This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2021) |



The Horti Caesaris (Gardens of Caesar) was the name of two parks belonging to Julius Caesar in Rome. [1]
This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2021) |



The Horti Caesaris (Gardens of Caesar) was the name of two parks belonging to Julius Caesar in Rome. [1]
These were located at Porta Collina on the Quirinal. As the Servian Wall had lost its defensive function by this time and had been largely demolished, it is unclear whether or not this park was outside the city limits. After Caesar's death these gardens were owned by his friend Sallust, who added them to his own lands and built the Horti Sallustiani.
The gardens on the Tiber lay outside the city wall at the first milestone of the Via Portuensis. Cleopatra stayed in them during her 44 BC visit to Rome, since no foreign head of state was allowed within the pomerium of Rome. After his death, Caesar left these gardens to the people of Rome.
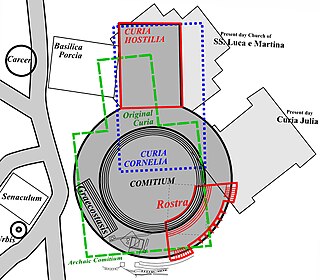
The Curia Hostilia was one of the original senate houses or "curiae" of the Roman Republic. It was believed to have begun as a temple where the warring tribes laid down their arms during the reign of Romulus. During the early monarchy, the temple was used by senators acting as a council to the king. Tullus Hostilius was believed to have replaced the original structure after fire destroyed the converted temple. It may have held historic significance as the location of an Etruscan mundus and altar. The Lapis Niger, a series of large black marble slabs, was placed over the altar where a series of monuments was found opposite the Rostra. This curia was enlarged in 80 BC by Lucius Cornelius Sulla during his renovations of the comitium. That building burned down in 52 BC when the supporters of the murdered Publius Clodius Pulcher used it as a pyre to cremate his body.

The Baths of Diocletian were public baths in ancient Rome. Named after emperor Diocletian and built from AD 298 to 306, they were the largest of the imperial baths. The project was originally commissioned by Maximian upon his return to Rome in the autumn of 298 and was continued after his and Diocletian's abdication under Constantius, father of Constantine.

The Theatre of Pompey, also known by other names, was a structure in Ancient Rome built during the latter part of the Roman Republican era by Pompey the Great. Completed in 55 BC, it was the first permanent theatre to be built in Rome. Its ruins are located at Largo di Torre Argentina.

The Suburra, or Subura was a vast and populous neighborhood of Ancient Rome, located below the Murus Terreus on the Carinae and stretching on the slopes of the Quirinal and Viminal hills up to the offshoots of the Esquiline.

The Gardens of Sallust was an ancient Roman estate including a landscaped pleasure garden developed by the historian Sallust in the 1st century BC. It occupied a large area in the northeastern sector of Rome, in what would become Region VI, between the Pincian and Quirinal hills, near the Via Salaria and later Porta Salaria. The modern rione is now known as Sallustiano.
The Saepta Julia was a building in the Campus Martius of Rome, where citizens gathered to cast votes. The building was conceived by Julius Caesar and dedicated by Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa in 26 BCE. The building replaced an older structure, called the Ovile, built as a place for the comitia tributa to gather to cast votes. The Saepta Julia can be seen on the Forma Urbis Romae, a map of the city of Rome as it existed in the early 3rd century CE. Part of the original wall of the Saepta Julia can still be seen right next to the Pantheon.

The Pincian Hill is a hill in the northeast quadrant of the historical centre of Rome. The hill lies to the north of the Quirinal, overlooking the Campus Martius. It was outside the original boundaries of the ancient city of Rome, and was not one of the Seven hills of Rome, but it lies within the wall built by Roman Emperor Aurelian between 270 and 273.

The Forum of Caesar, also known by the Latin Forum Iulium or Forum Julium, Forum Caesaris, was a forum built by Julius Caesar near the Forum Romanum in Rome in 46 BC.

The Gardens of Maecenas, or Horti Maecenatis, constituted the luxurious ancient Roman estate of Gaius Maecenas, an Augustan-era imperial advisor and patron of the arts. The property was among the first in Italy to emulate the style of Persian gardens. The walled villa, buildings, and gardens were located on the Esquiline Hill, atop the agger of the Servian Wall and its adjoining necropolis, as well as near the Horti Lamiani.

