
X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by balloons, sounding rockets, and satellites. X-ray astronomy uses a type of space telescope that can see x-ray radiation which standard optical telescopes, such as the Mauna Kea Observatories, cannot.
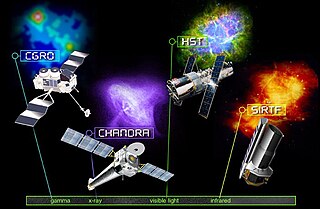
NASA's series of Great Observatories satellites are four large, powerful space-based astronomical telescopes launched between 1990 and 2003. They were built with different technology to examine specific wavelength/energy regions of the electromagnetic spectrum: gamma rays, X-rays, visible and ultraviolet light, and infrared light.
The Extreme Universe Space Observatory onboard Japanese Experiment Module (JEM-EUSO) is the first space mission concept devoted to the investigation of cosmic rays and neutrinos of extreme energy (E > 5×1019 eV). Using the Earth's atmosphere as a giant detector, the detection is performed by looking at the streak of fluorescence produced when such a particle interacts with the Earth's atmosphere.

NuSTAR is a NASA space-based X-ray telescope that uses a conical approximation to a Wolter telescope to focus high energy X-rays from astrophysical sources, especially for nuclear spectroscopy, and operates in the range of 3 to 79 keV.

Skyhook balloons were high-altitude balloons developed by Otto C. Winzen and General Mills, Inc. They were used by the United States Navy Office of Naval Research (ONR) in the late 1940s and 1950s for atmospheric research, especially for constant-level meteorological observations at very high altitudes. Instruments like the Cherenkov detector were first used on Skyhook balloons.

The Physical Research Laboratory is a National Research Institute for space and allied sciences, supported mainly by Department of Space, Government of India. This research laboratory has ongoing research programmes in astronomy and astrophysics, atmospheric sciences and aeronomy, planetary and geosciences, Earth sciences, Solar System studies and theoretical physics. It also manages the Udaipur Solar Observatory and Mount Abu InfraRed Observatory. The PRL is located in Ahmedabad.

An X-ray telescope (XRT) is a telescope that is designed to observe remote objects in the X-ray spectrum. X-rays are absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by balloons, sounding rockets, and satellites.

A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally it was an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observe distant objects – an optical telescope. Nowadays, the word "telescope" is defined as a wide range of instruments capable of detecting different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, and in some cases other types of detectors.

The Advanced Thin Ionization Calorimeter (ATIC) is a balloon-borne instrument flying in the stratosphere over Antarctica to measure the energy and composition of cosmic rays. ATIC was launched from McMurdo Station for the first time in December 2000 and has since completed three successful flights out of four.
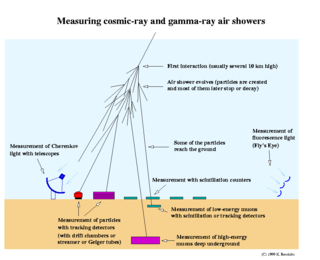
A cosmic-ray observatory is a scientific installation built to detect high-energy-particles coming from space called cosmic rays. This typically includes photons, electrons, protons, and some heavier nuclei, as well as antimatter particles. About 90% of cosmic rays are protons, 9% are alpha particles, and the remaining ~1% are other particles.
The Sunrise balloon-borne solar observatory consists of a 1m aperture Gregory telescope, a UV filter imager, an imaging vector polarimeter, an image stabilization system and further infrastructure. The first science flight of Sunrise yielded high-quality data that reveal the structure, dynamics and evolution of solar convection, oscillations and magnetic fields at a resolution of around 100 km in the quiet Sun.

