
HMS Java was a British Royal Navy 38-gun fifth-rate frigate. She was originally laid down in 1805 as Renommée, described as a 40-gun Pallas-class French Navy frigate, but the vessel actually carried 46 guns. The British captured her in 1811 in a noteworthy action during the Battle of Tamatave, but she is most famous for her defeat on 29 December 1812 in a three-hour single-ship action against USS Constitution. Java had a complement of about 277, but during her engagement with Constitution she allegedly had 426 aboard, in comparison with her opponent's 475.

HMS La Hogue was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 3 October 1811 at Deptford. She was named after the 1692 Battle of La Hogue. "The La Hogue of 1811 [...] sported a green and chocolate lion, its grinning mouth displaying rows of white teeth and a huge red tongue."

HMS Phoebe was a 36-gun fifth rate of the Royal Navy. She had a career of almost twenty years and fought in the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars and the War of 1812. Overall, her crews were awarded six clasps to the Naval General Service Medals, with two taking place in the French Revolutionary Wars, three during the Napoleonic Wars and the sixth in the War of 1812. Three of the clasps carried the name Phoebe. During her career, Phoebe sailed to the Mediterranean and Baltic seas, the Indian Ocean, South East Asia, North and South America.

Astrée was a 44-gun Pallas-class frigate of the French Navy, launched at Cherbourg in 1809. In December of the next year she captured HMS Africaine. The Royal Navy captured Astrée in 1810 and took her into service under her French name, rating her as a 38-gun frigate, but then in 1811 recommissioned her as HMS Pomone. She served during the War of 1812 and was broken up in 1816.

HMS Vengeur was a 74-gun third rate Vengeur-class ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 19 June 1810 at Harwich. She had an uneventful career, having participated in no battles or engagements.

D'Hautpoul was a Téméraire class 74-gun French Navy ship of the line launched at Lorient on 2 September 1807. She was previously named Alcide and Courageux.
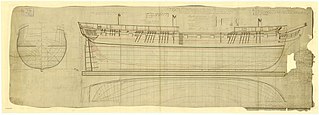
HMS Galatea was an Apollo-class fifth rate of the Royal Navy. The frigate was built at Deptford Dockyard, London, England and launched on 31 August 1810. In 1811 she participated in the Battle of Tamatave, which battle confirmed British dominance of the seas east of the Cape of Good Hope for the rest of the Napoleonic Wars. She was hulked in 1836 and broken up in 1849.

HMS Avon was a Royal Navy Cruizer-class brig-sloop built at Falmouth and launched in 1805. In the War of 1812 she fought a desperate action with USS Wasp that resulted in Avon sinking on 27 August 1814.

Furieuse was a 38-gun frigate of the French Navy. The Royal Navy captured her in 1809 and took her into service as the fifth rate HMS Furieuse. She spent most of her British career in the Mediterranean Sea, though towards the end of the War of 1812 she served briefly on the North American station. She was laid up in 1815 and sold for breaking up in 1816.

Néréide was a Sibylle-class, 32-gun, copper-hulled frigate of the French Navy. On 22 December 1797 HMS Phoebe captured her and she was taken into British service as HMS Nereide. The French recaptured her at the Battle of Grand Port, only to lose her again when the British took Isle de France, in 1810. After the Battle of Grand Port she was in such a poor condition that she was laid up and sold for breaking up in 1816.

HMS Nisus was a Royal Navy 38-gun fifth rate frigate, launched in 1810 at Plymouth, named for Virgil's character Nisus from The Aeneid.

HMS Otter was a Royal Navy 16-gun Merlin-class sloop, launched in 1805 at Hull. She participated in two notable actions in the Indian Ocean and was sold in 1828.

HMS Eclipse was a Royal Navy Cruizer-class brig-sloop built by John King at Dover and launched in 1807. She served off Portugal and then in the Indian Ocean at the capture of the Île de France. Shortly thereafter she captured Tamatave. She was sold for mercantile service in 1815. She traded with India until 1823. Then between 1823 and 1845 she made seven voyages as a whaler.

HMS Astraea was a Royal Navy 36-gun fifth rate Apollo-class frigate, launched- in 1810 at Northam. She participated in the Battle of Tamatave and in an inconclusive single-ship action with the French frigate Etoile. Astrea was broken up in 1851.

HMS Recruit was an 18-gun Cruizer-class brig-sloop of the Royal Navy, launched in 1806 at Sandwich, Kent. She is best known for an act of pique by Commander Warwick Lake, who marooned a seaman, and for an inconclusive but hard-fought ship action under Commander Charles John Napier against the French corvette Diligente. She captured a number of American vessels as prizes during the War of 1812 before being laid up in 1815 and sold for breaking up in 1822.

Palinure was the nameship for the Palinure-class of 16-gun brigs of the French Navy, and was launched in 1804. In French service she captured Carnation before Circe captured her in turn. After being taken into the Royal Navy as HMS Snap, she participated in two campaigns that qualified her crew for the Naval General Service Medal (NGSM). She was broken up in 1811.

HMS Lightning was launched in 1806 as a Thais-class fireship. Like the other members of her class she was quickly converted to a sloop. She participated in the second Battle of Copenhagen, captured a number of small prizes, and was sold in 1816.
Iris was a 20-gun corvette of the French Navy. The Royal Navy captured her in 1809 and took her into service as HMS Rainbow. She was sold in 1815.
HMS Childers was a Royal Navy 18-gun Cruizer-class brig-sloop that Nicholas Diddams built at Portsmouth Dockyard and launched in 1812. She was broken up in 1822.
Two vessels named His Majesty's hired armed lugger Sandwich served the British Royal Navy, one during the French Revolutionary Wars, and the other during the Napoleonic Wars.














