Related Research Articles
Analysis is the branch of mathematics dealing with limits and related theories, such as differentiation, integration, measure, sequences, series, and analytic functions.

In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation which imposes relations between the various partial derivatives of a multivariable function.

Numerical methods for ordinary differential equations are methods used to find numerical approximations to the solutions of ordinary differential equations (ODEs). Their use is also known as "numerical integration", although this term can also refer to the computation of integrals.

Jacques Salomon Hadamard was a French mathematician who made major contributions in number theory, complex analysis, differential geometry and partial differential equations.

In mathematics, separation of variables is any of several methods for solving ordinary and partial differential equations, in which algebra allows one to rewrite an equation so that each of two variables occurs on a different side of the equation.
In mathematics, a Dirichlet problem is the problem of finding a function which solves a specified partial differential equation (PDE) in the interior of a given region that takes prescribed values on the boundary of the region.

In mathematics, a differential equation is an equation that relates one or more functions and their derivatives. In applications, the functions generally represent physical quantities, the derivatives represent their rates of change, and the differential equation defines a relationship between the two. Such relations are common; therefore, differential equations play a prominent role in many disciplines including engineering, physics, economics, and biology.
In mathematics, a hyperbolic partial differential equation of order is a partial differential equation (PDE) that, roughly speaking, has a well-posed initial value problem for the first derivatives. More precisely, the Cauchy problem can be locally solved for arbitrary initial data along any non-characteristic hypersurface. Many of the equations of mechanics are hyperbolic, and so the study of hyperbolic equations is of substantial contemporary interest. The model hyperbolic equation is the wave equation. In one spatial dimension, this is
A Cauchy problem in mathematics asks for the solution of a partial differential equation that satisfies certain conditions that are given on a hypersurface in the domain. A Cauchy problem can be an initial value problem or a boundary value problem. It is named after Augustin-Louis Cauchy.

Hans Lewy was a Jewish American mathematician, known for his work on partial differential equations and on the theory of functions of several complex variables.
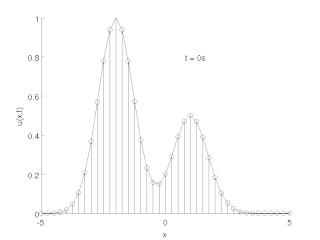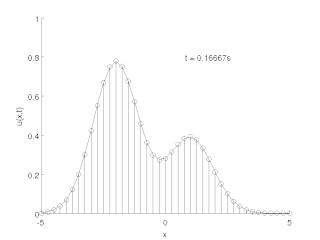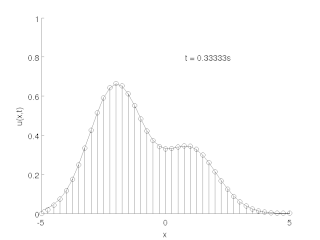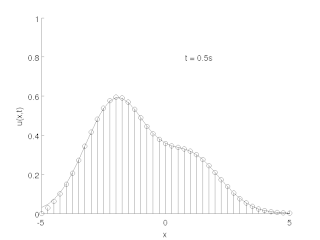
The method of lines is a technique for solving partial differential equations (PDEs) in which all but one dimension is discretized. By reducing a PDE to a single continuous dimension, the method of lines allows solutions to be computed via methods and software developed for the numerical integration of ordinary differential equations (ODEs) and differential-algebraic systems of equations (DAEs). Many integration routines have been developed over the years in many different programming languages, and some have been published as open source resources.
In mathematics, Hadamard regularization is a method of regularizing divergent integrals by dropping some divergent terms and keeping the finite part, introduced by Hadamard. Riesz showed that this can be interpreted as taking the meromorphic continuation of a convergent integral.
In mathematics, and specifically the field of partial differential equations (PDEs), a parametrix is an approximation to a fundamental solution of a PDE, and is essentially an approximate inverse to a differential operator.
Hadamard may refer to:

Steven George Krantz is an American scholar, mathematician, and writer. He has authored more than 280 research papers and more than 135 books. Additionally, Krantz has edited journals such as the Notices of the American Mathematical Society and The Journal of Geometric Analysis.
Tatyana Olegovna Shaposhnikova is a Russian-born Swedish mathematician. She is best known for her work in the theory of multipliers in function spaces, partial differential operators and history of mathematics, some of which was partly done jointly with Vladimir Maz'ya. She is also a translator of both scientific and literary texts.

In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation (ODE) is a differential equation containing one or more functions of one independent variable and the derivatives of those functions. The term ordinary is used in contrast with the term partial differential equation which may be with respect to more than one independent variable.
J. (Jean) François Trèves is a French mathematician, specializing in partial differential equations.

In mathematics, the Cauchy–Kovalevskaya theorem is the main local existence and uniqueness theorem for analytic partial differential equations associated with Cauchy initial value problems. A special case was proven by Augustin Cauchy (1842), and the full result by Sophie Kovalevskaya (1875).
References
- Hadamard, Jacques (1923), Lectures on Cauchy's Problem in Linear Partial Differential Equations, Dover Publications, p. 49, ISBN 0486495493
- Bers, Lipman; John, Fritz; Schechter, Martin (1964), Partial differential equations, American Mathematical Society, p. 16, ISBN 0821800493
- Courant, Richard; Hilbert, David (1953), Methods of mathematical physics, Vol. II, Interscience, p. 205
- Folland, Gerald B. (1995), Introduction to partial differential equations, Princeton University Press, p. 171, ISBN 0691043612
- Maz'ya, V. G.; Shaposhnikova, T. O. (1998), Jacques Hadamard: a universal mathematician, American Mathematical Society, p. 472, ISBN 0821819232