
Multiple endocrine neoplasia is a condition which encompasses several distinct syndromes featuring tumors of endocrine glands, each with its own characteristic pattern. In some cases, the tumors are malignant, in others, benign. Benign or malignant tumors of nonendocrine tissues occur as components of some of these tumor syndromes.

A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from transformed cells of mesenchymal origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, fat, vascular, or hematopoietic tissues, and sarcomas can arise in any of these types of tissues. As a result, there are many subtypes of sarcoma, which are classified based on the specific tissue and type of cell from which the tumor originates. Sarcomas are primary connective tissue tumors, meaning that they arise in connective tissues. This is in contrast to secondary connective tissue tumors, which occur when a cancer from elsewhere in the body spreads to the connective tissue. The word sarcoma is derived from the Greek σάρκωμα sarkōma 'fleshy excrescence or substance', itself from σάρξsarx meaning 'flesh'.

Osteosclerosis is a disorder that is characterized by abnormal hardening of bone and an elevation in bone density. It may predominantly affect the medullary portion and/or cortex of bone. Plain radiographs are a valuable tool for detecting and classifying osteosclerotic disorders. It can manifest in localized or generalized osteosclerosis. Localized osteosclerosis can be caused by Legg–Calvé–Perthes disease, sickle-cell disease and osteoarthritis among others. Osteosclerosis can be classified in accordance with the causative factor into acquired and hereditary.

Waardenburg syndrome is a group of rare genetic conditions characterised by at least some degree of congenital hearing loss and pigmentation deficiencies, which can include bright blue eyes, a white forelock or patches of light skin. These basic features constitute type 2 of the condition; in type 1, there is also a wider gap between the inner corners of the eyes called telecanthus, or dystopia canthorum. In type 3, which is rare, the arms and hands are also malformed, with permanent finger contractures or fused fingers, while in type 4, the person also has Hirschsprung's disease. There also exist at least two types that can result in central nervous system (CNS) symptoms such as developmental delay and muscle tone abnormalities.

Fibrous dysplasia is a disorder where normal bone and marrow is replaced with fibrous tissue, resulting in formation of bone that is weak and prone to expansion. As a result, most complications result from fracture, deformity, functional impairment, and pain. Disease occurs along a broad clinical spectrum ranging from asymptomatic, incidental lesions, to severe disabling disease. Disease can affect one bone (monostotic), multiple (polyostotic), or all bones (panostotic) and may occur in isolation or in combination with café au lait skin macules and hyperfunctioning endocrinopathies, termed McCune–Albright syndrome. More rarely, fibrous dysplasia may be associated with intramuscular myxomas, termed Mazabraud's syndrome. Fibrous dysplasia is very rare, and there is no known cure. Fibrous dysplasia is not a form of cancer.

Fibrosarcoma is a malignant mesenchymal tumour derived from fibrous connective tissue and characterized by the presence of immature proliferating fibroblasts or undifferentiated anaplastic spindle cells in a storiform pattern. Fibrosarcomas mainly arise in people between the ages of 25–79 It originates in fibrous tissues of the bone and invades long or flat bones such as the femur, tibia, and mandible. It also involves the periosteum and overlying muscle.

McCune–Albright syndrome is a complex genetic disorder affecting the bone, skin and endocrine systems. It is a mosaic disease arising from somatic activating mutations in GNAS, which encodes the alpha-subunit of the Gs heterotrimeric G protein.
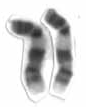
Chromosome 9 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Humans normally have two copies of this chromosome, as they normally do with all chromosomes. Chromosome 9 spans about 150 million base pairs of nucleic acids and represents between 4.0 and 4.5% of the total DNA in cells.
A histiocytoma is a tumour consisting of histiocytes. Histiocytes are cells that are a part of the mononuclear phagocytic system, a part of the body's immune system that consists of phagocytic cells, which are responsible for engulfing solid particles by the cell membrane to form an internal phagosome by phagocytes and protists. Myxofibrosarcoma had been classified as a type of histiocytoma. However, the World Health Organization (2020) reclassified myxofibrosarcoma as a malignant tumor in the category of fibroblastic/myofibroblastic tumors.
Osteochondrodysplasia is a general term for a disorder of the development (dysplasia) of bone ("osteo") and cartilage ("chondro"). Osteochondrodysplasias are rare diseases. About 1 in 5,000 babies are born with some type of skeletal dysplasia. Nonetheless, if taken collectively, genetic skeletal dysplasias or osteochondrodysplasias comprise a recognizable group of genetically determined disorders with generalized skeletal affection. Osteochondrodysplasias can result in marked functional limitation and even mortality.
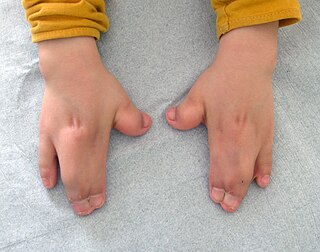
Acrocephalosyndactyly is a group of autosomal dominant congenital disorders characterized by craniofacial (craniosynostosis) and hand and foot (syndactyly) abnormalities. When polydactyly is present, the classification is acrocephalopolysyndactyly. Acrocephalosyndactyly is mainly diagnosed postnatally, although prenatal diagnosis is possible if the mutation is known to be within the family genome. Treatment often involves surgery in early childhood to correct for craniosynostosis and syndactyly.

