A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the coordination centre, and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals, are coordination complexes.

A clathrate is a chemical substance consisting of a lattice that traps or contains molecules. The word clathrate is derived from the Latin clathratus, meaning 'with bars, latticed'. Most clathrate compounds are polymeric and completely envelop the guest molecule, but in modern usage clathrates also include host–guest complexes and inclusion compounds. According to IUPAC, clathrates are inclusion compounds "in which the guest molecule is in a cage formed by the host molecule or by a lattice of host molecules." The term refers to many molecular hosts, including calixarenes and cyclodextrins and even some inorganic polymers such as zeolites.

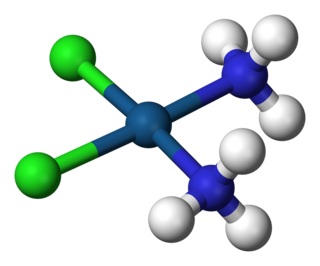
Nickel(II) chloride (or just nickel chloride) is the chemical compound NiCl2. The anhydrous salt is yellow, but the more familiar hydrate NiCl2·6H2O is green. Nickel(II) chloride, in various forms, is the most important source of nickel for chemical synthesis. The nickel chlorides are deliquescent, absorbing moisture from the air to form a solution. Nickel salts have been shown to be carcinogenic to the lungs and nasal passages in cases of long-term inhalation exposure.
In chemistry, a trimer is a molecule or polyatomic anion formed by combination or association of three molecules or ions of the same substance. In technical jargon, a trimer is a kind of oligomer derived from three identical precursors often in competition with polymerization.

Nickelocene is the organonickel compound with the formula Ni(η5-C5H5)2. Also known as bis(cyclopentadienyl)nickel or NiCp2, this bright green paramagnetic solid is of enduring academic interest, although it does not yet have any known practical applications.
Phosphorus trifluoride (formula PF3), is a colorless and odorless gas. It is highly toxic and reacts slowly with water. Its main use is as a ligand in metal complexes. As a ligand, it parallels carbon monoxide in metal carbonyls, and indeed its toxicity is due to its binding with the iron in blood hemoglobin in a similar way to carbon monoxide.

In coordination chemistry, metal ammine complexes are metal complexes containing at least one ammonia ligand. "Ammine" is spelled this way for historical reasons; in contrast, alkyl or aryl bearing ligands are spelt with a single "m". Almost all metal ions bind ammonia as a ligand, but the most prevalent examples of ammine complexes are for Cr(III), Co(III), Ni(II), Cu(II) as well as several platinum group metals.

1,3,5,7-Cyclooctatetraene (COT) is an unsaturated derivative of cyclooctane, with the formula C8H8. It is also known as [8]annulene. This polyunsaturated hydrocarbon is a colorless to light yellow flammable liquid at room temperature. Because of its stoichiometric relationship to benzene, COT has been the subject of much research and some controversy.

A coordination polymer is an inorganic or organometallic polymer structure containing metal cation centers linked by ligands. More formally a coordination polymer is a coordination compound with repeating coordination entities extending in 1, 2, or 3 dimensions.

In organometallic chemistry, a sandwich compound is a chemical compound featuring a metal bound by haptic, covalent bonds to two arene (ring) ligands. The arenes have the formula CnHn, substituted derivatives and heterocyclic derivatives. Because the metal is usually situated between the two rings, it is said to be "sandwiched". A special class of sandwich complexes are the metallocenes.

Organonickel chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic compounds featuring nickel-carbon bonds. They are used as a catalyst, as a building block in organic chemistry and in chemical vapor deposition. Organonickel compounds are also short-lived intermediates in organic reactions. The first organonickel compound was nickel tetracarbonyl Ni(CO)4, reported in 1890 and quickly applied in the Mond process for nickel purification. Organonickel complexes are prominent in numerous industrial processes including carbonylations, hydrocyanation, and the Shell higher olefin process.

Chlorodiphenylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2PCl, abbreviated Ph2PCl. It is a colourless oily liquid with a pungent odor that is often described as being garlic-like and detectable even in the ppb range. It is useful reagent for introducing the Ph2P group into molecules, which includes many ligands. Like other halophosphines, Ph2PCl is reactive with many nucleophiles such as water and easily oxidized even by air.
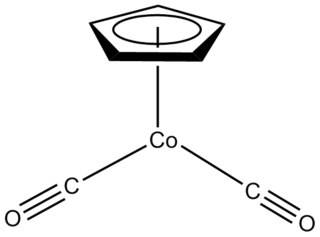
Half sandwich compounds, also known as piano stool complexes, are organometallic complexes that feature a cyclic polyhapto ligand bound to an MLn center, where L is a unidentate ligand. Thousands of such complexes are known. Well-known examples include cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl and (C5H5)TiCl3. Commercially useful examples include (C5H5)Co(CO)2, which is used in the synthesis of substituted pyridines, and methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl, an antiknock agent in petrol.

The cyanonickelates are a class of chemical compound containing anions consisting of nickel atoms, and cyanide groups. The most important of these are the tetracyanonickelates containing four cyanide groups per nickel. The tetracyanonickelates contain the [Ni(CN)4]2− anion. This can exist in solution or in solid salts. The ion has cyanide groups arranged in a square around the central nickel ion. The symmetry of the ion is D4h. The distance from the nickel atom to the carbon is 1.87 Å, and the carbon-nitrogen distance is 1.16 Å. In their crystals, the tetracyanonickelate(II) anions are often arranged in a columnar structure (e.g. in K2[Ni(CN)4]). Tetracyanonickelate(II) can be oxidised electrochemically in solution to yield tetracyanonickelate(III) [Ni(CN)4]−. [Ni(CN)4]− is unstable and Ni(III) oxidises the cyanide to cyanate OCN−. Tetracyanonickelate(III) can add two more cyanide groups to form hexacyanonickelate(III).
Nickel compounds are chemical compounds containing the element nickel which is a member of the group 10 of the periodic table. Most compounds in the group have an oxidation state of +2. Nickel is classified as a transition metal with nickel(II) having much chemical behaviour in common with iron(II) and cobalt(II). Many salts of nickel(II) are isomorphous with salts of magnesium due to the ionic radii of the cations being almost the same. Nickel forms many coordination complexes. Nickel tetracarbonyl was the first pure metal carbonyl produced, and is unusual in its volatility. Metalloproteins containing nickel are found in biological systems.
The tetrabromonickelate anion contains a doubly-charged nickel atom (Ni2+) surrounded by four bromide ions in a tetrahedral arrangement. The formula is [NiBr4]2−.
Metal arene complexes are organometallic compounds of the formula (C6R6)xMLy. Common classes are of the type (C6R6)ML3 and (C6R6)2M. These compounds are reagents in inorganic and organic synthesis. The principles that describe arene complexes extend to related organic ligands such as many heterocycles (e.g. thiophene) and polycyclic aromatic compounds (e.g. naphthalene).
The nickel organic acid salts are organic acid salts of nickel. In many of these the ionised organic acid acts as a ligand.
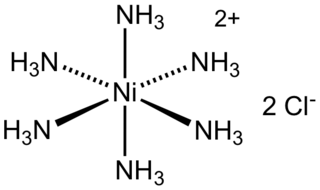
Hexaamminenickel chloride is the chemical compound with the formula [Ni(NH3)6]Cl2. It is the chloride salt of the metal ammine complex [Ni(NH3)6]2+. The cation features six ammonia (called ammines in coordination chemistry) ligands attached to the nickel(II) ion.

Potassium tetracyanonickelate (IUPAC: Potassium tetracyanido nickelate(II)) is the inorganic compound with the formula K2Ni(CN)4. It is usually encountered as the monohydrate but the anhydrous salt is also known. Both are yellow, water-soluble, diamagnetic solids. The salt consists of potassium ions and the tetracyanonickelate coordination complex, which is square planar. The [Ni(CN)4]2- anions are arranged in a columnar structure with Ni---Ni distances of 4.294 Å, which is well beyond the sum of the van der Waals radius of the nickel cation. This columnar structure resembles those of the other [M(CN)4]2- anions of the heavy congeners of the group 10 metals (M = Pd, Pt).














