
A soft-tissue sarcoma (STS) is a malignant tumour, a type of cancer, that develops in soft tissue. A soft tissue sarcoma is often a painless mass that grows slowly over months or years. They may be superficial or deep-seated. Any such unexplained mass must be diagnosed by biopsy. Treatment may include, surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and targeted drug therapy. The other type of sarcoma is a bone sarcoma.

A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from transformed cells of mesenchymal origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, fat, vascular, or hematopoietic tissues, and sarcomas can arise in any of these types of tissues. As a result, there are many subtypes of sarcoma, which are classified based on the specific tissue and type of cell from which the tumor originates. Sarcomas are primary connective tissue tumors, meaning that they arise in connective tissues. This is in contrast to secondary connective tissue tumors, which occur when a cancer from elsewhere in the body spreads to the connective tissue. The word sarcoma is derived from the Greek σάρκωμα sarkōma "fleshy excrescence or substance", itself from σάρξsarx meaning "flesh".

A bone tumor is an abnormal growth of tissue in bone, traditionally classified as noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). Cancerous bone tumors usually originate from a cancer in another part of the body such as from lung, breast, thyroid, kidney and prostate. There may be a lump, pain, or neurological signs from pressure. A bone tumor might present with a pathologic fracture. Other symptoms may include fatigue, fever, weight loss, anemia and nausea. Sometimes there are no symptoms and the tumour is found when investigating another problem.

A dermatofibroma, or benign fibrous histiocytomas, is a benign nodule in the skin, typically on the legs, elbows or chest of an adult. It is usually painless.

A benign tumor is a mass of cells (tumor) that does not invade neighboring tissue or metastasize. Compared to malignant (cancerous) tumors, benign tumors generally have a slower growth rate. Benign tumors have relatively well differentiated cells. They are often surrounded by an outer surface or stay contained within the epithelium. Common examples of benign tumors include moles and uterine fibroids.

Liposarcomas are the most common subtype of soft tissue sarcomas, accounting for at least 20% of all sarcomas in adults. Soft tissue sarcomas are rare neoplasms with over 150 different histological subtypes or forms. Liposarcomas arise from the precursor lipoblasts of the adipocytes in adipose tissues. Adipose tissues are distributed throughout the body, including such sites as the deep and more superficial layers of subcutaneous tissues as well as in less surgically accessible sites like the retroperitoneum and visceral fat inside the abdominal cavity.

Fibrosarcoma is a malignant mesenchymal tumour derived from fibrous connective tissue and characterized by the presence of immature proliferating fibroblasts or undifferentiated anaplastic spindle cells in a storiform pattern. Fibrosarcomas mainly arise in people between the ages of 25–79 It originates in fibrous tissues of the bone and invades long or flat bones such as the femur, tibia, and mandible. It also involves the periosteum and overlying muscle.
The International Classification of Diseases for Oncology (ICD-O) is a domain-specific extension of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems for tumor diseases. This classification is widely used by cancer registries.

Pleomorphic adenoma is a common benign salivary gland neoplasm characterised by neoplastic proliferation of epithelial (ductal) cells along with myoepithelial components, having a malignant potentiality. It is the most common type of salivary gland tumor and the most common tumor of the parotid gland. It derives its name from the architectural Pleomorphism seen by light microscopy. It is also known as "Mixed tumor, salivary gland type", which refers to its dual origin from epithelial and myoepithelial elements as opposed to its pleomorphic appearance.

A histiocytoma in the dog is a benign tumor. It is an abnormal growth in the skin of histiocytes (histiocytosis), a cell that is part of the immune system. A similar disease in humans, Hashimoto-Pritzker disease, is also a Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Dog breeds that may be more at risk for this tumor include Bulldogs, American Pit Bull Terriers, American Staffordshire Terriers, Scottish Terriers, Greyhounds, Boxers, and Boston Terriers. They also rarely occur in goats and cattle.
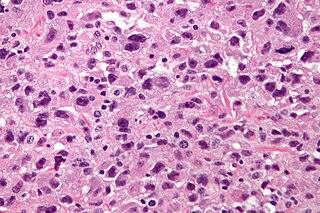
Undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (UPS), also termed pleomorphic myofibrosarcoma, high-grade myofibroblastic sarcoma, and high-grade myofibrosarcoma, is characterized by the World Health Organization (WHO), 2020, as a rare, poorly differentiated neoplasm, i.e. an abnormal growth of cells that have an unclear identity and/or cell of origin. WHO classified it as one of the undifferentiated/unclassified sarcomas in the category of tumors of uncertain differentiation. Sarcomas are cancers known or thought to derive from mesenchymal stem cells that typically develop in bone, muscle, fat, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, tendons, and ligaments. More than 70 sarcoma subtypes have been described. The UPS subtype of these sarcomas consists of tumor cells that are poorly differentiated and may appear as spindle-shaped cells, histiocytes, and giant cells. UPS is considered a diagnosis that defies formal sub-classification after thorough histologic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural examinations fail to identify the type of cells involved.
An ameloblastic fibroma is a fibroma of the ameloblastic tissue, that is, an odontogenic tumor arising from the enamel organ or dental lamina. It may be either truly neoplastic or merely hamartomatous. In neoplastic cases, it may be labeled an ameloblastic fibrosarcoma in accord with the terminological distinction that reserves the word fibroma for benign tumors and assigns the word fibrosarcoma to malignant ones. It is more common in the first and second decades of life, when odontogenesis is ongoing, than in later decades. In 50% of cases an unerupted tooth is involved.
A mixed tumor is a tumor that derives from multiple tissue types. A biplastic tumor or biphasic tumor has two tissue types.

