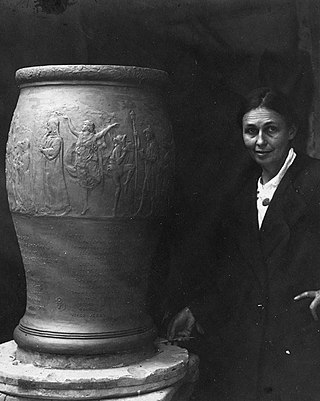Henry Wadsworth Longfellow was an American poet and educator. His original works include the poems "Paul Revere's Ride", "The Song of Hiawatha", and "Evangeline". He was the first American to completely translate Dante Alighieri's Divine Comedy and was one of the fireside poets from New England.

Hiawatha, also known as Ayenwatha or Aiionwatha, was a precolonial Native American leader and co-founder of the Iroquois Confederacy. He was a leader of the Onondaga people, the Mohawk people, or both. According to some accounts, he was born an Onondaga but adopted into the Mohawks.

The Song of Hiawatha is an 1855 epic poem in trochaic tetrameter by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow which features Native American characters. The epic relates the fictional adventures of an Ojibwe warrior named Hiawatha and the tragedy of his love for Minnehaha, a Dakota woman. Events in the story are set in the Pictured Rocks area of Michigan on the south shore of Lake Superior. Longfellow's poem is based on oral traditions surrounding the figure of Manabozho, but it also contains his own innovations.

Augustus Saint-Gaudens was an American sculptor of the Beaux-Arts generation who embodied the ideals of the American Renaissance. From an Irish-French family, Saint-Gaudens was raised in New York City. He traveled to Europe for further training and artistic study. After he returned to New York, he achieved major critical success for his monuments commemorating heroes of the American Civil War, many of which still stand. Saint-Gaudens created works such as the Robert Gould Shaw Memorial on Boston Common, Abraham Lincoln: The Man, and grand equestrian monuments to Civil War generals: General John Logan Memorial in Chicago's Grant Park and William Tecumseh Sherman at the corner of New York's Central Park. In addition, he created the popular historicist representation of The Puritan.
Hiawatha (Haiëñ'wa'tha) is a Native American semi-historical figure who was the co-founder of the Iroquois Confederacy.

Minnehaha is a Native American woman documented in Henry Wadsworth Longfellow's 1855 epic poem The Song of Hiawatha. She is the lover of the titular protagonist Hiawatha and comes to a tragic end. The name, often said to mean "laughing water", literally translates to "waterfall" or "rapid water" in Dakota.

Saint-Gaudens National Historical Park in Cornish, New Hampshire, preserves the home, gardens, and studios of Augustus Saint-Gaudens (1848–1907), one of America's foremost sculptors. The house and grounds of the National Historic Site served as his summer residence from 1885 to 1897, his permanent home from 1900 until his death in 1907, and the center of the Cornish Art Colony. There are three hiking trails that explore the park's natural areas. Original sculptures are on exhibit, along with reproductions of his greatest masterpieces. It is located on Saint-Gaudens Road in Cornish, 0.5 miles (0.80 km) off New Hampshire Route 12A.

The Adams Memorial is a grave marker for Marian Hooper Adams and Henry Adams located in Section E of Rock Creek Cemetery, Washington, D.C. The memorial features a cast bronze allegorical sculpture by Augustus Saint-Gaudens. Saint-Gaudens' shrouded-figure statue is seated against a granite block which takes up one side of a hexagonal plaza, designed by architect Stanford White. Across from the statue is a stone bench for visitors. The whole is sheltered by a close screen of dense conifers.

Abraham Lincoln: The Man is a larger-than-life size 12-foot (3.7 m) bronze statue of Abraham Lincoln, the 16th president of the United States. The original statue is in Lincoln Park in Chicago, and later re-castings of the statue have been given as diplomatic gifts from the United States to the United Kingdom, and to Mexico.

