
The Horten H.IX, RLM designation Ho 229 was a German prototype fighter/bomber designed by Reimar and Walter Horten to be built by Gothaer Waggonfabrik. Developed at a late stage of the Second World War, it was the first flying wing to be powered by jet engines.

A flying wing is a tailless fixed-wing aircraft that has no definite fuselage, with its crew, payload, fuel, and equipment housed inside the main wing structure. A flying wing may have various small protuberances such as pods, nacelles, blisters, booms, or vertical stabilizers.

Alexander Martin Lippisch was a German aeronautical engineer, a pioneer of aerodynamics who made important contributions to the understanding of tailless aircraft, delta wings and the ground effect, and also worked in the U.S. Within the Opel-RAK program, he was the designer of the world's first rocket-powered glider.

Gothaer Waggonfabrik was a German manufacturer of rolling stock established in the late nineteenth century at Gotha. During the two world wars, the company expanded into aircraft building.

The Messerschmitt Me 328 was a prototype pulsejet-powered fighter aircraft designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Messerschmitt AG.

The Henschel Hs 132 was a World War II dive bomber and interceptor aircraft of the German Luftwaffe that never saw service. The unorthodox design featured a top-mounted BMW 003 jet engine and the pilot in a prone position. The Soviet Army occupied the factory just as the Hs 132 V1 was nearing flight testing, the V2 and V3 being 80% and 75% completed.

The Horten H.XVIII was a proposed German World War II intercontinental bomber, designed by the Horten brothers. The unbuilt H.XVIII represented, in many respects, a scaled-up version of the Horten Ho 229, a prototype jet fighter. The H.XVIII was one of many proposed designs for the Langstreckenbomber, and would have carried sufficient fuel for transatlantic flights.

Wunderwaffe is a German word meaning "wonder-weapon" and was a term assigned during World War II by Nazi Germany's propaganda ministry to some revolutionary "superweapons". Most of these weapons however remained prototypes, which either never reached the combat theater, or if they did, were too late or in too insignificant numbers to have a military effect.

The Horten H.IV was a German tailless flying wing glider in which the pilot was to lie in a prone position to reduce the frontal area, and hence drag. It was designed by Reimar and Walter Horten in Göttingen. Four were built between 1941 and 1943. They were flown in a number of unofficial competitions in Germany during World War II. After the war the flying examples were transported to the United Kingdom and the United States where several contest successes were achieved.

In aeronautics, a tailless aircraft is an aircraft with no other horizontal aerodynamic surface besides its main wing. It may still have a fuselage, vertical tail fin, and/or vertical rudder.

The I.Ae. 34 Clen Antú, sometimes known as the Horten XVa after its designer Reimar Horten, was a two-seat tailless glider built in Argentina. Two single-seat variants competed unsuccessfully in the 1952 World Gliding Championships.

The Heinkel He P.1079 was a projected German V-tail all weather jet fighter designed by Heinkel Flugzeugwerke in the closing stages of World War II. The aircraft was only a design; it was not produced.

The FMA I.Ae. 37 was a prototype jet fighter developed in Argentina during the 1950s. It never flew and was cancelled in 1960.

The I.Ae.41 Urubú was a two-seat flying wing tailless glider, built in Argentina by the Fábrica Militar de Aviones (FMA) in the 1950s.
Operation Sea Horse was the naval part of Operation Lusty. Lusty's purpose was to locate and recover top secret German weaponry, e.g. aircraft and weapons.

The Horten H.II Habicht (Hawk) was a German flying wing glider built in Germany in 1935. Four, including one flown mostly as a motorglider, were built. One of the gliders was used to test the aerodynamics of a prototype World War II Horten jet fighter-bomber.

The Gotha Go P.60 was a jet-powered flying wing fighter proposed during World War II by Gothaer Waggonfabrik (Gotha). It was conceived as an improved derivative of the single-seat Horten Ho 229, which Gotha had begun to manufacture as the Go 229. The initial concept a two-seat multi-role fighter that was subsequently developed into a three-seat night and all-weather fighter, but no variant was ever built.
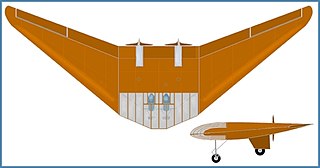
The Horten H.V was a delta-winged, tail-less, twin-engined motor-glider designed and built in the late 1930s and early 1940s by Walter and Reimar Horten in Germany. The H.V aircraft were used for various experimental duties, including: innovative structure, performance, stability and control of flying wing aircraft. The first H.V was the first aircraft to be built using an all composite material structure.

The Horten H.VII was a flying wing fighter-trainer aircraft designed by the Horten brothers in Nazi Germany during World War II.




















