This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(August 2021) |
Numerous designated cultural heritage sites are located in Xiguan, China.
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(August 2021) |
Numerous designated cultural heritage sites are located in Xiguan, China.
There are two Major Sites Protected at the National Level in Xiguan:

There are 3 Provincial Cultural Heritages in Xiguan:
There are 13 Municipal Cultural Heritages in Xiguan:

Hualin Temple (Chinese :華林寺; pinyin :Huálín Sì; Jyutping :Waa4 Lam4 Zi2) is located in Hualinsi Qianjie (Chinese :華林寺前街; pinyin :Huálínsì Qiánjiē; Jyutping :Waa4 Lam4 Zi2 Cin4 Gaai1; lit.'Hualin Temple Frontstreet'), Xilai Chudi (Chinese :西來初地; pinyin :Xīlái Chūdì; Jyutping :Sai1 Loi4 Co1 Dei6-2; lit.'The first place where a monk from the West (i.e.', 'Bodhidharma) arrived'), Xiajiu Lu (Chinese :下九路; pinyin :Xiàjiǔ Lù; Jyutping :Haa6 Gau2 Lou6; lit.'Lower 9th Rd.'). Its predecessor was Xilai Buddhist Convent (Chinese :西來庵; pinyin :Xīlái Ān; Jyutping :Sai1 Loi4 Am1), set up during Emperor Wu of Liang (Chinese :梁武帝) years (20s, 6th century), Southern and Northern Dynasties (Chinese :南北朝) by an Indian eminent monk, Bodhidharma (Chinese :達摩), after he set up an altar to preach Buddhism. In 1655 (12th year of Shunzhi Emperor (Chinese :順治帝), Qing Dynasty), Zen Master Zongfu (Chinese :宗符禪師) initiated its rehabilitation and changed its name to Hualin Temple. There used to be an Gilded Ashoka Pagoda (Chinese :阿育王塔) and 500 Arhats' statues (Chinese :五百羅漢像) but some of them were destroyed afterwards.

Locate at front street of Renwei Temple, Longjin West Rd. It is in the old Bantang village, around 2,200 square kilometers area. The temple is for Zhenwu Emperor of Taoism, originally named Beidi Temple. It established in 1052 and it was the largest temple by the period. The government used to repair it in 1622, 1736 - 1795 and 1862 - 1874.
Five-mouthed Wells (Chinese :五眼井; pinyin :Wǔyǎn Jǐng; Jyutping :Ng5 Ngaan5 Zeng2), alternatively known as (Chinese :五眼泉; pinyin :Wǔyǎn Quán; Jyutping :Ng5 Ngaan5 Cyun4), lie next to Hualin Temple.
Taihua Building (Chinese :泰華樓; pinyin :Tàihuá Loú; Jyutping :Taai3 Waa4 Lau4) is located at No.27, Duobao Fang (Chinese :多寶坊; pinyin :Duōbǎo Fāng; Jyutping :Do1 Bou2 Fong1; lit.'Treasure Lane'), Enning Lu. It used to be the study of Li Wentian (Chinese :李文田), the Tanhua (Chinese :探花; pinyin :Tànhuā; Jyutping :Taam3 Faa1; lit.'No.3 in national civil examinations in feudal China or the 3rd place in imperial examination or No.3 scholar') during Xianfeng Emperor (Chinese :咸豐帝) years, Qing Dynasty. The building had a collection of 100 thousand books, some of which were lost during Second Sino-Japanese War (Chinese :抗日戰爭). Moreover, some of the calligraphy works and paintings were taken away during Cultural Revolution (Chinese :文化大革命).
There are 11 Registered Cultural Heritages in Xiguan: [1]
With a height of 13 meters, the Wen Tower (Chinese :文塔; pinyin :Wéntǎ; Jyutping :Man4 Taap8; lit.'Pagoda of the God of Culture and Literature') stands in Pantang (Chinese :泮塘; pinyin :Pàntáng; Jyutping :Bun6-3 Tong4-2; lit.'Half Pond'), which used to be the flowery orchard of King Liu (Chinese :劉王; pinyin :Liúwáng; Jyutping :Lau4 Wong4) in Southern Han (Chinese :南漢; pinyin :Nánhàn; Jyutping :Naam4 Hon3). It was built to enshrine and worship Wenquxing sometime between Mid-Ming Period and Early Qing.
Cultural Heritages Management Office of Liwan District (Chinese :荔灣區文物管理所) was founded in 1998.
The Cultural Heritages Preservation Liaison System among the District, Subdistricts and residential communities (Chinese :區、街道、社區三級文物保護聯絡制度) was founded in 2001.
Liwan Government had invested funds of totally 59.383 million RMB yuan to preserve cultural heritages by 2001.

