Related Research Articles

The Federal Housing Administration (FHA), also known as the Office of Housing within the Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD), is a United States government agency founded by President Franklin Delano Roosevelt, established in part by the National Housing Act of 1934. Its primary function is to provide insurance for mortgages originated by private lenders for various types of properties, including single-family homes, multifamily rental properties, hospitals, and residential care facilities. FHA mortgage insurance serves to safeguard these private lenders from financial losses. In the event that a property owner defaults on their mortgage, FHA steps in to compensate the lender for the outstanding principal balance.

In finance, a loan is the transfer of money by one party to another with an agreement to pay it back. The recipient, or borrower, incurs a debt and is usually required to pay interest for the use of the money.

In Ireland and the United Kingdom, housing associations are private, non-profit making organisations that provide low-cost "social housing" for people in need of a home. Any budget surplus is used to maintain existing housing and to help finance new homes and it cannot be used for personal benefit of directors or shareholders. Although independent, they are regulated by the state and commonly receive public funding. They are now the United Kingdom's major providers of new housing for rent, while many also run shared ownership schemes to help those who cannot afford to buy a home outright.

A student loan is a type of loan designed to help students pay for post-secondary education and the associated fees, such as tuition, books and supplies, and living expenses. It may differ from other types of loans in the fact that the interest rate may be substantially lower and the repayment schedule may be deferred while the student is still in school. It also differs in many countries in the strict laws regulating renegotiating and bankruptcy. This article highlights the differences of the student loan system in several major countries.
A variable-rate mortgage, adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM), or tracker mortgage is a mortgage loan with the interest rate on the note periodically adjusted based on an index which reflects the cost to the lender of borrowing on the credit markets. The loan may be offered at the lender's standard variable rate/base rate. There may be a direct and legally defined link to the underlying index, but where the lender offers no specific link to the underlying market or index, the rate can be changed at the lender's discretion. The term "variable-rate mortgage" is most common outside the United States, whilst in the United States, "adjustable-rate mortgage" is most common, and implies a mortgage regulated by the Federal government, with caps on charges. In many countries, adjustable rate mortgages are the norm, and in such places, may simply be referred to as mortgages.

An FHA insured loan is a US Federal Housing Administration mortgage insurance backed mortgage loan that is provided by an FHA-approved lender. FHA mortgage insurance protects lenders against losses. They have historically allowed lower-income Americans to borrow money to purchase a home that they would not otherwise be able to afford. Because this type of loan is more geared towards new house owners than real estate investors, FHA loans are different from conventional loans in the sense that the house must be owner-occupant for at least a year. Since loans with lower down-payments usually involve more risk to the lender, the home-buyer must pay a two-part mortgage insurance that involves a one-time bulk payment and a monthly payment to compensate for the increased risk. Frequently, individuals "refinance" or replace their FHA loan to remove their monthly mortgage insurance premium. Removing mortgage insurance premium by paying down the loan has become more difficult with FHA loans as of 2013.
Buy-to-let is a British phrase referring to the purchase of a property specifically to let out, that is to rent it out. A buy-to-let mortgage is a mortgage loan specifically designed for this purpose. Buy-to-let properties are usually residential but the term also encompasses student property investments and hotel room investments.
This article gives descriptions of mortgage terminology in the United Kingdom.
Mortgage insurance is an insurance policy which compensates lenders or investors in mortgage-backed securities for losses due to the default of a mortgage loan. Mortgage insurance can be either public or private depending upon the insurer. The policy is also known as a mortgage indemnity guarantee (MIG), particularly in the UK.
Peer-to-peer lending, also abbreviated as P2P lending, is the practice of lending money to individuals or businesses through online services that match lenders with borrowers. Peer-to-peer lending companies often offer their services online, and attempt to operate with lower overhead and provide their services more cheaply than traditional financial institutions. As a result, lenders can earn higher returns compared to savings and investment products offered by banks, while borrowers can borrow money at lower interest rates, even after the P2P lending company has taken a fee for providing the match-making platform and credit checking the borrower. There is the risk of the borrower defaulting on the loans taken out from peer-lending websites.
Mortgage fraud refers to an intentional misstatement, misrepresentation, or omission of information relied upon by an underwriter or lender to fund, purchase, or insure a loan secured by real property.

