HMS Cormorant was a 16-gun ship sloop of the Cormorant class in the Royal Navy, launched in 1794 at Rotherhithe. She captured four French privateers before an accidental fire destroyed her in 1796.

HMS Foxhound was an 18-gun Cruizer-class brig-sloop built by King at Dover and launched in 1806. She participated in the battle of the Basque Roads in early 1809 and foundered later that year.

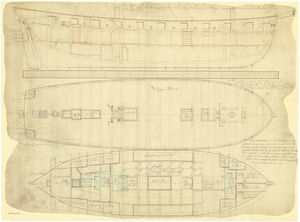
HMS Primrose was a Royal Navy Cruizer-class brig-sloop built by Thomas Nickells, at Fowey and launched in 1807.

HMS Crane was a Royal Navy Cruizer-class brig-sloop launched in 1809. She had an unusually uneventful five-year career before she foundered in 1814.
HMS Barracouta was a Royal Navy Ballahoo-class schooner. The prime contractor for the vessel was Goodrich & Co., in Bermuda, and she was launched in 1804. Like many of her class and the related Cuckoo-class schooners, she succumbed to the perils of the sea relatively early in her career.
HMS Capelin was a Royal Navy Ballahoo-class schooner carrying four 12-pounder carronades and a crew of 20. The prime contractor for the vessel was Goodrich & Co., in Bermuda, and she was launched in 1804. Like many of her class and the related Cuckoo-class schooners, she succumbed to the perils of the sea relatively early in her career.
HMS Crane was a Royal Navy Cuckoo-class schooner of four 12-pounder carronades and a crew of 20. She was built by Custance & Stone at Great Yarmouth and launched in 1806. Like many of her class and the related Ballahoo-class schooners, she succumbed to the perils of the sea relatively early in her career.
HMS Pigeon was a Royal Navy Cuckoo-class schooner. Custance & Stone built and launched her at Great Yarmouth in 1806. Like many of her class and the related Ballahoo-class schooners, she succumbed to the perils of the sea relatively early in her career.
HMS Widgeon was a Royal Navy Cuckoo-class schooner built by William Wheaton at Brixham and launched in 1806. Like many of her class and the related Ballahoo-class schooners, she succumbed to the perils of the sea relatively early in her career.
HMS Sealark was a Royal Navy Cuckoo-class schooner armed with four 12-pounder carronades and manned by a crew of 20. She was built by William Wheaton at Brixham and launched in 1806. Like many of her class and the related Ballahoo-class schooners, she succumbed to the perils of the sea relatively early in her career.

HMS Arab was the French 20-gun corvette Jean Bart, launched in 1793. The British captured her in 1795 and the Royal Navy took her into service. She was wrecked in 1796.

HMS Redbridge was one of four schooner-rigged gunboats built to an experimental design by Sir Samuel Bentham. Her launch date is unknown, but the Admiralty purchased her in April 1798. She had a short, relatively uneventful career before the French captured her in 1803. The French Navy sold her in January 1814.
His Majesty's hired armed lugger Venus, which was renamed Agnes in 1804, served the British Royal Navy from 8 March 1804 until she foundered in the Texel in March 1806.
HMS Avenger was a sloop-of-war, previously the civilian vessel Elizabeth, launched in 1801 at Bridlington. The British Royal Navy purchased her in 1803 and commissioned her in October 1803 under Commander Francis Snell. but she foundered in Heligoland Bight, off the Weser, on 5 December 1803; the crew were saved.
HMS Shamrock was a schooner built at Bermuda in 1808 of Bermuda cedar. She was built for the Royal Navy and was the name-ship of her class of 10-gun schooners. She was wrecked in 1811.
HMS Biter was a 12-gun Archer-class gun-brig of the Royal Navy. She was wrecked in 1805.
HMS Volador was an ex-Spanish prize that the Royal Navy acquired in 1807 in the West Indies. Commander Francis George Dickens commissioned her.
HDMS Delphinen was a brig of the Royal Dano-Norwegian Navy, launched in 1805 at Nyholm. The British Royal Navy captured her in 1807 at the Danish surrender after the Battle of Copenhagen. The Royal Navy commissioned her in 1808 as HMS Dolphinen but she was already lost later that year.
HMS Fox was a schooner that the Royal Navy purchased in 1799; she may have been a French prize. Lieutenant James Woolridge commissioned her in Jamaica.
HMS Fly was launched in March 1804. She was wrecked in March 1805.