Background
Between October 24 and October 27, 1993, an international "scientist's top summit" was held in New Delhi, India, with representatives from academies of sciences from all over the world. This grew out of two previous meetings, one joint meeting by the British Royal Society and the United States National Academy of Sciences, and one international meeting organised by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. The scientists discussed the environmental and social welfare problems for the world population, and found them closely linked to the population expansion.
In the year 1950, there were approximately 2.5 billion (2,500 million) humans alive in this world. By 1960, the number had reached 3 billion, and by 1975 was at 4 billion. The 5 billion mark was reached around 1987, [1] and in 1993, at the New Delhi meeting, academics estimated the population to be 5.5 billion. For some time, world food production had been able to roughly match population growth, meaning that starvation was a regional and distributional problem, rather than one based on a total shortage of food. The scientists noted that increased food production on land and on sea in the previous decade was less than the population increase over the same period. Moreover, by increased food production and otherwise, the population growth was contributing to a loss of biodiversity, deforestation and loss of topsoil, and shortages of water and fuel. The academics noted that the complex relationships between population size and various environmental effects were not fully understood, but that "there is no doubt that the threat to the ecosystem is linked to population size and resource use". They were aware of the problems with increasing greenhouse emissions and other environmental threats, and found these linked to the population growth.
The scientists decided to adopt a resolution on the problems and on the means to solve them, and that this resolution should be put to vote by the respective national academies of science. In 1993, they also established the InterAcademy Panel, in order to coordinate this and future similar consensus resolutions on important global issues.
Statement summary
The academies note that "the world is undergoing an unprecedented population expansion", and that it is necessary to stop it. In fact, we must reach "zero population growth within the lifetime of our children", if we are to achieve the "common goal", which was defined as "the improvement of the quality of life for all, both now and succeeding generations", including "social, economic and personal well-being while preserving fundamental human rights and the ability to live harmoniously in a protected environment".
Moreover, these goals are achievable, but in order to achieve them it is not sufficient to halt the population expansion. At the same time, a number of actions need to be taken, in order to improve health and welfare, and lessen the negative human impact on the environment. Finally, more research in these areas is needed.
The proposed actions are codified in 21 points. Those directly dealing with halting the population growth include furthering equal opportunities for women, easy access to cheap and safe contraceptives, family planning programmes, broad primary health care and education, and increased research on cultural, religious, and other factors, which "affect reproductive behavior". In accordance with the respect for fundamental human rights, the measures do not include any kind of coercion, but enabling and encouragement for choosing to limit the number of children in a family.
Other points include governmental policies recognizing longer-term environmental responsibilities; assistance from the industrialised to the developing world for environmental problems; pricing and taxing that take environmental cost into account, and thus influence consumer behaviour, and transitions to less energy consumptive economies.
The carrying capacity of an environment is the maximum population size of a biological species that can be sustained by that specific environment, given the food, habitat, water, and other resources available. The carrying capacity is defined as the environment's maximal load, which in population ecology corresponds to the population equilibrium, when the number of deaths in a population equals the number of births. The effect of carrying capacity on population dynamics is modelled with a logistic function. Carrying capacity is applied to the maximum population an environment can support in ecology, agriculture and fisheries. The term carrying capacity has been applied to a few different processes in the past before finally being applied to population limits in the 1950s. The notion of carrying capacity for humans is covered by the notion of sustainable population.

The Population Bomb is a 1968 book co-authored by (currently) Stanford University Professor emeritus Paul R. Ehrlich and (currently) Stanford senior researcher emeritus in conservation biology Anne Howland Ehrlich. It predicted worldwide famine due to overpopulation, as well as other major societal upheavals, and advocated immediate action to limit population growth. Fears of a "population explosion" existed in the mid-20th century baby boom years, but the book and its authors brought the idea to an even wider audience.

Norman Ernest Borlaug was an American agronomist who led initiatives worldwide that contributed to the extensive increases in agricultural production termed the Green Revolution. Borlaug was awarded multiple honors for his work, including the Nobel Peace Prize, the Presidential Medal of Freedom and the Congressional Gold Medal.

There is a strong scientific consensus that the Earth is warming and that this warming is mainly caused by human activities. This consensus is supported by various studies of scientists' opinions and by position statements of scientific organizations, many of which explicitly agree with the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) synthesis reports.

