
Thurston Island is an ice-covered, glacially dissected island, 215 km (134 mi) long, 90 km (56 mi) wide and 15,700 km2 (6,062 sq mi) in area, lying a short way off the northwest end of Ellsworth Land, Antarctica. It is the third largest island of Antarctica, after Alexander Island and Berkner Island.

Dundee Island is an ice-covered island lying east of the northeastern tip of Antarctic Peninsula and south of Joinville Island.

Lillie Glacier is a large glacier in Antarctica, about 100 nautical miles (190 km) long and 10 nautical miles (19 km) wide. It lies between the Bowers Mountains on the west and the Concord Mountains and Anare Mountains on the east, flowing to Ob' Bay on the coast and forming the Lillie Glacier Tongue.

The Dailey Islands are a group of small volcanic islands lying off the coast of Victoria Land, 9 kilometres (5 nmi) northeast of Cape Chocolate, in the northern part of the ice shelf bordering McMurdo Sound. They were discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Robert Falcon Scott, and named for Fred E. Dailey, the expedition carpenter.

Cape Longing is a rocky cape on the east coast of Graham Land, Antarctica, forming the south end of a large ice-covered promontory which marks the west side of the south entrance to Prince Gustav Channel. It was discovered by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskiöld in 1902, and so named by him because from the position of his winter hut on Snow Hill Island the cape lay in the direction of his "land of longing" which he was anxious to explore.

Snow Hill Island is an almost completely snowcapped island, 33 km (21 mi) long and 12 km (7.5 mi) wide, lying off the east coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. It is separated from James Ross Island to the north-east by Admiralty Sound and from Seymour Island to the north by Picnic Passage. It is one of several islands around the peninsula known as Graham Land, which is closer to South America than any other part of the Antarctic continent.

Cape Evans is a rocky cape on the west side of Ross Island, Antarctica, forming the north side of the entrance to Erebus Bay.
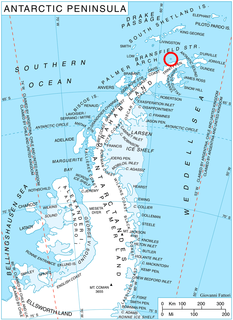
Astrolabe Island, located at 63°17′S58°40′W, is an island 5 km (3 mi) long, lying in the Bransfield Strait 23 km (14 mi) northwest of Cape Ducorps, Trinity Peninsula in Antarctica. It was discovered by the French expedition, 1837–40, under Captain Jules Dumont d'Urville, and named by him for his chief expedition ship, the Astrolabe. The island was photographed from the air and triangulated by FIDASE, 1956-57.

The Danco Coast is that portion of the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula between Cape Sterneck and Cape Renard. This coast was explored in January and February 1898 by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition under Adrien de Gerlache, who named it for Lieutenant Emile Danco who died on the expedition.

The Curzon Islands are a small group of rocky islands lying close off Cape Découverte, Adélie Coast. They were probably sighted in January 1840 by a French expedition under Captain Jules Dumont d'Urville, though not identified as islands on d'Urville's maps. The islands were roughly charted in 1912 by Captain J.K. Davis of the Australasian Antarctic Expedition ship Aurora and named by Mawson for Lord Curzon, the President of the Royal Geographical Society, 1911–14. The islands were mapped in detail by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1950–52.

Posadowsky Glacier is a glacier about 9 nautical miles long, flowing north to Posadowsky Bay immediately east of Gaussberg. Posadowsky Bay is an open embayment, located just east of the West Ice Shelf and fronting on the Davis Sea in Kaiser Wilhelm II Land. Kaiser Wilhelm II Land is the part of East Antarctica lying between Cape Penck, at 87°43'E, and Cape Filchner, at 91°54'E, and is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory. Other notable geographic features in this area include Drygalski Island, located 45 mi NNE of Cape Filchner in the Davis Sea, and Mirny Station, a Russian scientific research station.