The history of X-ray astronomy begins in the 1920s, with interest in short wave communications for the U.S. Navy. This was soon followed by extensive study of the earth's ionosphere. By 1927, interest in the detection of X-ray and ultraviolet (UV) radiation at high altitudes inspired researchers to launch Goddard's rockets into the upper atmosphere to support theoretical studies and data gathering. The first successful rocket flight equipped with instrumentation able to detect solar ultraviolet radiation occurred in 1946. X-ray solar studies began in 1949. By 1973 a solar instrument package orbited on Skylab providing significant solar data.
The Nuclear Compton Telescope (NCT) is a balloon-borne Compton telescope to observe the gamma-ray sky in the energy range from a few hundred keV to several MeV. Its main goals are to improve the understanding of Galactic nucleosynthesis, gamma-ray bursts, supernovae, black holes, and more.
PoGOLite is a balloon-borne astroparticle physics experiment which is to measure polarisation in hard X-rays and soft gamma-rays. It is sensitive to photons with an energy range of 25-80 keV. PoGOLite contains 217 phoswich detector cells (PDC) which are surrounded by a ring of side anticoincidence shield (SAS) detectors.

A balloon-borne telescope is a type of airborne telescope, a sub-orbital astronomical telescope that is suspended below one or more stratospheric balloons, allowing it to be lifted above the lower, dense part of the Earth's atmosphere. This has the advantage of improving the resolution limit of the telescope at a much lower cost than for a space telescope. It also allows observation of frequency bands that are blocked by the atmosphere.

The International X-ray Observatory (IXO) is a cancelled X-ray telescope that was to be launched in 2021 as a joint effort by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). In May 2008, ESA and NASA established a coordination group involving all three agencies, with the intent of exploring a joint mission merging the ongoing XEUS and Constellation-X Observatory (Con-X) projects. This proposed the start of a joint study for IXO. NASA was forced to cancel the observatory due to budget constraints in fiscal year 2012. ESA however decided to reboot the mission on its own developing Advanced Telescope for High Energy Astrophysics as a part of Cosmic Vision program.

The Focusing Optics X-ray Solar Imager, or FOXSI, is a sounding rocket payload built by UC Berkeley and led by Säm Krucker to test high energy grazing-incidence focusing optics paired with solid-state pixelated detectors to observe the Sun. FOXSI is composed of seven identical Wolter-I telescope modules, as well as Silicon and Cadmium Telluride strip detectors originally developed for the HXT telescope on the Japanese Hitomi mission. The FOXSI payload flew two times, most recently in 2014 and previously in 2012. Like most sounding rockets, FOXSI flew for approximately 15 minutes per mission and observed the Sun for about 5 minutes while in space. During its first flight, FOXSI successfully imaged a solar microflare in the hard x-ray band for the first time.

The X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission, formerly the X-ray Astronomy Recovery Mission (XARM), is an X-ray space telescope mission of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) in partnership with NASA to provide breakthroughs in the study of structure formation of the universe, outflows from galaxy nuclei, and dark matter. As the only international X-ray observatory project of its period, XRISM will function as a next generation space telescope in the X-ray astronomy field, similar to how the James Webb Space Telescope, Fermi Space Telescope, and the Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA) Observatory are placed in their respective fields.
Giovanni Fazio is an American physicist at Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian. He is an astrophysicist who has initiated and participated in multiple observation programs.

The Super-pressure Balloon-borne Imaging Telescope (SuperBIT) is a highly stabilized, high-resolution telescope that operates in the stratosphere via NASA's superpressure balloon (SPB) system. At 40 km altitude above sea level, the football-stadium-sized balloon carries SuperBIT to a suborbital environment above 99.2% of the Earth's atmosphere in order to obtain space-quality imaging. As a research instrument, SuperBIT's primary science goal is to provide insight into the distribution of dark matter in galaxy clusters and throughout the large-scale structure of the universe. As demonstrated by numerous test flights, the survey data generated by SuperBIT is expected to have similar quality and data collection efficiency as the Hubble Space Telescope while complementing surveys from other up-and-coming observatories such as the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), the Vera C. Rubin Observatory, and the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope.