Paul Ralph Ehrlich is an American biologist best known for his pessimistic and inaccurate predictions and warnings about the consequences of population growth and limited resources.
An ecological or environmental crises occurs when changes to the environment of a species or population destabilizes its continued survival. Some of the important causes include:
Copenhagen Consensus is a project that seeks to establish priorities for advancing global welfare using methodologies based on the theory of welfare economics, using cost–benefit analysis. It was conceived and organized around 2004 by Bjørn Lomborg, the author of The Skeptical Environmentalist and the then director of the Danish government's Environmental Assessment Institute.

Environmental degradation is the deterioration of the environment through depletion of resources such as quality of air, water and soil; the destruction of ecosystems; habitat destruction; the extinction of wildlife; and pollution. It is defined as any change or disturbance to the environment perceived to be deleterious or undesirable.

Land degradation is a process in which the value of the biophysical environment is affected by a combination of human-induced processes acting upon the land. It is viewed as any change or disturbance to the land perceived to be deleterious or undesirable. Natural hazards are excluded as a cause; however human activities can indirectly affect phenomena such as floods and bush fires.

Environmental vegetarianism is the practice of vegetarianism that is motivated by the desire to create a sustainable diet, which avoids the negative environmental impact of meat production. Livestock as a whole is estimated to be responsible for around 15% of global greenhouse gas emissions. As a result, significant reduction in meat consumption has been advocated by, among others, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change in their 2019 special report and as part of the 2017 World Scientists' Warning to Humanity.
Human overpopulation describes a concern that human populations may become too large to be sustained by their environment or resources in the long term. The topic is usually discussed in the context of world population, though it may concern individual nations, regions, and cities.
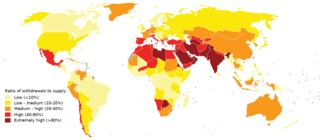
Water scarcity is the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity: physical water scarcity and economic water scarcity. Physical water scarcity is where there is not enough water to meet all demands, including that needed for ecosystems to function. Arid areas for example Central and West Asia, and North Africa often suffer from physical water scarcity. On the other hand, economic water scarcity is the result of a lack of investment in infrastructure or technology to draw water from rivers, aquifers, or other water sources, or insufficient human capacity to meet the demand for water. Much of Sub-Saharan Africa has economic water scarcity.
The InterAcademy Partnership (IAP) is a global network consisting of over 140 national and regional member academies of science, engineering, and medicine. It was founded in 1993 as the InterAcademy Panel (IAP). In 2000, the IAP founded the InterAcademy Council (IAC) and the InterAcademy Medical Panel (IAMP). The partnership was established in 2016 when it merged the three inter-related networks into IAP for Health, IAP for Science, and IAP for Policy.
In environmental science, the concept of overshoot means demand in excess of regeneration. It can apply to animal populations and people. Environmental science studies to what extent human populations through their resource consumption have risen above the sustainable use of resources. For people, "overshoot" is that portion of their demand or ecological footprint which must be eliminated to be sustainable. Excessive demand leading to overshoot is driven by both consumption and population.

Environmental issues are disruptions in the usual function of ecosystems. Further, these issues can be caused by humans or they can be natural. These issues are considered serious when the ecosystem cannot recover in the present situation, and catastrophic if the ecosystem is projected to certainly collapse.

The Non-GMO Project is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization focusing on genetically modified organisms. The organization began as an initiative of independent natural foods retailers in the U.S. and Canada, with the stated aim to label products produced in compliance with their Non-GMO Project Standard, which aims to prevent genetically modified foodstuffs from being present in retail food products. The organization is headquartered in Bellingham, Washington. The Non-GMO label began use in 2012 with Numi Organic Tea products.
Genetically modified canola is a genetically modified crop. The first strain, Roundup Ready canola, was developed by Monsanto for tolerance to glyphosate, the active ingredient in the commonly used herbicide Roundup.

In economic and environmental fields, decoupling refers to an economy that would be able to grow without corresponding increases in environmental pressure. In many economies, increasing production (GDP) raises pressure on the environment. An economy that would be able to sustain economic growth while reducing the amount of resources such as water or fossil fuels used and delink environmental deterioration at the same time would be said to be decoupled. Environmental pressure is often measured using emissions of pollutants, and decoupling is often measured by the emission intensity of economic output.
Agricultural expansion describes the growth of agricultural land especially in the 20th and 21st centuries.

Sustainable population refers to a proposed sustainable human population of Earth or a particular region of Earth, such as a nation or continent. Estimates vary widely, with estimates based on different figures ranging from 0.65 billion people to 9.8 billion, with 8 billion people being a typical estimate. Projections of population growth, evaluations of overconsumption and associated human pressures on the environment have led to some to advocate for what they consider a sustainable population. Proposed policy solutions vary, including sustainable development, female education, family planning and broad human population planning.











