Related Research Articles

Von Hippel–Lindau disease (VHL), also known as VonHippel–Lindau syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder with multisystem involvement. It is characterized by visceral cysts and benign tumors with potential for subsequent malignant transformation. It is a type of phakomatosis that results from a mutation in the Von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 3p25.3.
Trench fever is a moderately serious disease transmitted by body lice. It infected armies in Flanders, France, Poland, Galicia, Italy, Macedonia, Mesopotamia, Russia and Egypt in World War I. Three noted cases during WWI were the authors J. R. R. Tolkien, A. A. Milne, and C. S. Lewis. From 1915 to 1918 between one-fifth and one-third of all British troops reported ill had trench fever while about one-fifth of ill German and Austrian troops had the disease. The disease persists among the homeless. Outbreaks have been documented, for example, in Seattle and Baltimore in the United States among injection drug users and in Marseille, France, and Burundi.

Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta is a disease of the immune system. It is the more severe version of pityriasis lichenoides chronica. The disease is characterized by rashes and small lesions on the skin. The disease is more common in males and usually occurs in young adulthood, although it has been seen in every age group and every race. It is possible for the disease to go into remission for short periods of time or forever.
The Pirbright Institute is a research institute in Surrey, England, dedicated to the study of infectious diseases of farm animals. It forms part of the UK government's Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC). The institute employs scientists, vets, PhD students, and operations staff.

Angiomas are benign tumors derived from cells of the vascular or lymphatic vessel walls (endothelium) or derived from cells of the tissues surrounding these vessels.
Bartonellosis is an infectious disease produced by bacteria of the genus Bartonella. Bartonella species cause diseases such as Carrión's disease, trench fever, cat-scratch disease, bacillary angiomatosis, peliosis hepatis, chronic bacteremia, endocarditis, chronic lymphadenopathy, and neurological disorders.
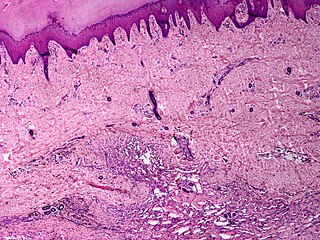
Angiomatosis is a non-neoplastic condition characterised by nests of proliferating capillaries arranged in a lobular pattern, displacing adjacent muscle and fat. It consists of many angiomas.

Bacillary angiomatosis (BA) is a form of angiomatosis associated with bacteria of the genus Bartonella.

Eugen Adolf Arthur von Hippel was a German ophthalmologist born in Königsberg.

Arvid Vilhelm Lindau was a Swedish pathologist and bacteriologist born in Malmö.
Bartonella quintana, originally known as Rochalimaea quintana, and "Rickettsia quintana", is a bacterium transmitted by the human body louse that causes trench fever. This bacterial species caused outbreaks of trench fever affecting 1 million soldiers in Europe during World War I.

Periorbital dermatitis is a skin condition, a variant of perioral dermatitis, occurring on the lower eyelids and skin adjacent to the upper and lower eyelids.
Multifocal lymphangioendotheliomatosis, also known as congenital cutaneovisceral angiomatosis with thrombocytopenia and multifocal lymphangioendotheliomatosis with thrombocytopenia (MLT), is a skin condition that presents at birth with hundreds of red-brown plaques as large as several centimeters.
Cutaneous actinomycosis is a chronic disease that affects the deep subcutaneous tissue of the skin. Caused by an anaerobic, Gram-positive, filamentous type of bacteria in the genus Actinomyces, invasion of the soft tissue leads to the formation of abnormal channels leading to the skin surface that discharge pale yellow sulfur granules.

Elephantiasis nostras is a disease that usually affects the lower legs or scrotum. Swelling is accompanied by rough nodules or wart-like plaques on the skin. If the disease is not treated, it eventually results in pain and immobility.

Borderline leprosy is a cutaneous skin condition with numerous skin lesions that are red irregularly shaped plaques.

Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia refers to a groups of benign cutaneous disorders characterized by collections of lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells in the skin. Conditions included in this groups are:

Cat-scratch disease (CSD) is an infectious disease that most often results from a scratch or bite of a cat. Symptoms typically include a non-painful bump or blister at the site of injury and painful and swollen lymph nodes. People may feel tired, have a headache, or a fever. Symptoms typically begin within 3–14 days following infection.
References
- ↑ James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. (10th ed.). Saunders. Page 169. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.