
Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC) is a rare multisystem autosomal dominant genetic disease that causes non-cancerous tumours to grow in the brain and on other vital organs such as the kidneys, heart, liver, eyes, lungs and skin. A combination of symptoms may include seizures, intellectual disability, developmental delay, behavioral problems, skin abnormalities, lung disease, and kidney disease.

A benign tumor is a mass of cells (tumor) that does not invade neighboring tissue or metastasize. Compared to malignant (cancerous) tumors, benign tumors generally have a slower growth rate. Benign tumors have relatively well differentiated cells. They are often surrounded by an outer surface or stay contained within the epithelium. Common examples of benign tumors include moles and uterine fibroids.

A glomus tumor is a rare neoplasm arising from the glomus body and mainly found under the nail, on the fingertip or in the foot. They account for less than 2% of all soft tissue tumors. The majority of glomus tumors are benign, but they can also show malignant features. Glomus tumors were first described by Hoyer in 1877 while the first complete clinical description was given by Masson in 1924.

A synovial sarcoma is a rare form of cancer which occurs primarily in the extremities of the arms or legs, often in proximity to joint capsules and tendon sheaths. It is a type of soft-tissue sarcoma.

Hemangioendotheliomas are a family of vascular neoplasms of intermediate malignancy.

Angiomyolipomas are the most common benign tumour of the kidney. Although regarded as benign, angiomyolipomas may grow such that kidney function is impaired or the blood vessels may dilate and burst, leading to bleeding.
Malignant rhabdoid tumour (MRT) is a very aggressive form of tumour originally described as a variant of Wilms' tumour, which is primarily a kidney tumour that occurs mainly in children.

The history of tuberous sclerosis (TSC) research spans less than 200 years. TSC is a rare, multi-system genetic disease that can cause benign tumours to grow on the brain or other vital organs such as the kidneys, heart, eyes, lungs, and skin. A combination of symptoms may include seizures, developmental delay, behavioural problems and skin abnormalities, as well as lung and kidney disease. TSC is caused by mutations on either of two genes, TSC1 and TSC2, which encode for the proteins hamartin and tuberin respectively. These proteins act as tumour growth suppressors and regulate cell proliferation and differentiation. Originally regarded as a rare pathological curiosity, it is now an important focus of research into tumour formation and suppression.

Epithelioid sarcoma is a rare soft tissue sarcoma arising from mesenchymal tissue and characterized by epithelioid-like features. It accounts for less than 1% of all soft tissue sarcomas. It was first definitively characterized by F.M. Enzinger in 1970. It commonly presents itself in the distal limbs of young adults as a small, soft mass or a cluster of bumps. A proximal version has also been described, frequently occurring in the upper extremities. Less commonly, cases are reported in the pelvis, vulva, penis, and spine.
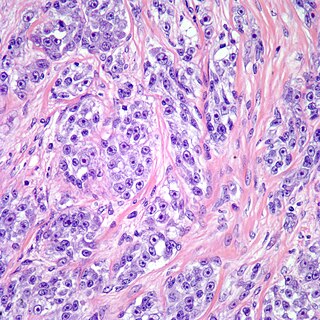
Clear cell sarcoma is a sub-type of a rare form of cancer called a sarcoma. It is known to occur mainly in the soft tissues and dermis. Rare forms were thought to occur in the gastrointestinal tract before they were discovered to be different and redesignated as gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumors.
Juxtaglomerular cell tumor is an extremely rare kidney tumour of the juxtaglomerular cells, with fewer than 100 cases reported in literature. This tumor typically secretes renin, hence the former name of reninoma. It often causes severe hypertension that is difficult to control, in adults and children, although among causes of secondary hypertension it is rare. It develops most commonly in young adults, but can be diagnosed much later in life. It is generally considered benign, but its malignant potential is uncertain.
Sharon Ann Whelan Weiss is an American pathologist who is best known for her contribution to the subspecialty of soft tissue pathology. She is the main author of Soft Tissue Tumors, one of the most widely used textbooks in the field of sarcoma and soft tissue pathology. She is also well known for her seminal descriptions of multiple soft tissue tumors, such as epithelioid hemangioendothelioma and pleomorphic hyalinizing angiectatic tumor of soft parts among others. She has also mentored and trained other well-known soft tissue pathologists.

Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (LGFMS) is a rare type of low-grade sarcoma first described by H. L. Evans in 1987. LGFMS are soft tissue tumors of the mesenchyme-derived connective tissues; on microscopic examination, they are found to be composed of spindle-shaped cells that resemble fibroblasts. These fibroblastic, spindle-shaped cells are neoplastic cells that in most cases of LGFMS express fusion genes, i.e. genes composed of parts of two different genes that form as a result of mutations. The World Health Organization (2020) classified LGFMS as a specific type of tumor in the category of malignant fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors.

Multifocal micronodular pneumocyte hyperplasia (MMPH) is a subtype of pneumocytic hyperplasia.
Vulvar tumors are those neoplasms of the vulva. Vulvar and vaginal neoplasms make up a small percentage (3%) of female genital cancers. They can be benign or malignant. Vulvar neoplasms are divided into cystic or solid lesions and other mixed types. Vulvar cancers are those malignant neoplasms that originate from vulvar epithelium, while vulvar sarcomas develop from non-epithelial cells such as bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels, or other connective or supportive tissue. Epithelial and mesenchymal tissue are the origin of vulvar tumors.

Proliferative fasciitis and proliferative myositis (PF/PM) are rare benign soft tissue lesions that increase in size over several weeks and often regress over the ensuing 1–3 months. The lesions in PF/PM are typically obvious tumors or swellings. Historically, many studies had grouped the two descriptive forms of PF/PM as similar disorders with the exception that proliferative fasciitis occurs in subcutaneous tissues while proliferative myositis occurs in muscle tissues. In 2020, the World Health Organization agreed with this view and defined these lesions as virtually identical disorders termed proliferative fasciitis/proliferative myositis or proliferative fasciitis and proliferative myositis. The Organization also classified them as one of the various forms of the fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors.
Fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors (FMTs) are tumors which develop from the mesenchymal stem cells which differentiate into fibroblasts and/or the myocytes/myoblasts that differentiate into muscle cells. FMTs are a heterogeneous group of soft tissue neoplasms. The World Health Organization (2020) defined tumors as being FMTs based on their morphology and, more importantly, newly discovered abnormalities in the expression levels of key gene products made by these tumors' neoplastic cells. Histopathologically, FMTs consist of neoplastic connective tissue cells which have differented into cells that have microscopic appearances resembling fibroblasts and/or myofibroblasts. The fibroblastic cells are characterized as spindle-shaped cells with inconspicuous nucleoli that express vimentin, an intracellular protein typically found in mesenchymal cells, and CD34, a cell surface membrane glycoprotein. Myofibroblastic cells are plumper with more abundant cytoplasm and more prominent nucleoli; they express smooth muscle marker proteins such as smooth muscle actins, desmin, and caldesmon. The World Health Organization further classified FMTs into four tumor forms based on their varying levels of aggressiveness: benign, intermediate, intermediate, and malignant.
The FET protein family consists of three similarly structured and functioning proteins. They and the genes in the FET gene family which encode them are: 1) the EWSR1 protein encoded by the EWSR1 gene located at band 12.2 of the long arm of chromosome 22; 2) the FUS protein encoded by the FUS gene located at band 16 on the short arm of chromosome 16; and 3) the TAF15 protein encoded by the TAF15 gene located at band 12 on the long arm of chromosome 7 The FET in this protein family's name derives from the first letters of FUS, EWSR1, and TAF15.
The nuclear protein in testis gene encodes a 1,132-amino acid protein termed NUT that is expressed almost exclusively in the testes, ovaries, and ciliary ganglion. NUT protein facilitates the acetylation of chromatin by histone acetyltransferase EP300 in testicular spermatids. This acetylation is a form of chromatin remodeling which compacts spermatid chromatin, a critical step required for the normal conduct of spermatogenesis, i.e. the maturation of spermatids into sperm. Male mice that lacked the mouse Nutm1 gene using a gene knockout method had abnormally small testes, lacked sperm in their cauda epididymis, and were completely sterile. These findings indicate that Nutm1 gene is essential for the development of normal fertility in male mice and suggest that the NUTM1 gene may play a similar role in men.












