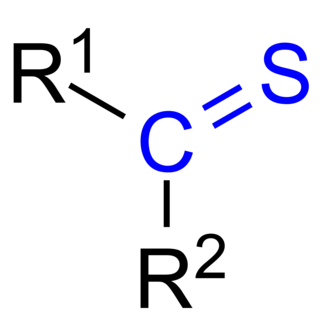In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected by the stabilization of conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. There is no general relationship between aromaticity as a chemical property and the olfactory properties of such compounds.
Chemical Markup Language is an approach to managing molecular information using tools such as XML and Java. It was the first domain specific implementation based strictly on XML, first based on a DTD and later on an XML Schema, the most robust and widely used system for precise information management in many areas. It has been developed over more than a decade by Murray-Rust, Rzepa and others and has been tested in many areas and on a variety of machines.
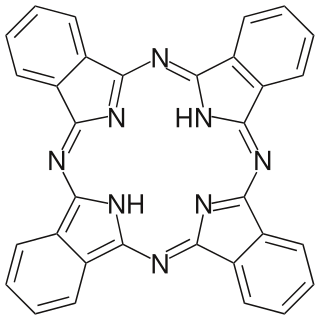
Phthalocyanine is a large, aromatic, macrocyclic, organic compound with the formula (C8H4N2)4H2 and is of theoretical or specialized interest in chemical dyes and photoelectricity.

Borazine, also known as borazole, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula B3H6N3. In this cyclic compound, the three BH units and three NH units alternate. The compound is isoelectronic and isostructural with benzene. For this reason borazine is sometimes referred to as “inorganic benzene”. Like benzene, borazine is a colourless liquid with an aromatic odor.
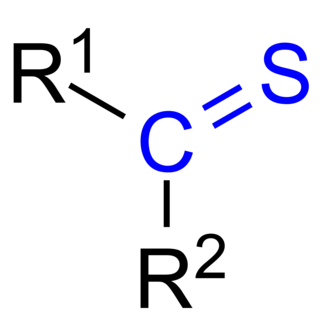
In organic chemistry, thioketones are organosulfur compounds related to conventional ketones in which the oxygen has been replaced by a sulfur. Instead of a structure of R2C=O, thioketones have the structure R2C=S, which is reflected by the prefix "thio-" in the name of the functional group. Thus the simplest thioketone is thioacetone, the sulfur analog of acetone. Unhindered alkylthioketones typically tend to form polymers or rings.

Michael James Steuart Dewar was an American theoretical chemist.

Open Babel is computer software, a chemical expert system mainly used to interconvert chemical file formats.

Peter Murray-Rust is a chemist currently working at the University of Cambridge. As well as his work in chemistry, Murray-Rust is also known for his support of open access and open data.

In organic chemistry, Möbius aromaticity is a special type of aromaticity believed to exist in a number of organic molecules. In terms of molecular orbital theory these compounds have in common a monocyclic array of molecular orbitals in which there is an odd number of out-of-phase overlaps, the opposite pattern compared to the aromatic character to Hückel systems. The nodal plane of the orbitals, viewed as a ribbon, is a Möbius strip, rather than a cylinder, hence the name. The pattern of orbital energies is given by a rotated Frost circle (with the edge of the polygon on the bottom instead of a vertex), so systems with 4n electrons are aromatic, while those with 4n + 2 electrons are anti-aromatic/non-aromatic. Due to incrementally twisted nature of the orbitals of a Möbius aromatic system, stable Möbius aromatic molecules need to contain at least 8 electrons, although 4 electron Möbius aromatic transition states are well known in the context of the Dewar-Zimmerman framework for pericyclic reactions. Möbius molecular systems were considered in 1964 by Edgar Heilbronner by application of the Hückel method, but the first such isolable compound was not synthesized until 2003 by the group of Rainer Herges. However, the fleeting trans-C9H9+ cation, one conformation of which is shown on the right, was proposed to be a Möbius aromatic reactive intermediate in 1998 based on computational and experimental evidence.
The Barton reaction, also known as the Barton nitrite ester reaction, is a photochemical reaction that involves the photolysis of an alkyl nitrite to form a δ-nitroso alcohol.
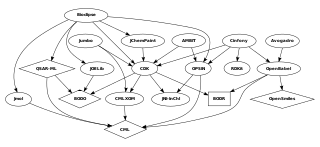
Blue Obelisk is an informal group of chemists who promote open data, open source, and open standards; it was initiated by Peter Murray-Rust and others in 2005. Multiple open source cheminformatics projects associate themselves with the Blue Obelisk, among which, in alphabetical order, Avogadro, Bioclipse, cclib, Chemistry Development Kit, GaussSum, JChemPaint, JOELib, Kalzium, Openbabel, OpenSMILES, and UsefulChem.
Organogold chemistry is the study of compounds containing gold–carbon bonds. They are studied in academic research, but have not received widespread use otherwise. The dominant oxidation states for organogold compounds are I with coordination number 2 and a linear molecular geometry and III with CN = 4 and a square planar molecular geometry.

The Birch reduction is an organic reaction that is used to convert arenes to 1,4-cyclohexadienes. The reaction is named after the Australian chemist Arthur Birch and involves the organic reduction of aromatic rings in an amine solvent with an alkali metal and a proton source. Unlike catalytic hydrogenation, Birch reduction does not reduce the aromatic ring all the way to a cyclohexane.
Metal carbon dioxide complexes are coordination complexes that contain carbon dioxide ligands. Aside from the fundamental interest in the coordination chemistry of simple molecules, studies in this field are motivated by the possibility that transition metals might catalyze useful transformations of CO2. This research is relevant both to organic synthesis and to the production of "solar fuels" that would avoid the use of petroleum-based fuels.

Antony John Williams is a British chemist and expert in the fields of both nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and cheminformatics at the United States Environmental Protection Agency. He is the founder of the ChemSpider website that was purchased by the Royal Society of Chemistry in May 2009. He is a science blogger and an author.

Christoph Steinbeck is a German chemist and has a professorship for analytical chemistry, cheminformatics and chemometrics at the Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena in Thuringia.
Proline organocatalysis is the use of proline as an organocatalyst in organic chemistry. This theme is often considered the starting point for the area of organocatalysis, even though early discoveries went unappreciated. Modifications, such as MacMillan’s catalyst and Jorgensen's catalysts, proceed with excellent stereocontrol.
Parisa Mehrkhodavandi is a Canadian chemist and Professor of Chemistry at the University of British Columbia (UBC). Her research focuses on the design of new catalysts that can effect polymerization of sustainably sourced or biodegradable polymers.

Jordi Burés is a Full Professor of Organic Chemistry in the Department of Chemistry at The University of Manchester. His research in general is on the areas of organic and physical chemistry, specializing in Mechanistic Studies, nuclear magnetic resonance and catalysis.
Concerted metalation-deprotonation (CMD) is a mechanistic pathway through which transition-metal catalyzed C–H activation reactions can take place. In a CMD pathway, the C–H bond of the substrate is cleaved and the new C–Metal bond forms through a single transition state. This process does not go through a metal hydride species that is bound to the cleaved hydrogen atom. Instead, a carboxylate or carbonate base deprotonates the substrate. The first proposal of a concerted metalation deprotonation pathway was by S. Winstein and T. G. Traylor in 1955 for the acetolysis of diphenylmercury. It was found to be the lowest energy transition state in a number of computational studies, was experimentally confirmed through NMR experiments, and has been hypothesized to occur in mechanistic studies.