Donglin Temple is a Buddhist temple approximately 20 kilometres (12 mi) from Jiujiang, in the north of Jiangxi province, China. Built in 386 CE at the foot of Mount Lu by Huiyuan, founder of the Pure Land Buddhism, it is well known for how long it has stood without collapsing.

Nanhua Temple is a Buddhist monastery of the Chan Buddhism, one of Five Great Schools of Buddhism where Huineng, the Sixth Patriarch of Chan Buddhism, once lived and taught. It is located in the town of Maba (马坝镇), Qujiang District, 25 km (16 mi) southeast of central Shaoguan, Guangdong province. The location is in the northern part of the province, within a few kilometers from the Bei River.

Mount Longhu is located in Yingtan, Jiangxi, China. It is famous for being one of the birthplaces of Taoism, with many Taoist temples built upon the mountainside. It is particularly important to the Zhengyi Dao as the Shangqing Temple and the Mansion of the Taoist Master (天师府) are located here. It is also known as one of the Four Sacred Mountains of Taoism.

Liwan District is one of 11 urban districts of the prefecture-level city of Guangzhou, the capital of Guangdong Province, China. The district is split into two parts by the Pearl River: Xiguan in the northeast and Fangcun in the southwest.

The Sakyamuni Pagoda of Fogong Temple of Ying County, Shanxi province, China, is a wooden Chinese pagoda. It is also known as the Wooden Pagoda of Ying County. It was constructed in 1056, during the second year of the Khitan-led Liao dynasty and was renovated and expended in 1195 during the sixth year of the Jin Dynasty. The pagoda was built by Emperor Daozong of Liao (Hongji) at the site of his grandmother's family home. The pagoda, which has survived several large earthquakes throughout the centuries, reached a level of such fame within China that it was given the generic nickname of the "Muta".

Tong lau or ke lau are tenement buildings built from the late 19th century to the 1960s in Hong Kong, Taiwan, Southern China, and Southeast Asia. Designed for both residential and commercial uses, they are similar in style and function to the shophouses with five-foot way of Southeast Asia. Over the years, tong lau construction has seen influences of Edwardian-style architecture and later the Bauhaus movement.

Huabiao is a type of ceremonial column used in traditional Chinese architecture. Huabiao are traditionally erected in pairs in front of palaces and tombs. The prominence of their placement have made them one of the emblems of traditional Chinese culture. When placed outside palaces, they can also be called bangmu. When placed outside a tomb, they can also be called shendaozhu.

Shangxiajiu Pedestrian Street, or simply as Shangxiajiu, is a commercial pedestrian street in Liwan District, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China. It is the first business street in Guangzhou, and it opened in September 1995.

The Shenhe District is one of ten districts of Shenyang, the capital of Liaoning province and the largest urban center in Northeast China. Shenhe District is where Shenyang's old city resided, currently serves as the one of the two central districts of Shenyang and hosts the seat of the City Government. It borders the Dadong District to the northeast, Hunnan District to the south, Heping District to the west, and Huanggu District to the northwest.
The Eight Views of Ram City, also known as the Eight Sights of Guangzhou is the collective name for various collections of the eight most famous tourist attractions in Guangzhou, China, during different periods of its history. Collections of "Eight Views" is a common trope in Chinese travel literature.
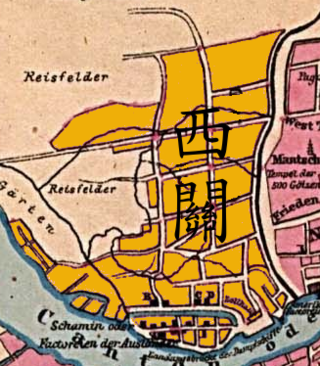
Sai Kwan or Xiguan is an ancient town and an area in the Liwan district of Guangzhou, China, which was located west of the old walled city. The Thirteen Factories trading enclave was located on its southern shore and the Shamian enclave was constructed beside it. Xiguan continues to have a distinctive culture within Guangzhou and some residents speak a distinctive dialect of Cantonese.

