
Interior Alaska is the central region of Alaska's territory, roughly bounded by the Alaska Range to the south and the Brooks Range to the north. It is largely wilderness. Mountains include Denali in the Alaska Range, the Wrangell Mountains, and the Ray Mountains. The native people of the interior are Alaskan Athabaskans. The largest city in the interior is Fairbanks, Alaska's second-largest city, in the Tanana Valley. Other towns include North Pole, just southeast of Fairbanks, Eagle, Tok, Glennallen, Delta Junction, Nenana, Anderson, Healy and Cantwell. The interior region has an estimated population of 113,154.

The geography of Iraq is diverse and falls into five main regions: the desert, Upper Mesopotamia, the northern highlands of Iraq, Lower Mesopotamia, and the alluvial plain extending from around Tikrit to the Persian Gulf.
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmosphere, the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers to day-to-day temperature, precipitation, and other atmospheric conditions, whereas climate is the term for the averaging of atmospheric conditions over longer periods of time. When used without qualification, "weather" is generally understood to mean the weather of Earth.

Death Valley is a desert valley in Eastern California, in the northern Mojave Desert, bordering the Great Basin Desert. It is thought to be the hottest place on Earth during summer.

The Sacramento Valley is the area of the Central Valley of the U.S. state of California that lies north of the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta and is drained by the Sacramento River. It encompasses all or parts of ten Northern California counties. Although many areas of the Sacramento Valley are rural, it contains several urban areas, including the state capital, Sacramento.

Khobar is a city and governorate in the Eastern Province of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, situated on the coast of the Persian Gulf. With a population of 409,549 as of 2022 in the city core and 658,550 in the governorate, Khobar is part of the 'Triplet Cities' area, or Dammam metropolitan area along with Dammam and Dhahran, forming the residential core of the region.

The climate of India consists of a wide range of weather conditions across a vast geographic scale and varied topography. Based on the Köppen system, India encompasses a diverse array of climatic subtypes. These range from arid and semi-arid regions in the west to highland, sub-arctic, tundra, and ice cap climates in the northern Himalayan regions, varying with elevation. The northern lowlands experience subtropical conditions, with some areas at higher altitudes, like Srinagar, touching continental climates. In contrast, much of the south and the east exhibit tropical climate conditions, which support lush rainforests in these territories. Many regions have starkly different microclimates, making it one of the most climatically diverse countries in the world. The country's meteorological department follows the international standard of four seasons with some local adjustments: winter, summer, monsoon or rainy season, and a post-monsoon period.

The climate of Chicago is classified as hot-summer humid continental with hot humid summers and cold, occasionally snowy winters. All four seasons are distinctly represented: Winters are cold and often see snow with below 0 Celsius temperatures and windchills, while summers are warm and humid with temperatures being hotter inland, spring and fall bring bouts of both cool and warm weather and fairly sunny skies. Annual precipitation in Chicago is moderate and relatively evenly distributed, the driest months being January and February and the wettest July and August. Chicago's weather is influenced during all four seasons by the nearby presence of Lake Michigan.
The climate of Salt Lake City, Utah features cold and snowy winters, hot and dry summers, and modest to light seasonal rainfall. Lying in the Salt Lake Valley, the city is surrounded by mountains and the Great Salt Lake. Under the Köppen climate classification, Salt Lake City has either a Mediterranean climate (Csa) or dry-summer continental climate (Dsa) depending on which variant of the system is used, though it borders on a cold semi-arid climate (BSk) due to the city's relatively low precipitation.

Ibri is a city and Wilāyat (Province) in the Ad Dhahirah Governorate, in northwest Oman.

