
HMS Kingfisher was a Doterel-class screw sloop of the Royal Navy. She was built at Sheerness Dockyard and launched on 16 December 1879. She conducted anti-slavery work in the East Indies in the late 1880s before being re-roled as a training cruiser, being renamed HMS Lark on 10 November 1892, and then HMS Cruizer on 18 May 1893. She was sold in 1919.

HMS Pegasus was a Doterel-class screw composite 6-gun sloop launched on 13 June 1878. She was sold for scrap in 1892.

The Osprey class was a Royal Navy class of screw-driven sloops built between 1874 and 1877. Nine additional ships were built to a revised design, the Doterel-class sloop. They were the first class of ship in the Royal Navy to use glass scuttles.

HMSGannet is a Royal Navy Doterel-class screw sloop-of-war launched on 31 August 1878. It became a training ship in the Thames in 1903, and was then loaned as a training ship for boys in the Hamble from 1913. It was restored in 1987 and is now part of the UK's National Historic Fleet.

HMS Niger was originally slated to be built as a Sampson designed sloop; however, she was ordered as a First-Class sloop with screw propulsion on 20 February 1845 to be built at Woolwich Dockyard, along the design developed by Oliver Lang and with a hull like the Basilisk designed paddle sloops. Her armament and engine were to be like the Encounter Design building at Pembroke. A second vessel (Florentia) was ordered on 26 March 1846 but after her keel was laid at Pembroke Dockyard, her construction was suspended on 6 October 1846 then cancelled three years later, on 22 May 1849. Niger She conducted important propulsion trials, finally proving the superiority of screw propulsion and served in West Africa, the Crimea, China, the East Indies and Australia. She took part in the New Zealand wars in 1860 and was sold for breaking in 1869.

HMS Cordelia was an 11-gun Racer-class sloop of the Royal Navy launched in 1856 and sold in 1870.

HMS Salamander was one of the initial steam powered vessels built for the Royal Navy. On 10 January 1831 the First Sea Lord gave orders that four paddle vessels be built to competitive designs. The vessels were to be powered by Maudslay, Son & Field steam engines, carry a schooner rig and mount one or two 10-inch shell guns. Initially classed simply as a steam vessel (SV), she was re-classed as a second-class steam sloop when that categorization was introduced on 31 May 1844. Designed by Joseph Seaton, the Master Shipwright of Sheerness, she was initially slated to be built in Portsmouth, and was changed to Sheerness Dockyard. She was launched and completed in 1832, took part in the Second Anglo-Burmese War and was broken up in 1883.
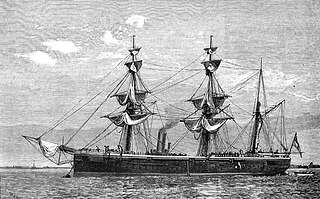
The Doterel class was a Royal Navy class of screw-driven sloops. They were of composite construction, with wooden hulls over an iron frame. They were a revised version of an 1874 design by the Royal Navy's Chief Constructor, William Henry White, the Osprey-class sloop. Two of the class were lost, one to an explosion off Chile and one wrecked off Canada. Gannet is preserved at Chatham Historic Dockyard.

HMS Penguin was an Osprey-class sloop. Launched in 1876, Penguin was operated by the Royal Navy from 1877 to 1881, then from 1886 to 1889. After being converted to a survey vessel, Penguin was recommissioned in 1890, and operated until 1908, when she was demasted and transferred to the Australian Commonwealth Naval Forces for use as a depot and training ship in Sydney Harbour. After this force became the Royal Australian Navy, the sloop was commissioned as HMAS Penguin in 1913. Penguin remained in naval service until 1924, when she was sold off and converted into a floating crane. The vessel survived until 1960, when she was broken up and burnt.

HMS Myrmidon was a Cormorant-class gunvessel of the Royal Navy, built at Chatham Dockyard and launched in 1867. She served on the North America and West Indies Station and surveyed parts of the Australian coast before being sold at Hong Kong in 1889.

HMS Basilisk was a first-class paddle sloop of the Royal Navy, built at the Woolwich Dockyard and launched on 22 August 1848.

HMS Miranda was a Doterel-class sloop of the Royal Navy, built at Devonport Dockyard and launched on 30 September 1879.
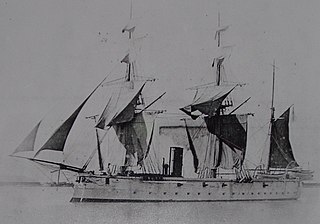
HMS Nymphe was an Amazon-class sloop, of the Royal Navy, built at the Deptford Dockyard and launched on 24 November 1866. She served in the East Indies and Australia, and was sold in 1884.

HMS Barracouta was the last paddle sloop built for the Royal Navy. She was built at Pembroke Dockyard and launched in 1851. She served in the Pacific theatre of the Crimean War, in the Second Opium War and in the Anglo-Ashanti wars. She paid off for the last time in 1877 and was broken up in 1881.

HMS Doterel was a Doterel-class sloop launched by the Royal Navy in 1880. She sank at anchor off Punta Arenas after an explosion on 26 April 1881. Her loss caused the deaths of 143 crew members, and there were 12 survivors. She was en route to join the Pacific Station. Her loss was initially the source of much speculation. Causes considered included an attack by the Fenians, a lost torpedo, and a coal gas explosion. An enquiry in September 1881 concluded coal gas was the cause.

HMS Phoenix was a Doterel-class sloop launched in 1879. She was wrecked off Prince Edward Island, Canada on 12 September 1882.

HMS Mutine was a Doterel-class sloop of the Royal Navy, built at the Devonport Dockyard and launched on 20 July 1880. She became a boom defence vessel at Southampton in 1899 and was renamed Azov in 1904. She was sold after World War I.

HMS Dragon was a Doterel-class sloop of the Royal Navy, built at Devonport Dockyard and launched on 30 May 1878. She served in the East Indies, including the Anglo-Egyptian War of 1882, and the suppression of slavery. She was sold for breaking in 1892.

HMS Wild Swan was an Osprey-class sloop built for the Royal Navy in the mid-1870s. She was launched in 1877 and became a base ship in 1904, being renamed Clyde. She was renamed Columbine in 1913 and was sold for breaking in 1920.

HMS Cadmus was a Cadmus-class sloop of the Royal Navy. She was launched at Sheerness in 1903, spent her entire career in the Far East and was sold at Hong Kong in 1921.

