The Cloud Platform at Juyongguan is a mid-14th-century architectural feature situated in the Guangou Valley at the Juyongguan Pass of the Great Wall of China, in the Changping District of Beijing Municipality, about 60 kilometres (37 mi) northwest of central Beijing. Although the structure looks like a gateway, it was originally the base for three white dagobas or stupas, with a passage through it, a type of structure known as a "crossing street tower". The platform is renowned for its Buddhist carvings and for its Buddhist inscriptions in six languages. The Cloud Platform was the 98th site included in the first batch of 180 Major Historical and Cultural Sites Protected at the National Level as designated by the State Council of China in April 1961.

The Kong Family Mansion was the historical residence of the direct descendants of Confucius in the City of Qufu, the hometown of Confucius in Shandong Province, China. The extant structures mainly date from the Ming and Qing dynasties. From the mansion, the family tended to the Confucian sites in Qufu and also governed the largest private rural estate in China. The Kong family was in charge of conducting elaborate religious ceremonies on occasions such as plantings, harvests, honoring the dead, and birthdays. Today, the mansion is a museum and part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site "Temple and Cemetery of Confucius and the Kong Family Mansion in Qufu".
Lychee Bay or Litchi Bay, a set of creeks and lakes that flow southwest to Pearl River, is a tourist attraction in Guangzhou (Canton), Guangdong. Liwan District, where Lychee Bay is located, was named after it. There are many historical relics and historical architectures in Lychee Bay, such as Wenta and Xiguan House. Various cultural activities are held on Lychee Bay, such as the Cantonese opera competition.

Lingnan architecture, or Cantonese architecture, refers to the characteristic architectural style(s) of the Lingnan region – the Southern Chinese provinces of Guangdong and Guangxi. Usually, it is referring to the architecture associated with the Cantonese people, with other peoples in the area having their own styles. This style began with the architecture of the ancient non-Han Nanyue people and absorbed certain architectural elements from the Tang Empire and Song Empire as the region sinicized in the later half of the first millennium AD.
The Industrial and Commercial Daily Press Limited was the editor and publisher of the three newspapers in British Hong Kong, The Kung Sheung Daily News, The Kung Sheung Evening News and The Tien Kwong Morning News. The company also wrote and published some special report, fiction and non-fiction.

The Wuying Pagoda, also known as the Xingfu Temple Pagoda and The Thousand Year-Old Pagoda of Wuhan, is a Buddhist pagoda in Wuchang, Wuhan, Hubei Province, China. Built of stone 750 years ago during the final years of the Southern Song Dynasty, it is the oldest standing architectural feature in Wuhan. Wuying Pagoda is a Major Historical and Cultural Site Protected at the National Level.

Hualin Temple is a Buddhist temple located in Gulou District, Fuzhou, Fujian, China. After the introduction of Chan Buddhism from China to Japan in the Song dynasty (960–1279), the architectural style of the Song dynasty had a profound influence on Japan's traditional cultural and folk customs. The oldest things in the temple is the Main Hall, which was built in the early Song dynasty (960–1279).

Xuanwang Temple, formerly known as Yunti Academy, is a temple in Xihu Township, Miaoli County, Taiwan. Established in 1829 as the first privately-owned school in Miaoli, it was subsequently converted into a temple of Confucius under pressure from the Japanese government. In the temple, a tower for joss paper named Jingshengting and a Tudigong shrine are protected as county-level historic buildings.

The Wudong Bridge, also known as Xiaoyou Bridge (孝友桥) and West Bridge (西桥), is a historic stone arch bridge over the West River in Huangyan District, Taizhou, Zhejiang, China. The bridge is 63.5 metres (208 ft) long and 4.3 metres (14 ft) wide with five arches.