
In marine geology, a guyot, also called a tablemount, is an isolated underwater volcanic mountain (seamount) with a flat top more than 200 m (660 ft) below the surface of the sea. The diameters of these flat summits can exceed 10 km (6 mi). Guyots are most commonly found in the Pacific Ocean, but they have been identified in all the oceans except the Arctic Ocean. They are analogous to tables on land.

A seamount is a large submarine landform that rises from the ocean floor without reaching the water surface, and thus is not an island, islet, or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from the seafloor to 1,000–4,000 m (3,300–13,100 ft) in height. They are defined by oceanographers as independent features that rise to at least 1,000 m (3,281 ft) above the seafloor, characteristically of conical form. The peaks are often found hundreds to thousands of meters below the surface, and are therefore considered to be within the deep sea. During their evolution over geologic time, the largest seamounts may reach the sea surface where wave action erodes the summit to form a flat surface. After they have subsided and sunk below the sea surface, such flat-top seamounts are called "guyots" or "tablemounts".

In geology, hotspots are volcanic locales thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Examples include the Hawaii, Iceland, and Yellowstone hotspots. A hotspot's position on the Earth's surface is independent of tectonic plate boundaries, and so hotspots may create a chain of volcanoes as the plates move above them.

The geology of the Pacific Northwest includes the composition, structure, physical properties and the processes that shape the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The region is part of the Ring of Fire: the subduction of the Pacific and Farallon Plates under the North American Plate is responsible for many of the area's scenic features as well as some of its hazards, such as volcanoes, earthquakes, and landslides.

The New England hotspot, also referred to as the Great Meteor hotspot and sometimes the Monteregian hotspot, is a volcanic hotspot in the North Atlantic Ocean. It created the Monteregian Hills intrusions in Montreal and Montérégie, the White Mountains intrusions in New Hampshire, the New England and Corner Rise seamounts off the coast of North America, and the Seewarte Seamounts east of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge on the African Plate, the latter of which include its most recent eruptive center, the Great Meteor Seamount. The New England, Great Meteor, or Monteregian hotspot track has been used to estimate the movement of the North American Plate away from the African Plate from the early Cretaceous period to the present using the fixed hotspot reference frame.

The Bowie hotspot is a volcanic hotspot, located 180 kilometres (110 mi) west of Haida Gwaii in the Pacific Ocean.

Bowie Seamount, or SG̱aan Ḵinghlas in the Haida language, is a large submarine volcano in the northeastern Pacific Ocean, located 180 km (110 mi) west of Haida Gwaii, British Columbia, Canada. The seamount is also known as Bowie Bank. The English name for the feature is after William Bowie of the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey.
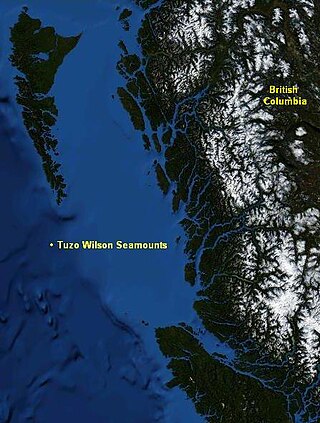
The Tuzo Wilson Seamounts, also called J. Tuzo Wilson Knolls and Tuzo Wilson Knolls, are two young active submarine volcanoes off the coast of British Columbia, Canada, located 200 km (124 mi) northwest of Vancouver Island and south of the Haida Gwaii archipelago The two seamounts are members of the Kodiak-Bowie Seamount chain, rising 500 m (1,640 ft) to 700 m (2,297 ft) above the mean level of the northeastern Pacific Ocean and is a seismically active site southwest of the southern end of the Queen Charlotte Fault. They are named after Canadian geologist John Tuzo Wilson.

The Kodiak–Bowie Seamount chain, also called the Pratt–Welker Seamount chain and the Kodiak Seamounts is a seamount chain in the southeastern Gulf of Alaska stretching from the Aleutian Trench in the north to Bowie Seamount, the youngest volcano in the chain, which lies 180 km (112 mi) west of Haida Gwaii, British Columbia, Canada. The oldest volcano in the chain is the Kodiak Seamount. Although the Kodiak Seamount is the oldest extant seamount in the Kodiak-Bowie chain, the adjacent lower slope contains transverse scars indicating earlier subduction of seamounts.

