Related Research Articles

Accra is the capital of Ghana covering an area of 225.67 km2 (87.13 sq mi) with an estimated urban population of 4.2 million as of 2020. It is organized into 12 local government districts – 11 municipal districts and the Accra Metropolitan District, which is the only district within the capital to be granted city status. "Accra" usually refers to the Accra Metropolitan Area, which serves as the capital of Ghana, while the district under the jurisdiction of the Accra Metropolitan Assembly is distinguished from the rest of the capital as the "City of Accra". In common usage, however, the terms "Accra" and "City of Accra" are used interchangeably.

Richard Bowdler Sharpe was an English zoologist and ornithologist who worked as curator of the bird collection at the British Museum of natural history. In the course of his career he published several monographs on bird groups and produced a multi-volume catalogue of the specimens in the collection of the museum. He described many new species of bird and also has had species named in his honour by other ornithologists including Sharpe's longclaw and Sharpe's starling.
John Mensah Sarbah was a lawyer and political leader in the Gold Coast.

The Dutch Gold Coast or Dutch Guinea, officially Dutch possessions on the Coast of Guinea was a portion of contemporary Ghana that was gradually colonized by the Dutch, beginning in 1612. The Dutch began trading in the area around 1598, joining the Portuguese which had a trading post there since the late 1400s. Eventually, the Dutch Gold Coast became the most important Dutch colony in West Africa after Fort Elmina was captured from the Portuguese in 1637, but fell into disarray after the abolition of the slave trade in the early 19th century. On 6 April 1872, the Dutch Gold Coast was, in accordance with the Anglo-Dutch Treaties of 1870–71, ceded to the United Kingdom.

Located directly east of the Korle Lagoon, Jamestown and Usshertown are the oldest districts of Accra, Ghana and emerged as communities around the 17th century British James Fort and Dutch Ussher Fort on the Gulf of Guinea coast. These districts were developed at the end of the 19th century, and following the rapid growth of the city during the 20th century, they became areas of a dense mixture of commercial and residential use.
Sir James Jamieson Thorburn was a British colonial administrator, Governor of the Gold Coast from 1910 to 1912.

Thomas Birch Freeman was an Anglo-African Wesleyan minister, missionary, botanist and colonial official in West Africa. He is widely regarded as a pioneer of the Methodist Church in colonial West Africa, where he also established multiple schools. Some scholars view him as the “Founder of Ghana Methodism”. Freeman's missionary activities took him to Dahomey, now Benin as well as to Western Nigeria.
Frederick Victor Nanka-Bruce was a physician, journalist and politician in the Gold Coast. He was the third African to practise orthodox medicine in the colony, after Benjamin Quartey-Papafio and Ernest James Hayford.
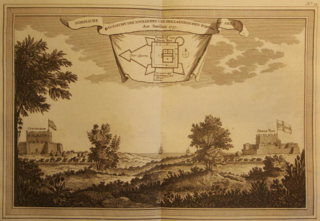
Ussher Fort is a fort in Accra, Ghana. It was built by the Dutch in 1649 as Fort Crèvecœur, and is a day's march from Elmina and to the east of Accra on a rocky point between two lagoons. It was one of three forts that Europeans built in the region during the middle of the 17th century. Fort Crèvecœur was part of the Dutch Gold Coast. The Anglo-Dutch Gold Coast Treaty (1867), which defined areas of influence on the Gold Coast, transferred it to the British in 1868.

Fort Amsterdam, a World Heritage Site is a former slave fort in Kormantin, Central region, Ghana. It was built by the English between 1638 and 1645 as Fort Cormantin or Fort Courmantyne, and was captured by admiral Michiel de Ruyter of the Dutch West India Company in 1665, in retaliation for the capture of several Dutch forts by the English Admiral Holmes in 1664. It was subsequently made part of the Dutch Gold Coast, and remained part of it until the fort was traded with the British in 1868. The Fort is located at Abandze ,on the north-east of Cape Coast in the Mfantseman District of the Central Region of Ghana.

Fort de Goede Hoop or Fort Good Hope was a fort on the Dutch Gold Coast, established in 1667 near Senya Beraku.

Cornelis Johannes Marius Nagtglas was a Dutch politician and civil servant, who made a career in the administration on the Dutch Gold Coast. After originally beginning his career at the advanced age of 36, he was promoted through the ranks to eventually become Governor of the Dutch Gold Coast in 1858. He retired to the Netherlands in 1862, but returned to the Gold Coast as governor in 1869, to restore order in the embattled colony. In 1871, he left the Gold Coast again, one year before the transfer of the colony to the United Kingdom.
George Emil Eminsang was a prominent Euro-African merchant and political leader on the Gold Coast, who played a prominent role in the last years of Dutch colonial rule on the Gold Coast. After the Dutch Gold Coast was transferred to the United Kingdom, Eminsang became a diplomat for the Netherlands and later for the United States and the Congo Free State. Together with James Bannerman Hyde and James Hutton Brew, Eminsang was one of the first so-called "country lawyers" on the Gold Coast.

Sir William Edward Maxwell, was a British colonial official who served as Colonial Secretary of the Straits Settlements and Governor of the Gold Coast, then a British colony.
The 1872 Birthday Honours were appointments by Queen Victoria to various orders and honours to reward and highlight good works by citizens of the British Empire. The appointments were made to celebrate the official birthday of the Queen, and were published in The London Gazette on 31 May 1872 and 4 June 1872.
Sir George Basil Haddon-Smith was a British colonial administrator who was Governor of the Bahamas and Governor of the Windward Islands.
Willem Pieter Antonie Le Jeune, born as Willem Pieter Antonie Tenwinkel, was a Dutch colonial administrator and diplomat, who made a career in the administration on the Dutch Gold Coast and who was interim governor between 28 October 1871 and 15 November 1871. After the Netherlands sold its possessions on the Gold Coast to the United Kingdom in 1872, Le Jeune became the first Dutch consul in Elmina.
John van der Puije was a Gold Coast merchant, newspaper publisher, traditional ruler and politician. Between 1894 and 1904, he was appointed a member of the Legislative Council. He was also instrumental in the re-introduction of the Anglican Communion and English Freemasonry to the colony. He also lobbied the British colonial government to have greater African representation in the civil service in the late nineteenth century.
Ghana–United Kingdom relations are the diplomatic, historical and trade relations between Ghana and the United Kingdom. Modern state Ghana-UK relations began when Ghana became independent from the UK in 1957.
References
- 1 2 The Ussher memoirs ; or, Genealogical memoirs of the Ussher families in Ireland (with appendix, pedigree and index of names), compiled from public and private sources. p. 183.
- ↑ "No. 23864". The London Gazette . 4 June 1872. p. 2620.
- ↑ Owusu-Ansah, David. Historical Dictionary of Ghana. p. 324.
- ↑ American Vital Records from the Gentleman's Magazine, 1731-1868. p. 285.
- ↑ Sharpe, Richard Bowdler (1871). "Ibis". ser.3:v.1 (1). Published for the British Ornithologists' Union by Academic Press.: 100–101.Cite journal requires
|journal=(help)