
A lipoma is a benign tumor made of fat tissue. They are generally soft to the touch, movable, and painless. They usually occur just under the skin, but occasionally may be deeper. Most are less than 5 cm (2.0 in) in size. Common locations include upper back, shoulders, and abdomen. It is possible to have several lipomas.

Cryosurgery is the use of extreme cold in surgery to destroy abnormal or diseased tissue; thus, it is the surgical application of cryoablation. Cryosurgery has been historically used to treat a number of diseases and disorders, especially a variety of benign and malignant skin conditions.

Fibrosarcoma is a malignant mesenchymal tumour derived from fibrous connective tissue and characterized by the presence of immature proliferating fibroblasts or undifferentiated anaplastic spindle cells in a storiform pattern. Fibrosarcomas mainly arise in people between the ages of 25 and 79. It originates in fibrous tissues of the bone and invades long or flat bones such as the femur, tibia, and mandible. It also involves the periosteum and overlying muscle.
Epulis fissuratum is a benign hyperplasia of fibrous connective tissue which develops as a reactive lesion to chronic mechanical irritation produced by the flange of a poorly fitting denture. More simply, epulis fissuratum is where excess folds of firm tissue form inside the mouth, as a result of rubbing on the edge of dentures that do not fit well. It is a harmless condition and does not represent oral cancer. Treatment is by simple surgical removal of the lesion, and also by adjustment of the denture or provision of a new denture.
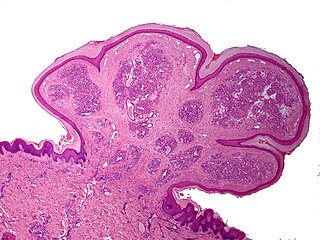
A pyogenic granuloma or lobular capillary hemangioma is a vascular tumor that occurs on both mucosa and skin, and appears as an overgrowth of tissue due to irritation, physical trauma, or hormonal factors. It is often found to involve the gums, skin, or nasal septum, and has also been found far from the head, such as in the thigh.
A peripheral ossifying fibroma, also known as ossifying fibrous epulis, is “a gingival nodule which is composed of a cellular fibroblastic connective tissue stroma which is associated with the formation of randomly dispersed foci of mineralised products, which consists of bone, cementum-like tissue, or a dystrophic calcification. The lesion is considered part of an ossifying fibroma, but that is usually considered to be a jaw tumor. Because of its overwhelming incidence on the gingiva, the condition is associated with two other diseases, though not because they occur together. Instead, the three are associated with each other because they appear frequently on gingiva: pyogenic granuloma and peripheral giant cell granuloma. Some researchers believe peripheral ossifying fibromas to be related to pyogenic fibromas and, in some instances, are the result of a pyogenic granuloma which has undergone fibrosis and calcification.
Giant-cell fibroma is a benign localized fibrous mass. It often mimics other fibroepithelial growths and can be distinguished by its histopathology. The exact cause of giant-cell fibromas is unknown however there is no evidence to show that it can be caused by irritation. Giant-cell fibromas can be removed by surgical incision, electrosurgery, or laser excision.

An ameloblastic fibroma is a fibroma of the ameloblastic tissue, that is, an odontogenic tumor arising from the enamel organ or dental lamina. It may be either truly neoplastic or merely hamartomatous. In neoplastic cases, it may be labeled an ameloblastic fibrosarcoma in accord with the terminological distinction that reserves the word fibroma for benign tumors and assigns the word fibrosarcoma to malignant ones. It is more common in the first and second decades of life, when odontogenesis is ongoing, than in later decades. In 50% of cases an unerupted tooth is involved.
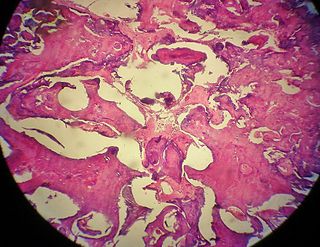
An odontoma, also known as an odontome, is a benign tumour linked to tooth development. Specifically, it is a dental hamartoma, meaning that it is composed of normal dental tissue that has grown in an irregular way. It includes both odontogenic hard and soft tissues. As with normal tooth development, odontomas stop growing once mature which makes them benign.
Peripheral odontogenic fibroma(PFO) is a fibrous connective tissue mass that is exophytic and covered in surface epithelium that contains odontogenic epithelium. The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies peripheral odontogenic fibroma as a fibroblastic neoplasm with variable amounts of odontogenic epithelium that appears to be dormant. Dentine and/or cementum-like material may be present.

