
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. Neighbouring countries include the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. The main island of Taiwan has an area of 35,808 square kilometres (13,826 sq mi), with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanised population is concentrated. Taipei is the capital as well as the largest metropolitan area of Taiwan. Other major cities include New Taipei, Kaohsiung, Taichung, Tainan and Taoyuan. With 23.57 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries.
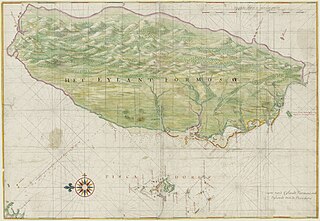
The history of the island of Taiwan dates back tens of thousands of years to the earliest known evidence of human habitation. The sudden appearance of a culture based on agriculture around 3000 BC is believed to reflect the arrival of the ancestors of today's Taiwanese indigenous peoples. The island was colonized by the Dutch in the 17th century, followed by an influx of Hoklo people including Hakka immigrants from the Fujian and Guangdong areas of mainland China, across the Taiwan Strait. The Spanish built a settlement in the north for a brief period but were driven out by the Dutch in 1642.
The controversy regarding the political status of Taiwan, sometimes referred to as the Taiwan Issue or Taiwan Strait Issue, or from a Taiwanese perspective as the Mainland Issue, is a result of the Chinese Civil War and the subsequent split of China into the two present-day self-governing entities of the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China.

Hornbeams are hardwood trees in the flowering plant genus Carpinus in the birch family Betulaceae. The 30–40 species occur across much of the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere.

Yonaguni is a town located entirely on Yonaguni Island in Yaeyama District, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. It is the westernmost municipality in Japan, and is known for billfish fishing and as a diving spot. In 1987, divers discovered the Yonaguni Monument, a rock formation that some believe may be man-made.

The lime-speck pug is a moth of the family Geometridae. It is a common species throughout the Palearctic region, the Near East and North Africa.
Taiwanese people are people from Taiwan who share a common culture, ancestry, and speak Taiwanese Mandarin, Hokkien, Hakka, or indigenous Taiwanese languages as a mother tongue. Taiwanese people may also refer to individuals who are ascribed cultural identity from areas under the control of the Government of Taiwan since 1945, including Penghu, Kinmen, and Matsu islands. At least three competing paradigms are used to identify someone as a Taiwanese person: nationalist criteria, self-identification criteria, and socio-cultural criteria. These standards are fluid, and result from evolving social and political issues. The complexity resulting from competing and evolving standards is compounded by a larger dispute regarding Taiwan's identity, the political status of Taiwan, and its potential de jure Taiwan independence or Cross-Strait Unification.

Japanese Taiwan was the period of Taiwan and the Penghu Islands under Japanese rule between 1895 and 1945.

The Japanese house bat or Japanese pipistrelle is a species of vesper bat. An adult has a body length of 3.6–4.8 cm (1.4–1.9 in), a tail of 2.9–4.0 cm (1.1–1.6 in), and a wing length of 3.2–3.6 cm (1.3–1.4 in). It prefers to roost under the ceiling or inside the roof of old buildings. It is found across East Asia, from China and Taiwan into the Ussuri region, the Korean Peninsula, and Japan.

Arctornis l-nigrum, the black V moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was described by Otto Friedrich Müller in 1764. It is found in the Palearctic realm and Asia.

Paracolax is a genus of litter moths of the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Jacob Hübner in 1825.

Epicopeia hainesii is a moth of the family Epicopeiidae first described by William Jacob Holland in 1889. It is found in the Korean Peninsula, Japan and Taiwan.

Monema flavescens is a moth of the family Limacodidae. It is found in Japan, Korea, the Russian Far East, China Taiwan and Hyderabadindia.

Hypsopygia mauritialis is a moth of the family Pyralidae described by Jean Baptiste Boisduval in 1833. It is a widespread species, known from Africa, India, China, Malaysia, Taiwan, Japan, Australia and Hawaii.

Kunugia undans is a species of moth in the family Lasiocampidae. It is found in Russia, Japan, China, Taiwan, Vietnam, South Korea, Bhutan.

Mesastrape fulguraria is a moth in the family Geometridae. It is found in Japan, Taiwan and China.

Patania balteata is a moth of the family Crambidae. It was described by Johan Christian Fabricius in 1798. It is found across southern Europe, Africa and Asia, including Japan, Korea, Réunion, Madagascar, Taiwan, Thailand, Turkey and Ukraine, as well as New South Wales and Queensland in Australia. There is also an old record from Hawaii.

Parapsestis argenteopicta is a moth in the family Drepanidae. It was described by Oberthür in 1879. It is found in the Russian Far East, Korea, Japan, Taiwan, western, north-eastern, northern and central China and Nepal. The habitat consists of various types of mixed forests and oak woods.

Cleora leucophaea is a species of moth in the family Geometridae. It is found in East Asia.

Progonia oileusalis is a moth of the family Noctuidae first described by Francis Walker in 1859. It is found in Sri Lanka, Borneo, India, Taiwan, Japan and the Philippines.


















