| Glassy cell carcinoma of the cervix | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Glassy cell carcinoma |
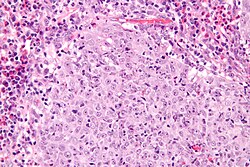 | |
| Micrograph of a glassy cell carcinoma of the cervix. H&E stain. | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
Glassy cell carcinoma of the cervix, also glassy cell carcinoma, is a rare aggressive malignant tumour of the uterine cervix. [1] The tumour gets its name from its microscopic appearance; its cytoplasm has a glass-like appearance.