Kodiak Seamount is the oldest seamount in the Kodiak-Bowie Seamount chain, with an estimated age of 24 million years. It lies at the northernmost end of the chain and its flat-topped summit is strewn with fault lines. Like the rest of the Kodiak-Bowie seamounts, it was formed by the Bowie hotspot.
Cobb Seamount is a seamount and guyot located 500 km (310 mi) west of Grays Harbor, Washington, United States. Cobb Seamount is one of the seamounts in the Cobb–Eickelberg Seamount chain, a chain of underwater volcanoes created by the Cobb hotspot that terminates near the coast of Alaska. It lies just west of the Cascadia subduction zone, and was discovered in August 1950 by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service fisheries research vessel R/V John N. Cobb. By 1967, over 927 km (576 mi) of soundings and dozens of samples from the seamount had been collected.

Peirce Seamount, also called Pierce Seamount, is a seamount located in the Pacific Ocean west of the Queen Charlotte Islands, British Columbia, Canada. It lies between Denson Seamount and Hodgkins Seamount and is member of the Kodiak-Bowie Seamount chain, a chain of seamounts in southeastern Gulf of Alaska stretching from the Aleutian Trench in the north to Bowie Seamount in the south.
The Dellwood Seamounts are a seamount range located in the Pacific Ocean northwest of Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. They are also known as the Dellwood Seamount Range or the Dellwood Seamount Chain.

The Newfoundland Seamounts are a group of seamounts offshore of Eastern Canada in the northern Atlantic Ocean. Named for the island of Newfoundland, this group of seamounts formed during the Cretaceous period and are poorly studied.
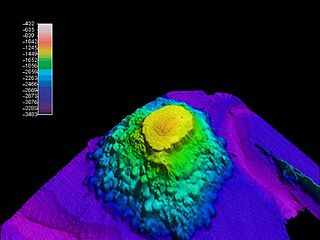
Denson Seamount is a submarine volcano in the Kodiak-Bowie Seamount chain, with an estimated age of 18 million years. It lies at the southern end of the chain near the Canada–United States border. It was one of the underground volcanic extrusions investigated by the 2004 Gulf of Alaska Seamount Expedition. The expedition's goal was:
"Our goal was to gain an understanding of the geologic histories of the five previously unexplored seamounts in the Gulf of Alaska. To achieve this we created a full-coverage swath bathymetry map of each seamount and its surroundings, and we collected rock samples at all possible depths." -Randy Keller, Oregon State University
The volcanism of Eastern Canada includes the hundreds of volcanic areas and extensive lava formations in Eastern Canada. The region's different volcano and lava types originate from different tectonic settings and types of volcanic eruptions, ranging from passive lava eruptions to violent explosive eruptions. Eastern Canada has very large volumes of magmatic rock called large igneous provinces. They are represented by deep-level plumbing systems consisting of giant dike swarms, sill provinces and layered intrusions. The most capable large igneous provinces in Eastern Canada are Archean age greenstone belts containing a rare volcanic rock called komatiite.

The Macdonald hotspot is a volcanic hotspot in the southern Pacific Ocean. The hotspot was responsible for the formation of the Macdonald Seamount, and possibly the Austral-Cook Islands chain. It probably did not generate all of the volcanism in the Austral and Cook Islands as age data imply that several additional hotspots were needed to generate some volcanoes.

Patton Seamount is a prominent seamount in the Cobb–Eickelberg Seamount chain in the Gulf of Alaska. Located 166 nmi east of Kodiak Island and reaching to within 160 m (520 ft) of the ocean surface, Patton is one of the largest seamounts in the Cobb–Eickelberg Seamount chain. It was originally created near the coast of Oregon by the Cobb hotspot 33 million years ago and was moved to its present location by tectonic plate movement. Patton is one of the most well-understood seamounts, as a major expedition using DSV Alvin in 1999 and another in 2002 helped define the scope of the seamount's biological community. Like other large seamounts, Patton acts as an ecological hub for sea life. Dives have revealed that the volcano is heavily encrusted in sea life of various forms, including sea stars, corals, king crabs, demersal rockfish, and other species.














