HMS Bluebell was a Flower-class corvette that served in the Royal Navy in World War II. Ordered from Fleming & Ferguson of Paisley, Scotland on 27 July 1939, she was launched on 24 April 1940 and commissioned in July 1940. She served in the Atlantic, Mediterranean and Arctic campaigns, escorting several convoys to Russia, and also took part in the invasions of Sicily and France. She was torpedoed and sunk by U-711 in the Kola Inlet on 17 February 1945 while escorting the convoy RA 64 from Murmansk. Only one member of her crew survived.

HMS Thetis (N25) was a Group 1 T-class submarine of the Royal Navy which sank during sea trials in Liverpool Bay, England on 1 June 1939. After being salvaged and repaired, the boat was recommissioned as HMS Thunderbolt in 1940. It served during the Second World War until being lost with all hands in the Mediterranean on 14 March 1943.

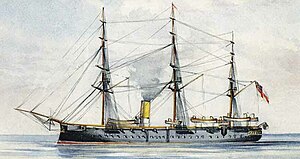
HMS Thunderer was one of two Devastation-class ironclad turret ships built for the Royal Navy in the 1870s. She suffered two serious accidents before the decade was out and gained a reputation as an unlucky ship for several years afterward. The ship was assigned to the Mediterranean Fleet in 1878 and was reduced to reserve in 1881 before being recommissioned in 1885. Thunderer returned home in 1887 and was again placed in reserve. She rejoined the Mediterranean Fleet in 1891, but was forced to return to the UK by boiler problems the following year. The ship became a coast guard ship in Wales in 1895 and was again placed in reserve in 1900. Thunderer was taken out of service in 1907 and sold for scrap in 1909.

HMS Thetis was a 38-gun fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy launched in 1782.

HMS Windsor Castle was a 98-gun second-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 3 May 1790 at Deptford Dockyard.

HMS Leith was a Grimsby-class sloop of the Royal Navy that served in the Second World War.

HMS Begonia was a Flower-class corvette that served in the Royal Navy during World War II. In 1942 she was lent to the United States Navy and commissioned as USS Impulse. Returned to the Royal Navy in 1945, Begonia was stricken and sold into merchant service. She was wrecked off the coast of Spain in 1970.

HMS Sapphire was an Amethyst-class corvette built for the Royal Navy at Devonport Dockyard and launched on 24 September 1874.

HMS Diamond was an Amethyst-class corvette in service 1874–89.

HMS Arab was an Arab-class composite gunvessel built for the Royal Navy in 1874. She served in the East Indies and was sold in 1889.
HMS Veronica was a Flower-class corvette, built for the Royal Navy during the Second World War, and was in service in the Battle of the Atlantic. In 1942 she was transferred to the United States Navy as part of the reverse Lend Lease arrangement and renamed USS Temptress, the name ship of the Temptress-class gunboats. With the end of hostilities she was returned to the Royal Navy and sold into mercantile service.
HMS Thyme was a Flower-class corvette which served in the Royal Navy during the Second World War. Laid down by Smiths Dock Company in April 1941, she was launched in July 1941, and commissioned in October 1941.

HMS Rhododendron was a Flower-class corvette that served with the Royal Navy during the Second World War. She served as an ocean escort in the Battle of the Atlantic.

HMS Mignonette was a Flower-class corvette that served with the Royal Navy during the Second World War. She served as an escort ship in the Battle of the Atlantic.
HMS Coreopsis was a Flower-class corvette, built for the Royal Navy during the Second World War which served in the Battle of the Atlantic. In 1943, she was transferred to the Royal Hellenic Navy as RHNS Kriezis and participated in the 1944 Invasion of Normandy. Shortly before she was scrapped, she took part in the British war film, The Cruel Sea.

HMS Dianella was a Flower-class corvette of the Royal Navy. She served during the Second World War.

HMS Cadmus was a wooden screw corvette launched on 20 May 1856 at Chatham Dockyard. On 4 January 1865, she ran aground at Chatham, Kent. She was refloated. Cadmus struck rocks at Salcombe on 5 June 1869 and was severely damaged. She was consequently beached. She was taken in to Plymouth the next day. She was broken up in 1879 at Devonport.
HMS Auricula was a Flower-class corvette that served in the Royal Navy and was built by George Brown and Company in 1940. She was named after Auricula. Commissioned in 1941 and sunk by a mine on 6 May 1942.

HMS Gardenia was a Flower-class corvette that served in the Royal Navy and was built by William Simons and Company in 1940. She was named after Gardenia. Commissioned in 1940, rammed and sunk by HMS Fluellen on 9 November 1942.
HMS Fleur de Lys was a Flower-class corvette that served in the Royal Navy and was built by Smith's Dock Company in 1940. She was named after Fleur de Lys. Commissioned in 1940, rammed and sunk by U-206 on 14 October 1941. Her name was originally La Dieppoise and built for the French Navy but was later changed.