Fat necrosis is a form of necrosis that is caused by the action of lipases on adipocytes.

Pulmonary hypoplasia is incomplete development of the lungs, resulting in an abnormally low number or small size of bronchopulmonary segments or alveoli. A congenital malformation, it most often occurs secondary to other fetal abnormalities that interfere with normal development of the lungs. Primary (idiopathic) pulmonary hypoplasia is rare and usually not associated with other maternal or fetal abnormalities.

Fryns syndrome is an autosomal recessive multiple congenital anomaly syndrome that is usually lethal in the neonatal period. Fryns (1987) reviewed the syndrome.

Retroperitoneal bleeding is an accumulation of blood in the retroperitoneal space. Signs and symptoms may include abdominal or upper leg pain, hematuria, and shock. It can be caused by major trauma or by non-traumatic mechanisms.
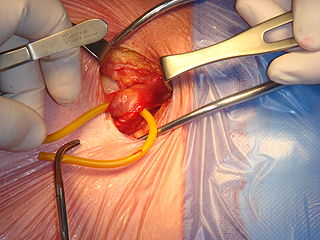
Inguinal hernia surgery is an operation to repair a weakness in the abdominal wall that abnormally allows abdominal contents to slip into a narrow tube called the inguinal canal in the groin region.
Wendy K. Chung is an American clinical and molecular geneticist and physician. She currently directs the clinical genetics program at NewYork–Presbyterian Hospital / Columbia University Medical Center in New York City and serves as the Kennedy Family Professor of Pediatrics. She is the author of 600 peer-reviewed articles and 75 chapters and has won several awards as a physician, researcher, and professor. Chung helped to initiate a new form of newborn screening for spinal muscular atrophy which is used nationally and was among the plaintiffs in the Supreme Court case which banned gene patenting.



















