Related Research Articles
Alexander Aetolus was a Greek poet and grammarian, the only known representative of Aetolian poetry.

Vacuna was an ancient Sabine goddess, identified by ancient Roman sources and later scholars with numerous other goddesses, including Ceres, Diana, Nike, Minerva, Bellona, Venus and Victoria. She was mainly worshipped at a sanctuary near Horace's villa, in sacred woods at Reate, and at Rome.
Crantor of Soli was an Ancient Greek philosopher and member of the Old Academy who was the first philosopher to write commentaries on the works of Plato.
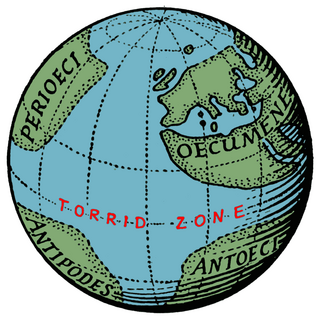
Crates of Mallus was a Greek grammarian and Stoic philosopher, leader of the literary school and head of the library of Pergamum. He was described as the Crates from Mallus to distinguish him from other philosophers by the same name. His chief work was a critical and exegetical commentary on Homer. He is also famous for constructing the earliest known globe of the Earth.
Apollodorus of Athens son of Asclepiades, was a Greek scholar, historian, and grammarian. He was a pupil of Diogenes of Babylon, Panaetius the Stoic, and the grammarian Aristarchus of Samothrace, under whom he appears to have studied together with his contemporary Dionysius Thrax. He left Alexandria around 146 BC, most likely for Pergamon, and eventually settled in Athens.
Pratinas was one of the early tragic poets who flourished at Athens at the beginning of the fifth century BCE, and whose combined efforts were thought by critics to have brought the art to its perfection.
Pomponius Porphyrion was a Latin grammarian and commentator on Horace.
Publius Consentius was a 5th-century Latin grammarian and the author of two treatises, which are perhaps the fragments of a complete grammar: Ars de duabus partibus orationis, nomine et verbo, on the noun and the verb, which was much used during the Carolingian period, and Ars de barbarismis et metaplasmis, on barbarisms and metaplasm. The latter refers to a third essay, De structurarum ratione, on the structure of sentences, which, if ever published, no longer exists.
(Marcus) Aristius Fuscus was a friend of the Roman poet Horace, and is mentioned in Satire I.9, Ode 1.22 and elsewhere. Horace addresses Epistle 1.10 to Fuscus and links Fuscus and himself as 'twins' separated by their love for the city and the country, respectively. In Horace's Satire 1.9, Fuscus meets Horace struggling with a boor but fails to save Horace.

Eustathius of Thessalonica was a Byzantine Greek scholar and Archbishop of Thessalonica. He is most noted for his contemporary account of the sack of Thessalonica by the Normans in 1185, for his orations and for his commentaries on Homer, which incorporate many remarks by much earlier researchers.

Acron, son of Xenon, was a Greek physician born at Agrigentum in Magna Graecia.

Alfenus Varus was an ancient Roman jurist and writer who lived around the 1st century BC.
Alphius Avitus was a Latin poet believed to have flourished during the reigns of the Roman emperors Augustus and Tiberius, that is, the late 1st century BC or early 1st century AD. Many suppose him to be the same person with Alfius Flavus—the precocious pupil of Lucius Cestius Pius and contemporary with Seneca the Elder, who while only a boy was so renowned for his eloquence that crowds flocked to listen to his orations—and with a "Flavius Alfius", who is referred to by Pliny the Elder as an authority for a story about dolphins. This has led some scholars to conjecture that this person's full, correct name may have been "Flavus Alfius Avitus". All this is very uncertain. We know from the ancient grammarian Terentianus that Alphius Avitus composed a work about "Illustrious Men", in iambic dimeters, extending to several books; and eight lines are cited by Priscian from the second book, forming a part of the legend of the Faliscan schoolteacher who betrayed his students to Marcus Furius Camillus; besides which, three lines more from the first book are contained in some manuscripts of the same grammarian. These fragments are given in the Latin Anthology of Pieter Burman the Younger.
The gens Ateia was a plebeian family at Rome. The gens does not appear to have been particularly large or important, and is known from a small number of individuals.
Theon of Alexandria was a grammarian who taught at Rome in the reigns of the emperors Augustus and Tiberius. He succeeded Areius in this role, and was succeeded by Apion. He was the son of the grammarian Artemidorus of Tarsus and the head of the school at Alexandria.
The gens Consentia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome, which first appears in history toward the end of the fourth century AD. Others are known from inscriptions.
Antonius Rufus was a Latin grammarian who was quoted by the rhetorician Quintilian and the grammarian Velius Longus. The scholiast on Horace who was historically called Cruquianus speaks of an Antonius Rufus who wrote plays both praetextatae and togatae, but whether he is the same as the grammarian is uncertain. This reference is considered by some scholars altogether unreliable.
The gens Maenia, occasionally written Mainia, was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are first mentioned soon after the establishment of the Republic, and occur in history down to the second century BC. Several of them held the position of tribune of the plebs, from which they strenuously advocated on behalf of their order. The most illustrious of the family was Gaius Maenius, consul in 338 BC, and dictator in both 320 and 314. In some manuscripts, the nomen Maenius appears to have been erroneously substituted for Menenius or Manlius; there are also instances of confusion with Manilius, Maelius, and Maevius.
The gens Orbilia was an obscure plebeian family of ancient Rome. None of its members are known to have held any magistracies. Its most famous representative may have been the grammarian Lucius Orbilius Pupillus, who operated a school at Rome, and was the master of Horace.
The gens Staberia was a minor plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are first mentioned in the final decades of the Republic, but they never achieved much importance. The most illustrious of the Staberii may have been the Grammarian Staberius Eros, though he was a freedman. One of this family served as a military tribune in the time of Vespasian, but none of the Staberii obtained any of the higher offices of the Roman state; the consul Marcus Pompeius Silvanus Staberius Flavianus belonged to the Pompeia gens, although he was probably descended from the Staberii through a female line.
References
- ↑ Allen, Alexander (1867). "Acron, Helenius". In Smith, William (ed.). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology . Vol. 1. Boston, MA. p. 15. Archived from the original on 2007-10-05. Retrieved 2007-10-11.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - 1 2 Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica . Vol. 1 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 155.