Angiofibroma (AGF) is a descriptive term for a wide range of benign skin or mucous membrane lesions in which individuals have:
- benign papules, i.e. pinhead-sized elevations that lack visible evidence of containing fluid;
- nodules, i.e. small firm lumps usually >0.1 cm in diameter; and/or
- tumors, i.e. masses often regarded as ~0.8 cm or larger.
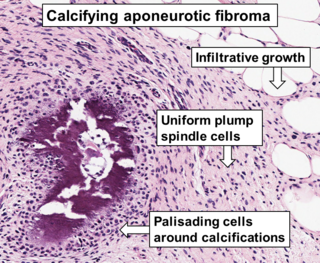
Aponeurotic fibroma, also known as calcifying aponeurotic fibroma, and juvenile aponeurotic fibroma is characterized by a lesion that usually presents as a painless, solitary, deep fibrous nodule, often adherent to tendon, fascia, or periosteum, on the hands and feet. The World Health Organization in 2020 reclassified aponeurotic fibroma nodules as a specific benign type of the fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors. Aponeurotic fibromas are diagnosed based on histopathology and treated by surgical excision. They are more common in males than females.
Infantile digital fibromatosis (IDF), also termed inclusion body fibromatosis, Reye tumor, or Reye's tumor, usually occurs as a single, small, asymptomatic, nodule in the dermis on a finger or toe of infants and young children. IMF is a rare disorder with approximately 200 cases reported in the medical literature as of 2021. The World Health Organization in 2020 classified these nodules as a specific benign tumor type in the category of fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors. IDF was first described by the Australian pathologist, Douglas Reye, in 1965.
Collagenous fibroma, also known as desmoplastic fibroblastoma, is a slow-growing, deep-set, benign fibrous tumor, usually located in the deep subcutis, fascia, aponeurosis, or skeletal muscle of the extremities, limb girdles, or head and neck regions. The World Health Organization in 2020 reclassified desmoplastic fibroblastoma/collagenous fibroma as a specific benign tumor type within the broad category of fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors.
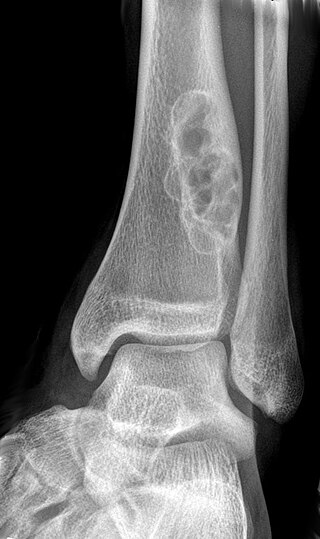
A non-ossifying fibroma (NOF) is a benign bone tumor of the osteoclastic giant cell-rich tumor type. It generally occurs in the metaphysis of long bones in children and adolescents. Typically, there are no symptoms unless there is a fracture. It can occur as part of a syndrome such as when multiple non-ossifying fibromas occur in neurofibromatosis, or Jaffe–Campanacci syndrome in combination with cafe-au-lait spots, mental retardation, hypogonadism, eye and cardiovascular abnormalities.
Epulis is any tumor like enlargement situated on the gingival or alveolar mucosa. The word literally means "(growth) on the gingiva", and describes only the location of the mass and has no further implications on the nature of the lesion. There are three types: fibromatous, ossifying and acanthomatous. The related term parulis refers to a mass of inflamed granulation tissue at the opening of a draining sinus on the alveolus over the root of an infected tooth. Another closely related term is gingival enlargement, which tends to be used where the enlargement is more generalized over the whole gingiva rather than a localized mass.

Fibroma of tendon sheath is a benign tumor that presents as a small subcutaneous nodule that slowly increases in size. This is a notably uncommon condition. According to case report literature, the tumors often have a multinodular growth pattern, with individual nodules being composed of bland, slender, spindle-shaped cells (myofibroblasts) in a dense, fibrous matrix.” A common microscopic finding is the presence of elongated, slit-like blood vessels. The lesions nearly always arise in the distal portions of the extremities. They often occur on the fingers, hands, toes, or feet. Although they are benign, they may recur after surgical excision in up to 40% of people.
A juvenile active ossifying fibroma is a benign fibro-osseous neoplasm composed of mixture of stroma and bone characterized by rapid and destructive growth.
Vulvar tumors are those neoplasms of the vulva. Vulvar and vaginal neoplasms make up a small percentage (3%) of female genital cancers. They can be benign or malignant. Vulvar neoplasms are divided into cystic or solid lesions and other mixed types. Vulvar cancers are those malignant neoplasms that originate from vulvar epithelium, while vulvar sarcomas develop from non-epithelial cells such as bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels, or other connective or supportive tissue. Epithelial and mesenchymal tissue are the origin of vulvar tumors.
Fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors (FMTs) develop from the mesenchymal stem cells which differentiate into fibroblasts and/or the myocytes/myoblasts that differentiate into muscle cells. FMTs are a heterogeneous group of soft tissue neoplasms. The World Health Organization (2020) defined tumors as being FMTs based on their morphology and, more importantly, newly discovered abnormalities in the expression levels of key gene products made by these tumors' neoplastic cells. Histopathologically, FMTs consist of neoplastic connective tissue cells which have differented into cells that have microscopic appearances resembling fibroblasts and/or myofibroblasts. The fibroblastic cells are characterized as spindle-shaped cells with inconspicuous nucleoli that express vimentin, an intracellular protein typically found in mesenchymal cells, and CD34, a cell surface membrane glycoprotein. Myofibroblastic cells are plumper with more abundant cytoplasm and more prominent nucleoli; they express smooth muscle marker proteins such as smooth muscle actins, desmin, and caldesmon. The World Health Organization further classified FMTs into four tumor forms based on their varying levels of aggressiveness: benign, intermediate, intermediate, and malignant.











