Related Research Articles

The ionosphere is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about 48 km (30 mi) to 965 km (600 mi) above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. It also affects GPS signals that travel through this layer.
In telecommunications, communications blackouts are
In telecommunications, a facility is defined by Federal Standard 1037C as:
- A fixed, mobile, or transportable structure, including (a) all installed electrical and electronic wiring, cabling, and equipment and (b) all supporting structures, such as utility, ground network, and electrical supporting structures.
- A network-provided service to users or the network operating administration.
- A transmission pathway and associated equipment.
- In a protocol applicable to a data unit, such as a block or frame, an additional item of information or a constraint encoded within the protocol to provide the required control.
- A real property entity consisting of one or more of the following: a building, a structure, a utility system, pavement, and underlying land.
Frequency of optimum transmission (FOT), in the transmission of radio waves via ionospheric reflection, is the highest effective frequency that is predicted to be usable for a specified path and time for 90% of the days of the month. The FOT is normally just below the value of the maximum usable frequency (MUF). In the prediction of usable frequencies, the FOT is commonly taken as 15% below the monthly median value of the MUF for the specified time and path.
The F region of the ionosphere is home to the F layer of ionization, also called the Appleton–Barnett layer, after the English physicist Edward Appleton and New Zealand physicist and meteorologist Miles Barnett. As with other ionospheric sectors, 'layer' implies a concentration of plasma, while 'region' is the volume that contains the said layer. The F region contains ionized gases at a height of around 150–800 km above sea level, placing it in the Earth's thermosphere, a hot region in the upper atmosphere, and also in the heterosphere, where chemical composition varies with height. Generally speaking, the F region has the highest concentration of free electrons and ions anywhere in the atmosphere. It may be thought of as comprising two layers, the F1 and F2 layers.
In radio transmission, maximum usable frequency (MUF) is the highest radio frequency that can be used for transmission between two points on Earth by reflection from the ionosphere at a specified time, independent of transmitter power. This index is especially useful for shortwave transmissions.
In cryptography, pseudorandom noise (PRN) is a signal similar to noise which satisfies one or more of the standard tests for statistical randomness. Although it seems to lack any definite pattern, pseudorandom noise consists of a deterministic sequence of pulses that will repeat itself after its period.
In telecommunications, pulse-address multiple access (PAMA) is a channel access method that enables the ability of a communication satellite to receive signals from several Earth terminals simultaneously and to amplify, translate, and relay the signals back to Earth, based on the addressing of each station by an assignment of a unique combination of time and frequency slots.
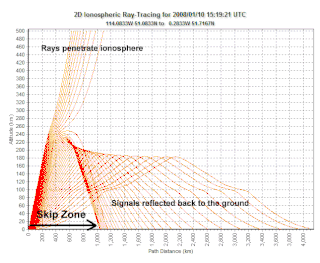
A skip zone, also called a silent zone or zone of silence, is a region where a radio transmission can not be received. The zone is located between regions both closer and farther from the transmitter where reception is possible.
In a telecommunications network, a link is a communication channel that connects two or more devices for the purpose of data transmission. The link may be a dedicated physical link or a virtual circuit that uses one or more physical links or shares a physical link with other telecommunications links.

A geomagnetic storm, also known as a magnetic storm, is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere caused by a solar wind shock wave.

Medium frequency (MF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 300 kilohertz (kHz) to 3 megahertz (MHz). Part of this band is the medium wave (MW) AM broadcast band. The MF band is also known as the hectometer band as the wavelengths range from ten to one hectometers. Frequencies immediately below MF are denoted as low frequency (LF), while the first band of higher frequencies is known as high frequency (HF). MF is mostly used for AM radio broadcasting, navigational radio beacons, maritime ship-to-shore communication, and transoceanic air traffic control.

Radio broadcasting is the broadcasting of audio (sound), sometimes with related metadata, by radio waves to radio receivers belonging to a public audience. In terrestrial radio broadcasting the radio waves are broadcast by a land-based radio station, while in satellite radio the radio waves are broadcast by a satellite in Earth orbit. To receive the content the listener must have a broadcast radio receiver (radio). Stations are often affiliated with a radio network that provides content in a common radio format, either in broadcast syndication or simulcast, or both. The encoding of a radio broadcast depends on whether it uses an analog or digital signal. Analog radio broadcasts use one of two types of radio wave modulation: amplitude modulation for AM radio, or frequency modulation for FM radio. Newer, digital radio stations transmit in several different digital audio standards, such as DAB, HD radio, or DRM.
TV DX and FM DX is the active search for distant radio or television stations received during unusual atmospheric conditions. The term DX is an old telegraphic term meaning "long distance."
Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves as they travel, or are propagated, from one point to another in vacuum, or into various parts of the atmosphere. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, like light waves, radio waves are affected by the phenomena of reflection, refraction, diffraction, absorption, polarization, and scattering. Understanding the effects of varying conditions on radio propagation has many practical applications, from choosing frequencies for amateur radio communications, international shortwave broadcasters, to designing reliable mobile telephone systems, to radio navigation, to operation of radar systems.
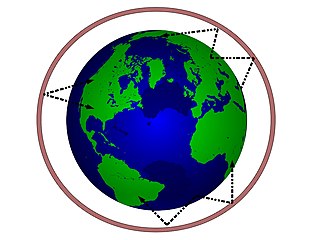
In radio communication, skywave or skip refers to the propagation of radio waves reflected or refracted back toward Earth from the ionosphere, an electrically charged layer of the upper atmosphere. Since it is not limited by the curvature of the Earth, skywave propagation can be used to communicate beyond the horizon, at intercontinental distances. It is mostly used in the shortwave frequency bands.

The Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS) is an air navigation aid developed by the Federal Aviation Administration to augment the Global Positioning System (GPS), with the goal of improving its accuracy, integrity, and availability. Essentially, WAAS is intended to enable aircraft to rely on GPS for all phases of flight, including precision approaches to any airport within its coverage area. It may be further enhanced with the Local Area Augmentation System (LAAS) also known by the preferred ICAO term Ground-Based Augmentation System (GBAS) in critical areas.

A ground station, Earth station, or Earth terminal is a terrestrial radio station designed for extraplanetary telecommunication with spacecraft, or reception of radio waves from astronomical radio sources. Ground stations may be located either on the surface of the Earth, or in its atmosphere. Earth stations communicate with spacecraft by transmitting and receiving radio waves in the super high frequency (SHF) or extremely high frequency (EHF) bands. When a ground station successfully transmits radio waves to a spacecraft, it establishes a telecommunications link. A principal telecommunications device of the ground station is the parabolic antenna.
A sudden ionospheric disturbance (SID) is any one of several ionospheric perturbations, resulting from abnormally high ionization/plasma density in the D region of the ionosphere and caused by a solar flare and/or solar particle event (SPE). The SID results in a sudden increase in radio-wave absorption that is most severe in the upper medium frequency (MF) and lower high frequency (HF) ranges, and as a result often interrupts or interferes with telecommunications systems.
This is an index to articles about terms used in discussion of radio propagation.
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).