The Delta Works is a series of construction projects in the southwest of the Netherlands to protect a large area of land around the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta from the sea. Constructed between 1954 and 1997, the works consist of dams, sluices, locks, dykes, levees, and storm surge barriers located in the provinces of South Holland and Zeeland.
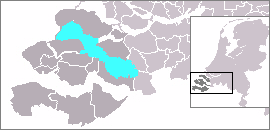
The Eastern Scheldt is a former estuary in the province of Zeeland, Netherlands, between Schouwen-Duiveland and Tholen on the north and Noord-Beveland and Zuid-Beveland on the south. It also features the largest national park in the Netherlands, founded in 2002.

The Thames Barrier is a retractable barrier system built to protect the floodplain of most of Greater London from exceptionally high tides and storm surges moving up from the North Sea. It has been operational since 1982. When needed, it is closed (raised) during high tide; at low tide, it can be opened to restore the river's flow towards the sea. Built about 2 miles east of the Isle of Dogs, its northern bank is in Silvertown in the London Borough of Newham and its southern bank is in the New Charlton area of the Royal Borough of Greenwich.

The Afsluitdijk is a major dam and causeway in the Netherlands. It was constructed between 1927 and 1932 and runs from Den Oever in North Holland province to the village of Zurich in Friesland province, over a length of 32 kilometres (20 mi) and a width of 90 metres (300 ft), at an initial height above Amsterdam Ordnance Datum of between 6.7 metres (22 ft) along the section at Friesland, and 7.4 metres (24 ft) where it crosses the deep channel of the Vlieter. The height at the greater sea depths west of Friesland was required to be a minimum of 7 metres everywhere when originally constructed.

The Maeslantkering is a storm surge barrier on the Nieuwe Waterweg, in South Holland, Netherlands. It was constructed from 1991 to 1997. As part of the Delta Works the barrier responds to water level predictions calculated by a centralized computer system called BOS. It automatically closes when Rotterdam is threatened by floods.

The 1953 North Sea flood was a major flood caused by a heavy storm surge that struck the Netherlands, north-west Belgium, England and Scotland. Most sea defences facing the surge were overwhelmed, resulting in extensive flooding.

The Oosterscheldekering, between the islands Schouwen-Duiveland and Noord-Beveland, is the largest of the Delta Works, a series of dams and storm surge barriers, designed to protect the Netherlands from flooding from the North Sea. The construction of the Delta Works was a response to the widespread damage and loss of life in the North Sea flood of 1953.

A flood barrier, surge barrier or storm surge barrier is a specific type of floodgate, designed to prevent a storm surge or spring tide from flooding the protected area behind the barrier. A surge barrier is almost always part of a larger flood protection system consisting of floodwalls, levees, and other constructions and natural geographical features.

MOSE is a project intended to protect the city of Venice, Italy, and the Venetian Lagoon from flooding.

The Port of Rotterdam is the largest seaport in Europe, and the world's largest seaport outside of East Asia, located in and near the city of Rotterdam, in the province of South Holland in the Netherlands. From 1962 until 2004, it was the world's busiest port by annual cargo tonnage. It was overtaken first in 2004 by the port of Singapore, and since then by Shanghai and other very large Chinese seaports. In 2020, Rotterdam was the world's tenth-largest container port in terms of twenty-foot equivalent units (TEU) handled. In 2017, Rotterdam was also the world's tenth-largest cargo port in terms of annual cargo tonnage.

Flood control is an important issue for the Netherlands, as due to its low elevation, approximately two thirds of its area is vulnerable to flooding, while the country is densely populated. Natural sand dunes and constructed dikes, dams, and floodgates provide defense against storm surges from the sea. River dikes prevent flooding from water flowing into the country by the major rivers Rhine and Meuse, while a complicated system of drainage ditches, canals, and pumping stations keep the low-lying parts dry for habitation and agriculture. Water control boards are the independent local government bodies responsible for maintaining this system.

The Fox Point Hurricane Barrier is a 3,000-foot (910 m) long tidal flood barrier spanning the Providence River in Providence, Rhode Island, located 750 feet (230 m) upstream from Fox Point. It was constructed between 1960 and 1966 to protect the low-lying downtown area of the city from damaging storm surge and floods associated with hurricanes and other major storm events.

Cyclone Tilo was a European windstorm which affected northern and western Europe in early November 2007. Combining with the remnants of Hurricane Noel, Tilo's storm surge led to the North Sea flood of 2007, affecting the coastlines of the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, Germany, Denmark, Norway and Belgium, starting on the night of 8–9 November 2007.

The Europoortkering or barrier of the Europoort is a program of engineering works in addition to the Delta Plan, designed to protect the maritime access routes from the port of Rotterdam and thus, the entire South Holland against storms and tides.

The Markiezaatskade is a compartmentalisation dam in The Netherlands, situated between South Beveland and Molenplaat, near Bergen op Zoom. The dam was constructed as part of the Delta Works, and has a length of 4 kilometres.

The Volkerakdam or Volkerakwerken is the name given to a group of hydraulic engineering structures located between Goeree-Overflakkee and North Brabant in The Netherlands. The works are not a single dam, but are composed of three distinct structures: a dam between Goeree-Overflakkee and Hellegatsplein, a series of locks from Hellegatsplein to North Brabant, and a bridge from Hellegatsplein to Hoekse Waard. The works cross three separate bodies of water: the Haringvliet, Hollands Diep and Volkerak. The works together comprise the fifth project of the Delta Works.

The Grevelingendam is a dam located in the Grevelingen sea inlet between Schouwen-Duiveland and Goeree-Overflakkee in The Netherlands. The Grevelingendam was the fourth structure constructed as part of the Delta Works.

The Stormvloedkering Hollandse IJssel, Hollandse IJsselkering or Algerakering is a storm surge barrier located on the Hollandse IJssel, at the municipal boundary of Capelle aan den IJssel and Krimpen aan den IJssel, east of Rotterdam in The Netherlands. The construction of the works comprised the first project of the Delta Works, undertaken in response to the disastrous effects of the North Sea flood of 1953. Prior to 1954, the spelling Hollandsche was used in the official name.

The Zandkreekdam is a compartmentalisation dam located approximately 3 kilometres north of the city of Goes in The Netherlands, which connects Zuid-Beveland with Noord-Beveland, and separates the Oosterschelde from the Veerse Meer.

Pieter Jacobus (P.J.) Wemelsfelder was a prominent Dutch hydraulic engineer who made significant contributions to the field of hydrometry in the Netherlands, and in hydraulic engineering internationally. In addition to his involvement in the design and planning of the Delta Works, he published widely and is notable for the first use of probability theory in the design of flood levels.




















