
AstraZeneca plc (AZ) is a British-Swedish multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company with its headquarters at the Cambridge Biomedical Campus in Cambridge, England. It has a portfolio of products for major diseases in areas including oncology, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, infection, neuroscience, respiratory, and inflammation. It has been involved in developing the Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine.

Fulbourn Hospital is a mental health facility located between the Cambridgeshire village of Fulbourn and the Cambridge city boundary at Cherry Hinton, about 5 miles (8 km) south-east of the city centre. It is managed by the Cambridgeshire and Peterborough NHS Foundation Trust. The Ida Darwin Hospital site is situated behind Fulbourn Hospital. It is run and managed by the same trust, with both hospitals sharing the same facilities and staff pool.
IQVIA, formerly Quintiles and IMS Health, Inc., is an American Fortune 500 and S&P 500 multinational company serving the combined industries of health information technology and clinical research. IQVIA is a provider of biopharmaceutical development, professional consulting and commercial outsourcing services, focused primarily on Phase I-IV clinical trials and associated laboratory and analytical services, including investment strategy and management consulting services. It has a network of more than 88,000 employees in more than 100 countries and a market capitalization of US$49 billion as of August 2021. As of 2023, IQVIA was reported to be one of the world's largest contract research organizations (CRO).
The Clinical Practice Research Datalink (CPRD) is an observational and interventional research service that operates as part of the UK Department of Health. It is jointly funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research(NIHR) and the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA). CPRD is working closely with the extensive primary care, topic specific and comprehensive NIHR research networks and with NHS Digital.

The Cambridge Biomedical Campus is the largest centre of medical research and health science in Europe. The site is located at the southern end of Hills Road in Cambridge, England.
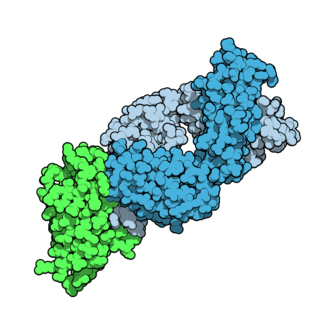
Tremelimumab, sold under the brand name Imjudo, is a fully human monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Tremelimumab is designed to attach to and block CTLA-4, a protein that controls the activity of T cells, which are part of the immune system.

Healthcare in the United Kingdom is a devolved matter, with England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales each having their own systems of publicly funded healthcare, funded by and accountable to separate governments and parliaments, together with smaller private sector and voluntary provision. As a result of each country having different policies and priorities, a variety of differences have developed between these systems since devolution.

The National Health Service (NHS) is the umbrella term for the publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom, comprising the NHS in England, NHS Scotland and NHS Wales. Health and Social Care in Northern Ireland was created separately and is often locally referred to as "the NHS". The original three systems were established in 1948 as part of major social reforms following the Second World War. The founding principles were that services should be comprehensive, universal and free at the point of delivery—a health service based on clinical need, not ability to pay. Each service provides a comprehensive range of health services, provided without charge for people ordinarily resident in the United Kingdom apart from dental treatment and optical care. In England, NHS patients have to pay prescription charges; some, such as those aged over 60, or those on certain state benefits, are exempt.
The National Cancer Intelligence Network (NCIN), was set up in 2008 to drive improvements in care standards and clinical outcomes. NCIN is now part of Public Health England, following the Health and Social Care Act 2012.

Olaparib, sold under the brand name Lynparza, is a medication for the maintenance treatment of BRCA-mutated advanced ovarian cancer in adults. It is a PARP inhibitor, inhibiting poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP), an enzyme involved in DNA repair. It acts against cancers in people with hereditary BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations, which include some ovarian, breast, and prostate cancers.
Palantir Technologies Inc. is a public American company that specializes in software platforms for big data analytics. Headquartered in Denver, Colorado, it was founded by Peter Thiel, Nathan Gettings, Joe Lonsdale, Stephen Cohen, and Alex Karp in 2003. The company's name is derived from The Lord of the Rings where the magical palantíri were "seeing-stones," described as indestructible balls of crystal used for communication and to see events in other parts of the world.
Cambridgeshire and Peterborough NHS Foundation Trust (CPFT) provides community, mental health and learning disability services in Cambridgeshire, England. The trust provides specialist services across the east of England and across Britain.

Genomics England is a British company set up and owned by the United Kingdom Department of Health and Social Care to run the 100,000 Genomes Project. The project aimed in 2014 to sequence 100,000 genomes from NHS patients with a rare disease and their families, and patients with cancer. An infectious disease strand is being led by Public Health England.

Dr. Carina Tyrrell is a British-Swiss public health physician, investor,philanthropist and beauty pageant titleholder who was crowned Miss England and Miss United Kingdom in 2014. Tyrrell graduated from the University of Cambridge with first-class honours, featured on the front page of The Times for her work to deliver the Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 vaccine, and is known for making international news for being the first woman from one of the world's top universities, to participate in Miss World.
Linguamatics, headquartered in Cambridge, England, with offices in the United States and UK, is a provider of text mining systems through software licensing and services, primarily for pharmaceutical and healthcare applications. Founded in 2001, the company was purchased by IQVIA in January 2019.
The National Data Guardian for Health and Social Care is an independent, non-regulatory, advice giving body in England sponsored by the Department of Health and Social Care. Dame Fiona Caldicott had held the position on a non-statutory basis since its inception in November 2014. She was appointed the first statutory National Data Guardian in March 2019 following the introduction of the Health and Social Care Act 2018, and remained in post until her death in February 2021. Dr Nicola Byrne was appointed to the role in March 2021 by the Secretary of State for Health and Social Care.
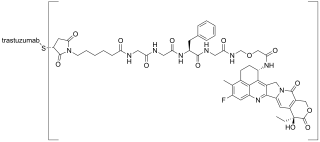
Trastuzumab deruxtecan, sold under the brand name Enhertu, is an antibody-drug conjugate consisting of the humanized monoclonal antibody trastuzumab (Herceptin) covalently linked to the topoisomerase I inhibitor deruxtecan. It is licensed for the treatment of breast cancer or gastric or gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. Trastuzumab binds to and blocks signaling through epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2/neu) on cancers that rely on it for growth. Additionally, once bound to HER2 receptors, the antibody is internalized by the cell, carrying the bound deruxtecan along with it, where it interferes with the cell's ability to make DNA structural changes and replicate its DNA during cell division, leading to DNA damage when the cell attempts to replicate itself, destroying the cell.

The Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID‑19 vaccine, sold under the brand names Covishield and Vaxzevria among others, is a viral vector vaccine for the prevention of COVID-19. It was developed in the United Kingdom by Oxford University and British-Swedish company AstraZeneca, using as a vector the modified chimpanzee adenovirus ChAdOx1. The vaccine is given by intramuscular injection. Studies carried out in 2020 showed that the efficacy of the vaccine is 76.0% at preventing symptomatic COVID-19 beginning at 22 days following the first dose and 81.3% after the second dose. A study in Scotland found that, for symptomatic COVID-19 infection after the second dose, the vaccine is 81% effective against the Alpha variant and 61% against the Delta variant.
The COVID-19 vaccination programme in the United Kingdom is an ongoing mass immunisation campaign for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom.
Jasmin Fisher, is an Israeli-British biologist who is Professor of computational biology at University College London. She is Group Leader of the Fisher Lab at UCL Cancer Institute, which develops state-of-the-art computational models and analysis techniques to study cancer evolution and mechanisms of drug resistance to identify better personalised treatments for cancer patients.