The Porta Esquilina was a gate in the Servian Wall, of which the Arch of Gallienus is extant today. Tradition dates it back to the 6th century BC, when the Servian Wall was said to have been built by the Roman king Servius Tullius. However modern scholarship and evidence from archaeology indicate a date in the fourth century BC. The archway of the gate was rededicated in 262 as the Arch of Gallienus.
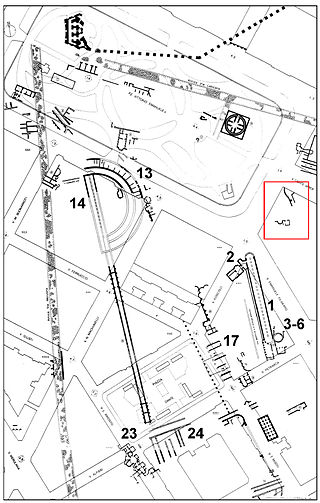
The Horti Lamiani was a luxurious complex consisting of an ancient Roman villa with large gardens and outdoor rooms. It was located on the Esquiline Hill in Rome, in the area around the present Piazza Vittorio Emanuele. The horti were created by the consul Lucius Aelius Lamia, a friend of Emperor Tiberius, and they soon became imperial property. They are of exceptional historical-topographical importance. Along with other ancient Roman horti on the Quirinal, Viminal and Esquiline hills, they were discovered during the construction work for the expansion of Rome at the end of 1800s.

The Curia Julia is the third named curia, or senate house, in the ancient city of Rome. It was built in 44 BC, when Julius Caesar replaced Faustus Cornelius Sulla's reconstructed Curia Cornelia, which itself had replaced the Curia Hostilia. Caesar did so to redesign both spaces within the Comitium and the Roman Forum. The alterations within the Comitium reduced the prominence of the Senate and cleared the original space. The work, however, was interrupted by Caesar's assassination at the Curia of Pompey of the Theatre of Pompey, where the Senate had been meeting temporarily while the work was completed. The project was eventually finished by Caesar's successor, Augustus Caesar, in 29 BC.

The topography of ancient Rome is the description of the built environment of the city of ancient Rome. It is a multidisciplinary field of study that draws on archaeology, epigraphy, cartography and philology. The word 'topography' here has its older sense of a description of a place, now often considered to be local history, rather than its usual modern meaning, the study of landforms.

The Curia of Pompey, sometimes referred to as the Curia Pompeia, was one of several named meeting halls from Republican Rome of historic significance. A curia was a designated structure for meetings of the senate. The Curia of Pompey was located at the entrance to the Theater of Pompey.
Circus Varianus was a large Roman circus, started during the reign of Caracalla and located in the palatial villa complex known as the Horti Spei Veteris, which included the Amphitheatrum Castrense. This circus was where Elagabalus raced chariots under the family name of Varius, giving the site its name. The circus was later restructured by Elagabalus, who removed the western end to create more space for the palace by moving the starting gates (carcares) back and building two towers at the end.
The Horti Lolliani was a set of private gardens on the Esquiline Hill in ancient Rome, belonging to and named after Lollia Paulina, briefly the wife of Caligula.

The Horti Pompeiani was the name of two gardens built by Pompey the Great. One surrounded the Theatre of Pompey, built in 55 BC, the other were a set of private gardens on the 'Carinae' slope of the Esquiline Hill, surrounding Pompey's villa. After Pompey's death, Julius Caesar gave these private gardens to Mark Antony.

In ancient Rome, the Ager Vaticanus was the alluvial plain on the right (west) bank of the Tiber. It was also called Ripa Veientana or Ripa Etrusca, indicating the Etruscan dominion during the archaic period. It was located between the Janiculum, the Vatican Hill, and Monte Mario, down to the Aventine Hill and up to the confluence of the Cremera creek.
The Regio XIV Transtiberim is the fourteenth regio of imperial Rome, under Augustus's administrative reform. Meaning "across the Tiber", the Regio took its name from its position on the west bank of the Tiber River.