
Mount Waddington, once known as Mystery Mountain, is the highest peak in the Coast Mountains of British Columbia, Canada. Although it is lower than Mount Fairweather and Mount Quincy Adams, which straddle the United States border between Alaska and British Columbia, Mount Waddington is the highest peak that lies entirely within British Columbia. It and the subrange which surround it, known as the Waddington Range, stand at the heart of the Pacific Ranges, a remote and extremely rugged set of mountains and river valleys.
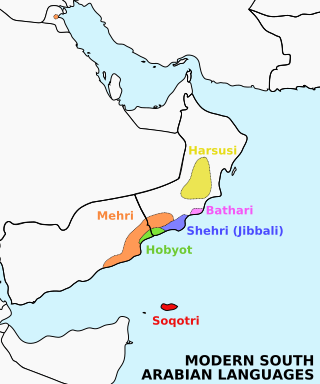
Soqotri is a South Semitic language spoken by the Soqotri people on the island of Socotra and the two nearby islands of Abd al Kuri and Samhah, in the Socotra archipelago, in the Guardafui Channel. Soqotri is one of six languages that form a group called Modern South Arabian languages (MSAL). These additional languages include Mehri, Shehri, Bathari, Harsusi and Hobyot. All are spoken in different regions of Southern Arabia.

Socotra, also known as Saqatri, is an island in the Indian Ocean part of Yemen. Lying between the Guardafui Channel and the Arabian Sea and near major shipping routes, Socotra is the largest of the six islands in the Socotra archipelago, which since 2013 constitutes one of Yemen's governorates.

The Großglockner, or just Glockner, is, at 3,798 metres above the Adriatic (12,461 ft), the highest mountain in Austria and highest mountain in the Alps east of the Brenner Pass. It is part of the larger Glockner Group of the Hohe Tauern range, situated along the main ridge of the Central Eastern Alps and the Alpine divide. The Pasterze, Austria's most extended glacier, lies on the Grossglockner's eastern slope.

The Twelve Bens or Twelve Pins, also called the Benna Beola, is a mountain range of mostly sharp-peaked quartzite summits and ridges in the Connemara National Park in County Galway, in the west of Ireland. The widest definition of the range includes the Garraun Complex to the north as well as several isolated peaks to the west, and is designated a 16,163-hectare (39,940-acre) Special Area of Conservation.

Jengish Chokusu or Victory Peak is the highest mountain in the Tian Shan mountain system in Central Asia at 7,439 metres (24,406 ft). It lies on the China–Kyrgyzstan border between the Ak-Suu District in the Issyk-Kul Region of far Eastern Kyrgyzstan and Wensu County, Xinjiang, China. It is part of the Kakshaal Too, the highest part of the Tian Shan, and is southeast of lake Issyk-Kul. Jengish Chokusu is the 16th most topographically prominent peak on Earth.

The Modern South Arabian languages (MSALs), also known as Eastern South Semitic languages, are a group of endangered languages spoken by small populations inhabiting the Arabian Peninsula, in Yemen and Oman, and Socotra Island. Together with the Ethiosemitic and Sayhadic languages, the Western branch, they form the South Semitic sub-branch of the Afroasiatic language family's Semitic branch.

The culture of Yemen has an ancient cultural history, influenced by Islam. Due to its unique geographic location, Yemen has acquired a very distinctive culture from its neighbors, historically and culturally.

The Mehri, also known as the al-Mahrah tribe, are an Arab ethnographic group primarily inhabiting South Arabia especially in the Al-Mahra Governorate in Yemen and the island of Socotra in the Guardafui Channel. They are named after Mahra bin Haydan. They can also be found in the Sultanate of Oman, and the eastern region of the Arabian Peninsula.

The Sarawat Mountains, also known as the Sarat in singular case, is a mountain range in the western part of the Arabian Peninsula. In a broad sense, it runs parallel to the eastern coast of the Red Sea, and thus encompasses the mountains of Fifa', 'Asir, Taif, and the Hijaz. In a narrow sense, the Sarawat start in Taif city in Saudi Arabia, and extend to the Gulf of Aden in the south, running along the entire western coast of Yemen, in what used to be North Yemen, and extend eastwards into part of what used to be South Yemen, thus running parallel to the Gulf of Aden.

The Socotra Island xeric shrublands is a terrestrial ecoregion that covers the large island of Socotra and several smaller islands that constitute the Socotra Archipelago. The archipelago is in the western Indian Ocean, east of the Horn of Africa and south of the Arabian Peninsula. Politically the archipelago is part of Yemen, and lies south of the Yemeni mainland.

Jabal Haraz is a mountainous region of Yemen, between Sanaa and Al-Hudaydah, which is considered to be within the Sarat range. In the 11th century, it was the stronghold of the Sulaihid dynasty, many of whose buildings still survive today. It includes Jabal An-Nabi Shu'ayb, the highest mountain in Yemen and the Arabian Peninsula.

The Socotra Archipelago, officially the Socotra Archipelago Governorate, abbreviated to Socotra Governorate, is one of the governorates of Yemen. It includes a number of islands in the Indian Ocean south of mainland Yemen, the largest of which is Socotra.

Qulensya is a town on the main island of Socotra, Yemen. It is located in the Qulensya wa Abd al Kuri District and its approximate population is 4,000.

The Soqotri people, sometimes referred to as Socotran, are a South Arabian ethnic group native to the Gulf of Aden island of Socotra. They speak the Soqotri language, a Modern South Arabian language in the Afroasiatic family.
Grant's leaf-toed gecko is a species of gecko, a lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is endemic to the island Socotra. Usually it can be found camouflaging at rocky areas such as cliffs and mountain peaks.

The geology of Yemen includes extremely ancient Precambrian igneous and metamorphic crystalline basement rocks overlain by sediments from the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic, deposited in shallow seas and lakebeds, overlain by thick volcanic rocks and loess. Erosion has played a major role in Yemen's geologic history and eliminated many rock units over time.

Leenaun Hill at 618 metres (2,028 ft), is the 201st–highest peak in Ireland on the Arderin scale, and the 243rd–highest peak on the Vandeleur-Lynam scale. Leenaun Hill lies on a massif that overlooks Leenaun village and Killary Harbour, and which is at the far northeastern sector of the Maumturks mountain range in the Connemara National Park in County Galway, Ireland; this massif is connected to the main range via the "Col of Despondency". Leenaun Hill is the 6th-highest mountain in the Maumturks, and its grassy massif, constructed from sandstone and siltstone, contrasts with the rocky ridges and summits constructed from quartzites, grits, and graphitic, of the middle and southern sectors of the range.

Annapurna is a massif in the Himalayas in north-central Nepal that includes one peak over 8,000 metres (26,247 ft), thirteen peaks over 7,000 metres (22,966 ft), and sixteen more over 6,000 metres (19,685 ft). The massif is 55 kilometres (34 mi) long, and is bounded by the Kali Gandaki Gorge on the west, the Marshyangdi River on the north and east, and by the Pokhara Valley on the south. At its western end, the massif encloses a high basin called the Annapurna Sanctuary. The highest peak of the massif, Annapurna I Main, is the 10th highest mountain in the world at 8,091 metres (26,545 ft) above sea level. Maurice Herzog led a French expedition to its summit through the north face in 1950, making it the first eight-thousander to be successfully climbed.

The Diksam Plateau or Dixam Plateau is a limestone plateau in Socotra, Yemen. The Firmihin forest, located east of the Dirhur canyon within the plateau, has the highest concentration of Dragon's Blood Trees on the entire island.






