Hiawatha is a 1952 American Western film based on the 1855 epic poem The Song of Hiawatha by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, centering on Native Americans in pre-Columbian times. Directed by Kurt Neumann, with stars Vincent Edwards and Yvette Dugay, it became the final feature produced by the low-budget Monogram Pictures, a mainstay of Hollywood's Poverty Row.
Louis Saint-Gaudens was a significant American sculptor of the Beaux-Arts generation. He was the brother of renowned sculptor Augustus Saint-Gaudens; Louis later changed the spelling of his name to St. Gaudens to differentiate himself from his well-known brother.

The Puritan is a bronze statue by sculptor Augustus St. Gaudens in Springfield, Massachusetts, United States, which became so popular it was reproduced for over 20 other cities, museums, universities, and private collectors around the world, and later became an official symbol of the city, emblazoned on its municipal flag. Originally designed to be part of Stearns Square, since 1899 the statue has stood at the corner of Chestnut and State Street next to The Quadrangle.

The Memorial to Robert Gould Shaw and the Massachusetts Fifty-Fourth Regiment is a bronze relief sculpture by Augustus Saint-Gaudens opposite 24 Beacon Street, Boston. It depicts Colonel Robert Gould Shaw leading members of the 54th Regiment Massachusetts Volunteer Infantry as it marched down Beacon Street on May 28, 1863 to depart the city to fight in the South. The sculpture was unveiled on May 31, 1897. This is the first civic monument to pay homage to the heroism of African American soldiers.

MV Hiawatha is a passenger ferry built in 1895 for the Royal Canadian Yacht Club, in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. The boat is 56 feet (17 m) long, 13.3 feet (4.1 m) wide, has a depth of 6.3 feet (1.9 m), and measures 46 gross tons. Her capacity is 100 passengers.
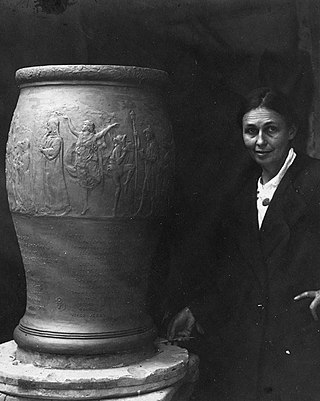
Annetta Johnson Saint-Gaudens (1869–1943) was an American sculptor, born in Flint, Ohio. She is best remembered for creating sculptures of "animals, children (and) fountains", but she also did the finishing carving on a "colossal marble figure", the allegorical sculpture Painting in front of the St. Louis Art Museum. She was also significant in the art world as being the wife of Louis Saint-Gaudens and the sister-in-law of Augustus Saint-Gaudens, with whom she studied and worked as an assistant.

Hiawatha and Minnehaha is a sculpture by Jacob Fjelde that has stood in Minnehaha Park in Minneapolis since the early twentieth century. Now a popular fixture of the park, its placement there was originally controversial.

Admiral David Glasgow Farragut, also known as the Admiral Farragut Monument, is an outdoor bronze statue of David Farragut by Augustus Saint-Gaudens on a stone sculptural exedra designed by the architect Stanford White, installed in Manhattan's Madison Square, in the U.S. state of New York.

Hiawatha is a 1913 American silent drama film directed by Edgar Lewis and based upon Henry Wadsworth Longfellow's epic poem The Song of Hiawatha (1855). The film stars Jesse Cornplanter of the Seneca people and Soon-goot, a 17-year-old unknown actress. The movie is the first feature film to use a cast of Native Americans.

Mrs. Schuyler Van Rensselaer is a bronze sculpture by American artist Augustus Saint-Gaudens. It was designed in 1888 and cast in 1890. This artwork portrays the American author, art critic, and reformer Mariana Griswold Van Rensselaer (1851–1934), who "championed Saint-Gaudens in articles on his public monuments and relief sculptures".

Hiawatha and Minnehaha are 1868 sculptures by Edmonia Lewis. They are in the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art on view in gallery 759.