Mammary-type myofibroblastoma (MFB), also named mammary and extramammary myofibroblastoma, was first termed myofibrolastoma of the breast, or, more simply, either mammary myofibroblastoma (MMFB) or just myofibroblastoma. The change in this terminology occurred because the initial 1987 study and many subsequent studies found this tumor only in breast tissue. However, a 2001 study followed by numerous reports found tumors with the microscopic histopathology and other key features of mammary MFB in a wide range of organs and tissues. Further complicating the issue, early studies on MFB classified it as one of various types of spindle cell tumors that, except for MFB, were ill-defined. These other tumors, which have often been named interchangeably in different reports, are: myelofibroblastoma, benign spindle cell tumor, fibroma, spindle cell lipoma, myogenic stromal tumor, and solitary stromal tumor. Finally, studies suggest that spindle cell lipoma and cellular angiofibroma are variants of MFB. Here, the latter two tumors are tentatively classified as MFB variants but otherwise MFB is described as it is more strictly defined in most recent publications. The World Health Organization, 2020, classified mammary type myofibroblastoma tumors and myofibroblastoma tumors as separate tumor forms within the category of fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors.
Vulvar tumors are those neoplasms of the vulva. Vulvar and vaginal neoplasms make up a small percentage (3%) of female genital cancers. They can be benign or malignant. Vulvar neoplasms are divided into cystic or solid lesions and other mixed types. Vulvar cancers are those malignant neoplasms that originate from vulvar epithelium, while vulvar sarcomas develop from non-epithelial cells such as bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels, or other connective or supportive tissue. Epithelial and mesenchymal tissue are the origin of vulvar tumors.
Fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors (FMTs) develop from the mesenchymal stem cells which differentiate into fibroblasts and/or the myocytes/myoblasts that differentiate into muscle cells. FMTs are a heterogeneous group of soft tissue neoplasms. The World Health Organization (2020) defined tumors as being FMTs based on their morphology and, more importantly, newly discovered abnormalities in the expression levels of key gene products made by these tumors' neoplastic cells. Histopathologically, FMTs consist of neoplastic connective tissue cells which have differented into cells that have microscopic appearances resembling fibroblasts and/or myofibroblasts. The fibroblastic cells are characterized as spindle-shaped cells with inconspicuous nucleoli that express vimentin, an intracellular protein typically found in mesenchymal cells, and CD34, a cell surface membrane glycoprotein. Myofibroblastic cells are plumper with more abundant cytoplasm and more prominent nucleoli; they express smooth muscle marker proteins such as smooth muscle actins, desmin, and caldesmon. The World Health Organization further classified FMTs into four tumor forms based on their varying levels of aggressiveness: benign, intermediate, intermediate, and malignant.
Myxofibrosarcoma (MFS), although a rare type of tumor, is one of the most common soft tissue sarcomas, i.e. cancerous tumors, that develop in the soft tissues of elderly individuals. Initially considered to be a type of histiocytoma termed fibrous histiocytoma or myxoid variant of malignant fibrous histiocytoma, Angervall et al. termed this tumor myxofibrosarcoma in 1977. In 2020, the World Health Organization reclassified MFS as a separate and distinct tumor in the category of malignant fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors.
The FET protein family the EWSR1 protein encoded by the EWSR1 gene located at band 12.2 of the long arm of chromosome 22; 2) the FUS protein encoded by the FUS gene located at band 16 on the short arm of chromosome 16; and 3) the TAF15 protein encoded by the TAF15 gene located at band 12 on the long arm of chromosome 7 The FET in this protein family's name derives form the first letters of FUS, EWSR1, and TAF15.
Low-grade myofibroblastic sarcoma (LGMS) is a subtype of the malignant sarcomas. As it is currently recognized, LGMS was first described as a rare, atypical myofibroblastic tumor by Mentzel et al. in 1998. Myofibroblastic sarcomas had been divided into low-grade myofibroblastic sarcomas, intermediate‐grade myofibroblasic sarcomas, i.e. IGMS, and high‐grade myofibroblasic sarcomas, i.e. HGMS based on their microscopic morphological, immunophenotypic, and malignancy features. LGMS and IGMS are now classified together by the World Health Organization (WHO), 2020, in the category of intermediate fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors. WHO, 2020, classifies HGMS as a soft tissue tumor in the category of tumors of uncertain differentiation. This article follows the WHO classification: here, LGMS includes IGMS but not HGMS which is a more aggressive and metastasizing tumor than LGMS and consists of cells of uncertain origin.










