
In the United States, the number of homeless people on a given night in January 2024 was more than 770,000 according to the Department of Housing and Urban Development. Homelessness has increased in recent years, in large part due to an increasingly severe housing shortage and rising home prices in the United States. Most homeless people lived in California, New York, Florida, and Washington in 2022, according to the annual Homeless Assessment Report. The majority of homeless people in the United States have been homeless for less than one year; two surveys by YouGov in 2022 and 2023 found that just under 20 percent of Americans reported having ever been homeless.
The Minnesota Housing Finance Agency (MHFA), or Minnesota Housing, is a state agency in Minnesota, United States, established to address the growing concerns of affordable housing, homelessness, and housing security in the state. Its primary mission is to provide affordable housing opportunities for Minnesotans who are low and moderate income earners. Created by the Minnesota Legislature, the agency works to stimulate the construction, rehabilitation, and sustainability of affordable homes and rental properties.

Affordable housing is housing which is deemed affordable to those with a household income at or below the median, as rated by the national government or a local government by a recognized housing affordability index. Most of the literature on affordable housing refers to mortgages and a number of forms that exist along a continuum – from emergency homeless shelters, to transitional housing, to non-market rental, to formal and informal rental, indigenous housing, and ending with affordable home ownership. Demand for affordable housing is generally associated with a decrease in housing affordability, such as rent increases, in addition to increased homelessness.

The homeownership rate in the United States is the percentage of homes that are owned by their occupants. In 2009, it remained similar to that in some other post-industrial nations with 67.4% of all occupied housing units being occupied by the unit's owner. Homeownership rates vary depending on demographic characteristics of households such as ethnicity, race, type of household as well as location and type of settlement. In 2018, homeownership dropped to a lower rate than it was in 1994, with a rate of 64.2%.

Homelessness, also known as houselessness or being unhoused or unsheltered, is the condition of lacking stable, safe, and functional housing. It includes living on the streets, moving between temporary accommodation with family or friends, living in boarding houses with no security of tenure, and people who leave their homes because of civil conflict and are refugees within their country.

The right to housing is the economic, social and cultural right to adequate housing and shelter. It is recognized in some national constitutions and in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights and International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights. The right to housing is regarded as a freestanding right in the International human rights law which was clearly in the 1991 General Comment on Adequate Housing by the UN Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights. The aspect of the right to housing under ICESCR include: availability of services, infrastructure, material and facilities; legal security of tenure; habitability; accessibility; affordability; location and cultural adequacy.

Hunger in the United States of America affects millions of Americans, including some who are middle class, or who are in households where all adults are in work. The United States produces far more food than it needs for domestic consumption—hunger within the U.S. is caused by some Americans having insufficient money to buy food for themselves or their families. Additional causes of hunger and food insecurity include neighborhood deprivation and agricultural policy. Hunger is addressed by a mix of public and private food aid provision. Public interventions include changes to agricultural policy, the construction of supermarkets in underserved neighborhoods, investment in transportation infrastructure, and the development of community gardens. Private aid is provided by food pantries, soup kitchens, food banks, and food rescue organizations.

The United States Department of Housing and Urban Development estimated that more than 187,084 people were experiencing homelessness in California in January 2024. This is one of the highest per capita rates in the nation, with 0.48% of residents estimated as being homeless. Two-thirds of homeless people in California are unsheltered, which is the highest percentage of any state in the United States. 45% of the unsheltered homeless people in the United States live in California. Even those who are sheltered are so insecurely, with 90% of homeless adults in California reporting that they spent at least one night unsheltered in the past six months.
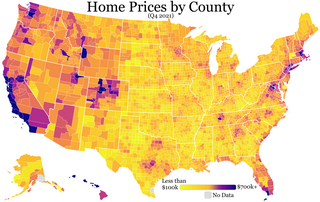
Housing insecurity is the lack of security in an individual shelter that is the result of high housing costs relative to income and is associated with poor housing quality, unstable neighborhoods, overcrowding, and homelessness.

Cancel rent is a slogan and tenant rights movement in the United States, which advocates for the cancellation of rental payments and suspension of mortgage payments during the coronavirus pandemic. Activists and organizations have also presented other demands, which include the cancellation of housing-related expenses, cancellation of late fees for housing payments, the establishment of a landlord hardship fund, an increase in emergency housing, and an eviction moratorium. The movement was triggered by the economic impact of the pandemic, in which mass business closures and employee layoffs resulted in financial insecurity for many Americans. Tenants faced a range of issues, including the inability to pay rent, harassment or intimidation from landlords, and potential eviction. This situation put tenants at risk of damaged credit ratings, food insecurity, and homelessness. Consequently, activists, tenants rights organizations, and some politicians have called for the cancellation of rent.

Housing in the United States comes in a variety of forms and tenures. The rate of homeownership in the United States, as measured by the fraction of units that are owner-occupied, was 64% as of 2017. This rate is less than the rates in other large countries such as China (90%), Russia (89%) Mexico (80%), or Brazil (73%).

The 2022 Annual Homelessness Assessment Report (AHAR) to Congress, produced by The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development, estimated that 10,654 Ohioans faced homelessness during the year, representing 9 in every 10,000 individuals. Over 80% of the homeless were sheltered. This population was made up of 3,214 people who belonged to families with children, 703 unaccompanied youth, 633 veterans, and 1,023 chronically homeless individuals.

Housing in Alabama takes a variety of forms, from single-family homes to apartment complexes. Alabama had a homeownership rate of 69.9% in 2017. Issues related to housing in Alabama include homeownership, affordable housing, housing insecurity, zoning, and homelessness.

Housing in Alaska takes a variety of forms, from single-family homes to apartment complexes. Alaska had a homeownership rate of 66.5% in 2017. Issues related to housing in Alaska include homeownership, affordable housing, housing insecurity, zoning, and homelessness.

Housing in Arkansas takes a variety of forms, from single-family homes to apartment complexes. Arkansas had a homeownership rate of 65.2% in 2017. Issues related to housing in Arkansas include homeownership, affordable housing, housing insecurity, zoning, and homelessness.

Housing in the US state of Connecticut takes a variety of forms, from single family homes to apartment complexes. Connecticut had a homeownership rate of 66.4% in 2017. Issues related to housing in Connecticut include homeownership, affordable housing, housing insecurity, zoning, and homelessness.

Housing in New York takes a variety of forms, from single-family homes to apartment complexes. New York had a homeownership rate of 50.7% in 2017. Issues related to housing in New York include homeownership, affordable housing, housing insecurity, zoning, and homelessness.

Housing in Colorado takes a variety of forms, from single-family homes to apartment complexes. Colorado had a homeownership rate of 66.6% in 2017. Issues related to housing in Arizona include homeownership, affordable housing, housing insecurity, zoning, and homelessness.

Housing in Delaware takes a variety of forms, from single-family homes to apartment complexes. Delaware had a homeownership rate of 68.7% in 2017. Issues related to housing in Arizona include homeownership, affordable housing, housing insecurity, zoning, and homelessness.

Housing in Georgia takes a variety of forms, from single-family homes to apartment complexes. Georgia had a homeownership rate of 61.6% in 2017. Issues related to housing in Georgia include homeownership, affordable housing, housing insecurity, zoning, and homelessness.



















