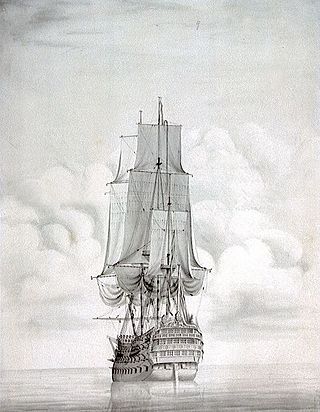
HMS Vanguard was a 90-gun second-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built at Portsmouth Dockyard and launched in 1678.

HMS Ajax was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Thomas Bucknall at Portsmouth Dockyard and launched on 23 December 1767. She was designed by William Bateley, and was the only ship built to her draught. She had a crew of 600 men.
HMS Somerset was an 80-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built to the 1719 Establishment at Woolwich and launched on 21 October 1731. She was the second ship to bear the name.

HMS Canada was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 17 September 1765 at Woolwich Dockyard.

HMS Superb was a 74-gun Bellona-class third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, designed by Sir Thomas Slade and built by Adam Hayes at Deptford Dockyard, launched on 27 October 1760 as a sister ship to HMS Dragon.

HMS Hercules was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, designed by Sir Thomas Slade and built at Deptford Dockyard by Adam Hayes and launched on 15 March 1759.

HMS London was a 90-gun second-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 24 May 1766 at Chatham Dockyard.

HMS Prince George was a 90-gun second-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 31 August 1772 at Chatham. During her career, she was upgraded to a 98-gun ship, through the addition of eight 12-pounder guns to her quarterdeck.

HMS Formidable was a 98-gun second rate man-of-war serving the Royal Navy.

HMS Monarch was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Adam Hayes and launched on 20 July 1765 at Deptford Dockyard.

HMS Grafton was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Adam Hayes launched on 26 September 1771 at Deptford Dockyard. One of the largest ships in the navy she had a crew of 550 men.

HMS Alcide, the French and Italian version of "Alcides", another name for Heracles, was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, designed by Sir Thomas Slade and built by Adam Hayes at Deptford Dockyard being launched on 30 July 1779.

HMS Belliqueux was a 64-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 5 June 1780 at Blackwall Yard, London. She was named after the French ship Belliqueux captured in 1758.

HMS Atlas was a 98-gun second-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 13 February 1782. She was a Duke-class ship of the line built at Chatham Dockyard by Nicholas Phillips.

HMS Resolution was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, designed by Sir Thomas Slade and built by Adam Hayes at Deptford Dockyard and launched on 12 April 1770. The ship had a huge crew of 600 men. As one of the Royal Navy's largest ships she took part in seven major naval battles.
HMS Alfred was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 22 October 1778 at Chatham Dockyard.

HMS America was a 64-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, designed by John Williams and built by Adam Hayes at Deptford Dockyard and was launched on 5 August 1777. The name was a traditional name in the Royal Navy and continued unabated despite the American War of Independence in 1776.
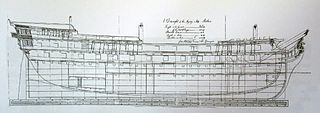
Protée was an Artésien-class 64-gun ship of the line of the French Navy, launched in 1772.
Caton was a 64-gun ship of the line of the French Navy, launched in 1777.
HMS Burford was a 70-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built at Chatham Dockyard to the draught specified by the 1745 Establishment as amended in 1754, and launched in 1757.

















