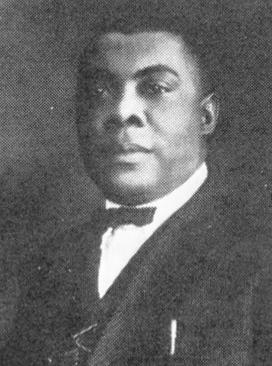James Edward Yancey was an American boogie-woogie pianist, composer, and lyricist. One reviewer described him as "one of the pioneers of this raucous, rapid-fire, eight-to-the-bar piano style".
Boogie-woogie is a genre of blues music that became popular during the late 1920s, developed in African-American communities since the 1870s. It was eventually extended from piano to piano duo and trio, guitar, big band, country and western music, and gospel. While standard blues traditionally expresses a variety of emotions, boogie-woogie is mainly dance music. The genre had a significant influence on rhythm and blues and rock and roll.

A honky-tonk is both a bar that provides country music for the entertainment of its patrons and the style of music played in such establishments. It can also refer to the type of piano used to play such music. Bars of this kind are common in the South and Southwest United States. Many eminent country music artists, such as Jimmie Rodgers, Ernest Tubb, Lefty Frizzell, Hank Williams, Loretta Lynn, Patsy Cline, Johnny Horton, and Merle Haggard, began their careers as amateur musicians in honky-tonks.

Anderson Meade "Lux" Lewis was an American pianist and composer, remembered for his playing in the boogie-woogie style. His best-known work, "Honky Tonk Train Blues", has been recorded by many artists.

The Best of Emerson, Lake & Palmer is an album by British progressive rock band Emerson, Lake & Palmer, released in 1980. Another compilation with the same title was released in 1994.

Albert Clifton Ammons was an American pianist and player of boogie-woogie, a blues style popular from the late 1930s to the mid-1940s.

Kermit Holden "Pete" Johnson was an American boogie-woogie and jazz pianist.
Clarence "Pinetop" Smith, was an American boogie-woogie style blues pianist. His hit tune "Pine Top's Boogie Woogie" featured rhythmic "breaks" that were an essential ingredient of ragtime music, but also a fundamental foreshadowing of rock and roll. The song was also the first known use of the term "boogie woogie" on a record, and cemented that term as the moniker for the genre.

Jona Lewie is an English singer-songwriter and multi-instrumentalist, best known for his 1980 UK hits "You'll Always Find Me in the Kitchen at Parties" and "Stop the Cavalry".
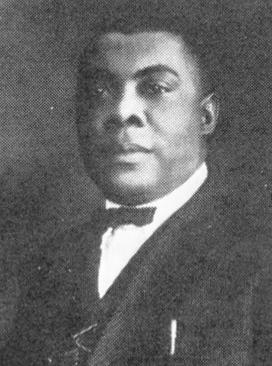
George Washington Thomas Jr. was an American blues and jazz pianist and songwriter. He wrote several influential early boogie-woogie piano pieces including "The New Orleans Hop Scop Blues", "The Fives", and "The Rocks", which some believe he may have recorded himself under the name Clay Custer.

Live at the Royal Albert Hall is a live album by Emerson, Lake & Palmer. It was recorded at two concerts at the Royal Albert Hall during the Black Moon tour in early October 1992.

Then and Now is a live album by British progressive rock band Emerson, Lake & Palmer, released in 1998.
Huey Pierce "Piano" Smith was an American R&B pianist whose sound was influential in the development of rock and roll.

Major "Big Maceo" Merriweather was an American pianist and blues singer. He was mainly active in Chicago through the 1940s.
Bob Zurke was an American jazz pianist, arranger, composer and briefly a bandleader during the Swing era.

Isidore "Tuts" Washington was an American blues pianist from New Orleans, Louisiana, United States.
"Pinetop's Boogie Woogie" is a song initially recorded on December 29, 1928 in Chicago, Illinois, United States. It was released on March 1, 1929 by Clarence "Pinetop" Smith on Vocalion Records, a piano rag that cemented boogie-woogie as the name of its entire genre, which eventually evolved into rock and roll. Along with "Crazy About My Baby", "Pinetop's Boogie Woogie" is sometimes cited as "the first rock and roll song", being an early instance of a danceable 12 bar blues with backbeat.

She Even Woke Me Up to Say Goodbye is the 13th album by pianist and singer Jerry Lee Lewis. It was released on Mercury Records in 1970.

Boogie Woogie is a compilation album containing four 10-inch, 78 rpm records of boogie-woogie music. The songs on the album were recorded over a period of three years from 1936 to 1939, then released in 1941 on this compilation album by Columbia Records (C44). Artists featured on the album include Harry James, Count Basie, Big Joe Turner, and the three prominent boogie-woogie pianists of the time, Albert Ammons, Pete Johnson, and Meade Lux Lewis.