The climate of Minneapolis–Saint Paul is the long term weather trends and historical events of the Minneapolis–Saint Paul metropolitan area in east central Minnesota. Minneapolis and St. Paul, together known as the Twin Cities, are the core of the 15th largest metropolitan area in the United States. With a population of 3.6 million people, the region contains approximately 60% of the population of Minnesota. Due to its location in the northern and central portion of the U.S., the Twin Cities has the coldest average temperature of any major metropolitan area in the nation. Winters are very cold, summer is warm and humid, snowfall is common in the winter and thunderstorms with heavy rainfall occur during the spring, summer and autumn. Though winter can be cold, the area receives more sunlight hours in mid-winter than many other warmer parts of the country, including all of the Great Lakes states, the Pacific Northwest, parts of the South, and almost all of the Northeast. Unless otherwise indicated, all normals data presented below are based on data at Minneapolis/St. Paul International Airport, the official Twin Cities climatology station, from the 1981−2010 normals period.
Oklahoma City lies in a temperate humid subtropical climate, with frequent variations in weather daily and seasonally, except during the consistently hot and humid summer months. Consistent winds, usually from the south or south-southeast during the summer, help temper the hotter weather. Consistent northerly winds during the winter can intensify cold periods. The normal annual mean temperature is 61.4 °F (16.3 °C); the coolest year was 1895 with a mean of 57.9 °F (14.4 °C), while the warmest 2012 at 64.1 °F (17.8 °C). Precipitation averages 36.52 inches (928 mm) annually, falling on an average 84 days, with the warmer months receiving more; annual precipitation has historically ranged from 15.74 in (400 mm) in 1901 to 56.95 in (1,447 mm) in 2007. The sun shines about 69% of the time, with monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 60% in December to 80% in July.
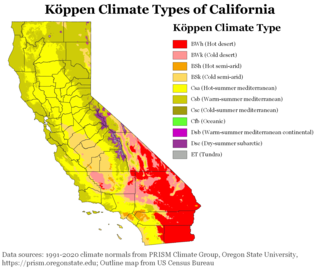
The climate of California varies widely from hot desert to alpine tundra, depending on latitude, elevation, and proximity to the Pacific Coast. California's coastal regions, the Sierra Nevada foothills, and much of the Central Valley have a Mediterranean climate, with warmer, drier weather in summer and cooler, wetter weather in winter. The influence of the ocean generally moderates temperature extremes, creating warmer winters and substantially cooler summers in coastal areas.

The climate of the United States varies due to changes in latitude, and a range of geographic features, including mountains and deserts. Generally, on the mainland, the climate of the U.S. becomes warmer the farther south one travels, and drier the farther west, until one reaches the West Coast.

The climate of New York (state) is generally humid continental, while the extreme southeastern portion of the state lies in the warmer humid subtropical climate zone. Winter temperatures average below freezing during January and February in much of the state of New York, but several degrees above freezing along the Atlantic coastline, including New York City.
Malta has a Subtropical-Mediterranean climate according to the Köppen climate classification (Csa), with very mild winters and warm to hot summers. Rain occurs mainly in winter, with summer being generally dry. According to the Troll-Paffen climate classification and the Siegmund/Frankenberg climate classification, Malta lies within the subtropical zone, being at 35ºN latitude.
Minjibir is a Local Government Area in Kano State, Nigeria. Its headquarters are in the town of Minjibir, about 20 km northeast of the state capital Kano.

Dubai features a tropical desert, hot arid climate. Dubai has two seasons – winter and summer. Rainfall has been increasing over the past few decades in the city accumulating to more than 130 mm (5.12 in) per year.

The Summer 2012 North American heat wave was one of the most severe heat waves in modern North American history. It resulted in more than 82 heat-related deaths across the United States and Canada, and an additional twenty-two people died in the resultant June 2012 North American derecho. This long-lived, straight-line wind and its thunderstorms cut electrical power to 3.7 million customers. Over 500,000 were still without power on July 6, as the heat wave continued. Temperatures generally decreased somewhat the week of July 9 in the east, but the high pressure shifted to the west, causing the core of the hot weather to build in the Mountain States and the Southwestern United States shifting eastwards again by mid-July. By early August, the core of the heat remained over the Southern Plains.

The 2013–14 North American winter was one of the most significant for the United States, due in part to the breakdown of the polar vortex in November 2013, which allowed very cold air to travel down into the United States, leading to an extended period of very cold temperatures. The pattern continued mostly uninterrupted throughout the winter and numerous significant winter storms affected the Eastern United States, with the most notable one being a powerful winter storm that dumped ice and snow in the Southeastern United States and the Northeastern United States in mid-February. Most of the cold weather abated by the end of March, though a few winter storms did affect the Western United States towards the end of the winter.

