A mortgage loan or simply mortgage, in civil law jurisdictions known also as a hypothec loan, is a loan used either by purchasers of real property to raise funds to buy real estate, or by existing property owners to raise funds for any purpose while putting a lien on the property being mortgaged. The loan is "secured" on the borrower's property through a process known as mortgage origination. This means that a legal mechanism is put into place which allows the lender to take possession and sell the secured property to pay off the loan in the event the borrower defaults on the loan or otherwise fails to abide by its terms. The word mortgage is derived from a Law French term used in Britain in the Middle Ages meaning "death pledge" and refers to the pledge ending (dying) when either the obligation is fulfilled or the property is taken through foreclosure. A mortgage can also be described as "a borrower giving consideration in the form of a collateral for a benefit (loan)".

The American subprime mortgage crisis was a multinational financial crisis that occurred between 2007 and 2010 that contributed to the 2007–2008 global financial crisis. The crisis led to a severe economic recession, with millions losing their jobs and many businesses going bankrupt. The U.S. government intervened with a series of measures to stabilize the financial system, including the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) and the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA).
The Public Works Loan Board (PWLB) was a statutory body of the UK Government that provided loans to public bodies from the National Loans Fund. In 2020, the PWLB was abolished as a statutory organisation, and its functions were allocated to HM Treasury, where they are discharged through the UK Debt Management Office. The members of the PWLB were known as the Public Works Loan Commissioners.
The subprime mortgage crisis impact timeline lists dates relevant to the creation of a United States housing bubble and the 2005 housing bubble burst and the subprime mortgage crisis which developed during 2007 and 2008. It includes United States enactment of government laws and regulations, as well as public and private actions which affected the housing industry and related banking and investment activity. It also notes details of important incidents in the United States, such as bankruptcies and takeovers, and information and statistics about relevant trends. For more information on reverberations of this crisis throughout the global financial system see 2007–2008 financial crisis.

Observers and analysts have attributed the reasons for the 2001–2006 housing bubble and its 2007–10 collapse in the United States to "everyone from home buyers to Wall Street, mortgage brokers to Alan Greenspan". Other factors that are named include "Mortgage underwriters, investment banks, rating agencies, and investors", "low mortgage interest rates, low short-term interest rates, relaxed standards for mortgage loans, and irrational exuberance" Politicians in both the Democratic and Republican political parties have been cited for "pushing to keep derivatives unregulated" and "with rare exceptions" giving Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac "unwavering support".
Public housing policies in Canada includes rent controls, as well as subsidized interest rates and grants. Early public housing policy in Canada consisted of public-private lending schemes which focused on expanding home ownership among the middle class. The first major housing initiative in Canada was the Dominion Housing Act of 1935, which increased the amount of credit available for mortgage loans.
A cram down or cramdown is the involuntary imposition by a court of a reorganization plan over the objection of some classes of creditors.
Loan modification is the systematic alteration of mortgage loan agreements that help those having problems making the payments by reducing interest rates, monthly payments or principal balances. Lending institutions could make one or more of these changes to relieve financial pressure on borrowers to prevent the condition of foreclosure. Loan modifications have been practiced in the United States since the 1930s. During the Great Depression, loan modification programs took place at the state level in an effort to reduce levels of loan foreclosures.
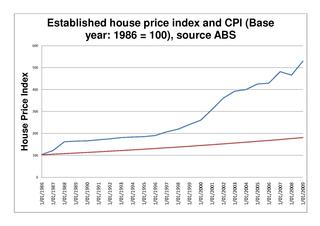
The Australian property bubble is the economic theory that the Australian property market has become or is becoming significantly overpriced and due for a significant downturn. Since the early 2010s, various commentators, including one Treasury official, have claimed the Australian property market is in a significant bubble.
References
- ↑ "Australian Trade Practices News 472 1999". Archived from the original on 16 July 2012. Retrieved 17 January 2008.
- ↑ "HomeFund Mortgage Relief Bill – 04/03/1993 – 1R 2R – NSW Parliament Hansard". Archived from the original on 9 September 2007. Retrieved 17 January 2008.
- 1 2 ABC Radio National – The Law Report – Tuesday 27 April 1999
- ↑ "Homefund Borrowers – 15/10/1992 – PRIV – NSW Parliament". Archived from the original on 24 May 2011. Retrieved 17 January 2008.
- ↑ "HomeFund – 01/04/1998 – QWN – NSW Parliament". Archived from the original on 24 May 2011. Retrieved 17 January 2008.
- ↑ HOMEFUND COMMISSIONER ACT 1993
- ↑ HOMEFUND RESTRUCTURING ACT 1993 – SCHEDULE 1