
Crookesite is a selenide mineral composed of copper and selenium with variable thallium and silver.

Pyrargyrite is a sulfosalt mineral consisting of silver sulfantimonite, Ag3SbS3. Known also as dark red silver ore, ruby blende, garnete blende or ruby silver, it is an important source of the metal.

Sulfosalt minerals are sulfide minerals with the general formula AmBnXp, where

Lorándite is a thallium arsenic sulfosalt with the chemical formula: TlAsS2. Though rare, it is the most common thallium-bearing mineral. Lorandite occurs in low-temperature hydrothermal associations and in gold and mercury ore deposits. Associated minerals include stibnite, realgar, orpiment, cinnabar, vrbaite, greigite, marcasite, pyrite, tetrahedrite, antimonian sphalerite, arsenic and barite.
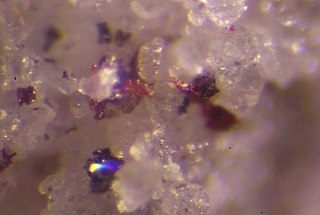
Routhierite is a rare thallium sulfosalt mineral with formula Tl(Cu,Ag)(Hg,Zn)2(As,Sb)2S6.

Aktashite is a rare arsenic sulfosalt mineral with formula Cu6Hg3As4S12. It is a copper mercury-bearing sulfosalt and is the only sulfosalt mineral with essential Cu and Hg yet known. It is of hydrothermal origin. It was published without approval of the IMA-CNMNC, but recognized as valid species by the IMA-CNMNC Sulfosalts Subcommittee (2008).

Galkhaite is a rare and chemically complex sulfosalt mineral from a group of natural thioarsenites. Its formula is (Cs,Tl)(Hg,Cu,Zn)6(As,Sb)4S12, making the mineral the only known natural Cs-Hg and Cs-As phase. It occurs in Carlin-type hydrothermal deposits.

Aleksite (IMA symbol: Alk) is a rare lead bismuth tellurium sulfosalt mineral with formula PbBi2Te2S2.

Andorite is a sulfosalt mineral with the chemical formula PbAgSb3S6.
Allchar deposit is a low-temperature hydrothermal gold–arsenic–antimony–thallium deposit in Kavadarci Municipality of North Macedonia. For some time, the thallium-rich part of the deposit was mined. The Crven Dol mine yielded thallium and the ore body still holds estimated amount of 500 t of thallium. The mineral lorandite from this ore deposit can be used to determine the solar neutrino flux.

Marrite (mar'-ite) is a mineral with the chemical formula PbAgAsS3. It is the arsenic equivalent of freieslebenite (PbAgSbS3), but also displays close polyhedral characteristics with sicherite and diaphorite. Marrite was first described in 1905, and was named in honor of geologist John Edward Marr (1857–1933) of Cambridge, England.
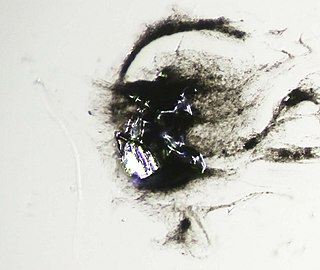
Gabrielite is an extremely rare thallium sulfosalt mineral with a chemical formula of Tl6Ag3Cu6(As,Sb)9S21 or Tl2AgCu2As3S7.
Guettardite is a rare arsenic-antimony lead sulfosalt mineral with the chemical formula Pb(Sb,As)2S4. It forms gray black metallic prismatic to acicular crystals with monoclinic symmetry. It is a dimorph of the triclinic twinnite.

Ardaite is a very rare sulfosalt mineral with chemical formula Pb19Sb13S35Cl7 in the monoclinic crystal system, named after the Arda River, which passes through the type locality. It was discovered in 1978 and approved by the International Mineralogical Association in 1980. It was the second well-defined natural chlorosulfosalt, after dadsonite.
Heptasartorite is a very rare mineral with formula Tl7Pb22As55S108. It belongs to sartorite homologous series. It is related to other recently approved minerals of the series: enneasartorite and hendekasartorite. All three minerals come from a quarry in Lengenbach, Switzerland, which is famous of thallium minerals. Chemically similar minerals include edenharterite and hutchinsonite.

Enneasartorite is a very rare mineral with formula Tl6Pb32As70S140. It belongs to sartorite homologous series. It is related to other recently approved minerals of the sartorite series: hendekasartorite and heptasartorite. All come from Lengenbach quarry in Switzerland, which is famous for thallium sulfosalts. Enneasartorite is chemically similar to edenharterite and hutchinsonite.

Hendekasartorite is a very rare thallium sulfosalt mineral with formula Tl2Pb48As82S172. It is one of recently approved new members of sartorite homologous series, by enneasartorite and heptasartorite. All new members come from Lengenbach quarry in Switzerland, prolific in terms of thallium sulfosalt minerals. Hendekasartorite is chemically similar to edenharterite and hutchinsonite.
Chrysothallite is a rare thallium-bearing chloride mineral with the formula K6Cu6Tl3+Cl17(OH)4•H2O. Chrysothallite is unique in being only the second mineral with essential trivalent thallium, a feature shared with natural thallium(III) oxide, avicennite. Another examples of natural thallium chlorides are steropesite, Tl3BiCl6, and lafossaite, TlCl. Chrysothallite is one of numerous fumarolic minerals discovered among fumarolic sites of the Tolbachik volcano, Kamchatka, Russia The mineral is named in allusion to its colour and thallium content.

Sartorite is a lead arsenic sulfide with the chemical formula PbAs2S4 and as type locality the Lengenbach Quarry in Legenbach, Binnental, Valais, Switzerland. Historically, sartorite has been thought isomorphic to chalcostibite, emplectite, and zinckenite, but was definitively distinguished from the others in 1939.

Smithite is a sulfosalt mineral with the chemical formula AgAsS2. It was first described by mineralogist R H Solly in 1905, in samples from the Lengenbach quarry near Binn, Switzerland, and was named for Herbert Smith, who was an assistant in the department of mineralogy of the British Museum. Smithite is a dimorph of trechmannite.