Buschke–Ollendorff syndrome (BOS) is a rare genetic disorder associated with LEMD3. It is believed to be inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. It is named for Abraham Buschke and Helene Ollendorff Curth, who described it in a 45-year-old woman. Its frequency is almost 1 case per every 20,000 people, and it is equally found in both males and females.

Doege–Potter syndrome (DPS) is a paraneoplastic syndrome in which hypoglycemia is associated with solitary fibrous tumors. The hypoglycemia is the result of the tumors producing insulin-like growth factor 2. The syndrome was first described in 1930, by Karl Walter Doege (1867–1932), a German-American physician and by Roy Pilling Potter (1879–1968), an American radiologist, working independently; the full term Doege–Potter syndrome was infrequently used until the publication of a 2000 article using the eponym.

Ghosal hematodiaphyseal dysplasia, is a rare, autosomal recessive disease, characterized by diaphyseal dysplasia and metaphyseal dysplasia of the long bones and refractory anemia.
Malignant infantile osteopetrosis is a rare osteosclerosing type of skeletal dysplasia that typically presents in infancy and is characterized by a unique radiographic appearance of generalized hyperostosis.
Kenny-Caffey syndrome type 2 (KCS2) is an extremely rare autosomal dominant genetic condition characterized by dwarfism, hypermetropia, microphthalmia, and skeletal abnormalities. This subtype of Kenny-Caffey syndrome is caused by a heterozygous mutation in the FAM111A gene (615292) on chromosome 11q12.
Fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors (FMTs) develop from the mesenchymal stem cells which differentiate into fibroblasts and/or the myocytes/myoblasts that differentiate into muscle cells. FMTs are a heterogeneous group of soft tissue neoplasms. The World Health Organization (2020) defined tumors as being FMTs based on their morphology and, more importantly, newly discovered abnormalities in the expression levels of key gene products made by these tumors' neoplastic cells. Histopathologically, FMTs consist of neoplastic connective tissue cells which have differented into cells that have microscopic appearances resembling fibroblasts and/or myofibroblasts. The fibroblastic cells are characterized as spindle-shaped cells with inconspicuous nucleoli that express vimentin, an intracellular protein typically found in mesenchymal cells, and CD34, a cell surface membrane glycoprotein. Myofibroblastic cells are plumper with more abundant cytoplasm and more prominent nucleoli; they express smooth muscle marker proteins such as smooth muscle actins, desmin, and caldesmon. The World Health Organization further classified FMTs into four tumor forms based on their varying levels of aggressiveness: benign, intermediate, intermediate, and malignant.
Ectrodactyly with tibia aplasia/hypoplasia also known as cleft hand absent tibia is a very rare limb malformation syndrome which is characterized by ectrodactyly, and aplasia/hypoplasia of the tibia bone. Additional findings include cup-shaped ears, pre-postaxial polydactyly, and hypoplasia of the big toes, femur, patella, and ulnae bone. It is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait with reduced penetrance.

Craniofacial dysostosis-diaphyseal hyperplasia syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by craniofacial dysostosis, small cranium with accompanying thin skullbone, generalized depressions on the frontoparietal and occipitoparietal sutures, underdevelopment of the chin, exophthalmos, long bone cortical sclerosis, and puberty-onset progressive bone cortex thickening. It is inherited following an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. Around 14 cases from 3 families worldwide have been described in medical literature.












