
Marburg is a university town in the German federal state (Bundesland) of Hesse, capital of the Marburg-Biedenkopf district (Landkreis). The town area spreads along the valley of the river Lahn and has a population of approximately 76,000.

Marburg virus disease is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and primates caused by either of the two Marburgviruses: Marburg virus (MARV) and Ravn virus (RAVV). Its clinical symptoms are very similar to those of Ebola virus disease (EVD).
Marburg-Biedenkopf is a Kreis (district) in the west of Hesse, Germany. Neighboring districts are Waldeck-Frankenberg, Schwalm-Eder, Vogelsbergkreis, Gießen, Lahn-Dill, Siegen-Wittgenstein.

The Philipps University of Marburg was founded in 1527 by Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse, which makes it one of Germany's oldest universities and the oldest still operating Protestant university in the world. It is now a public university of the state of Hesse, without religious affiliation. The University of Marburg has about 23,500 students and 7,500 employees and is located in Marburg, a town of 76,000 inhabitants, with university buildings dotted in or around the town centre. About 14 per cent of the students are international, the highest percentage in Hesse. It offers an International summer university programme and offers student exchanges through the Erasmus programme.

University of Giessen, official name Justus Liebig University Giessen, is a large public research university in Giessen, Hesse, Germany. It is named after its most famous faculty member, Justus von Liebig, the founder of modern agricultural chemistry and inventor of artificial fertiliser. It covers the areas of arts/humanities, business, dentistry, economics, law, medicine, science, social sciences, and veterinary medicine. Its university hospital, which has two sites, Giessen and Marburg, is the only private university hospital in Germany.

Marburg is a rural town in the City of Ipswich and a locality split between the City of Ipswich and the Somerset Region, both in Queensland, Australia. In the 2016 census, Marburg had a population of 873 people.

Biedenkopf is a spa town in western Hesse, Germany with a population of 13,588.
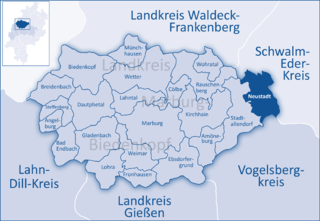
Neustadt is a town in the Marburg-Biedenkopf district in Hesse, Germany. For the town of the same name in Canada see Neustadt, Ontario.

The Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt was a State of the Holy Roman Empire, ruled by a younger branch of the House of Hesse. It was formed in 1567 following the division of the Landgraviate of Hesse between the four sons of Landgrave Philip I.

Marburg (Lahn) station is a through station at the 104.3 km mark of the Main-Weser Railway in the north-east of the city of Marburg in the German state of Hesse and is used daily by about 12,000 people. The station is classified by Deutsche Bahn (DB) as a category 3 station.

Dilschhausen is a borough (Ortsbezirk) of Marburg in Hesse.

Wehrda is a borough (Ortsbezirk) of Marburg in Hesse.

Marburg virus is a hemorrhagic fever virus of the Filoviridae family of viruses and a member of the species Marburg marburgvirus, genus Marburgvirus. Marburg virus (MARV) causes Marburg virus disease in primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic fever. The virus is considered to be extremely dangerous. The World Health Organization (WHO) rates it as a Risk Group 4 Pathogen. In the United States, the NIH/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases ranks it as a Category A Priority Pathogen and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention lists it as a Category A Bioterrorism Agent. It is also listed as a biological agent for export control by the Australia Group.
Ravn virus is a close relative of Marburg virus (MARV). RAVV causes Marburg virus disease in humans and nonhuman primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic fever. RAVV is a Select agent, World Health Organization Risk Group 4 Pathogen, National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Category A Priority Pathogen, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Category A Bioterrorism Agent, and listed as a Biological Agent for Export Control by the Australia Group.

The 1967 Marburg virus outbreak was the first recorded outbreak of Marburg virus disease. It started in early August 1967 when 30 people became ill in the West German towns of Marburg and Frankfurt and later two in Belgrade, Yugoslavia. The infections were traced back to three laboratories in the separate locations which received a shared shipment of infected African green monkeys. The outbreak involved 25 primary Marburg virus infections and seven deaths, and six non-lethal secondary cases.

Dirk Spaniel is a German politician. Born in Marburg, Hesse, he represents Alternative for Germany (AfD). Dirk Spaniel has served as a member of the Bundestag from the state of Baden-Württemberg since 2017.

Marburg is an electoral constituency represented in the Bundestag. It elects one member via first-past-the-post voting. Under the current constituency numbering system, it is designated as constituency 171. It is located in northern Hesse, comprising the Marburg-Biedenkopf district.

The outbreak of Marburg virus disease in Gueckedou district, Guinea started in July 2021, and ended in September. A single individual got sick and died of the virus, with no other known cases.
Andreas Philippi is a German politician for the SPD and since 2021 member of the Bundestag, the federal diet.

Stefan Heck is a German politician for the CDU and since 2021 has been a member of the Bundestag, the federal diet.





