Borradaile Island is one of the Balleny Islands. It was the site of the first landing south of the Antarctic Circle, and features the "remarkable pinnacle" called Beale Pinnacle, near Cape Beale on its south-eastern coast, and Cape Scoresby on its north-western coast.
Buchanan Point is a headland 5 km (3.1 mi) north-west of Cape Dundas and 2 km (1.2 mi) south-east of Mackintosh Cove, at the north-eastern end of Laurie Island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica.

Bulnes Island is a small island lying 4 kilometres (2 nmi) northwest of Cape Legoupil, Trinity Peninsula. It was charted by the Chilean Antarctic Expedition of 1947–48 under Capitan de Fragata Ernesto Gonzalez Navarrete, and named by him for Manuel Bulnes Sanfuentes, Minister of National Defense during the preceding Chilean Antarctic Expedition of 1947.

Noville Peninsula is a high ice-covered peninsula about 30 nautical miles (60 km) long, between Peale and Murphy Inlets on the north side of Thurston Island in Antarctica. Delineated from aerial photographs made by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump in December 1946. Named for George O. Noville, executive officer of Byrd Antarctic Expedition, 1933-35.

Evans Peninsula is an ice-covered peninsula about 30 nautical miles (60 km) long, between Koether Inlet and Cadwalader Inlet in the northeast part of Thurston Island. Cape Braathen is an ice-covered cape at the northwest termination of Evans Peninsula. It was discovered in flights from the USS Burton Island and USS Glacier by personnel of the U.S. Navy Bellingshausen Sea Expedition in February 1960, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Commander Griffith Evans, Jr., commander of the icebreaker Burton Island during this expedition.

Lofgren Peninsula is an ice-covered peninsula about 22 nautical miles (40 km) long, projecting between Cadwalader Inlet and Morgan Inlet on the northeast side of Thurston Island, Antarctica. The northern extremity of the peninsula is Cape Menzel, a bold rock cape. These features were discovered in helicopter flights from the USS Burton Island and the USS Glacier of the U.S. Navy Bellingshausen Sea Expedition in February 1960, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names. The peninsula was named for Charles E. Lofgren, personnel officer with the Byrd Antarctic Expedition, 1928–30. The cape was named for Reinhard W. Menzel, a geomagnetist-seismologist with the Eights Station winter party, 1965.

Hawker Island is an irregularly shaped island about 2 km (1.2 mi) long, lying some 7 km south-west of Davis Station between Mule Island and Mule Peninsula, Vestfold Hills, in the eastern part of Prydz Bay, Antarctica. It was mapped by Norwegian cartographers from aerial photographs taken by the Lars Christensen Expedition, 1936–37. It was remapped by the Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (1957–58) and named after Alan Charles Hawker, a radio supervisor at Davis Station in 1957.

The Hobbs Islands are a group of islands 19 kilometres (10 nmi) northeast of William Scoresby Bay, Antarctica. The largest island of this group was discovered on February 18, 1931, by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition under Mawson who thought it to be a cape and called it "Cape Hobbs" for Professor William H. Hobbs. Later exploration by the William Scoresby expedition (1936) and the Lars Christensen Expedition (1936–37) showed it to be part of an island group.

Tierney Peninsula is an ice-covered peninsula about 14 nautical miles (26 km) long, between Savage Glacier and Morgan Inlet in the east end of Thurston Island. The east extremity of the peninsula is Cape Annawan. These features were discovered on helicopter flights from the USS Burton Island and Glacier of the U.S. Navy Bellingshausen Sea Expedition in February 1960 and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN). The peninsula was named for J.Q. Tierney, oceanographer aboard the Burton Island on this expedition. The cape was named for the ship Annawan of the United States Expedition of 1829-31, which with the Penguin sailed west from the South Shetland Islands in February 1830, holding a course between 62S and 58S and exploring as far as 103W, northward of this cape.













