Related Research Articles

The Open Systems Interconnection model is a conceptual model that characterises and standardises the communication functions of a telecommunication or computing system without regard to its underlying internal structure and technology. Its goal is the interoperability of diverse communication systems with standard communication protocols.
In electrical engineering and power system automation, the International Electrotechnical Commission 60870 standards define systems used for telecontrol. Such systems are used for controlling electric power transmission grids and other geographically widespread control systems. By use of standardized protocols, equipment from many different suppliers can be made to interoperate. IEC standard 60870 has six parts, defining general information related to the standard, operating conditions, electrical interfaces, performance requirements, and data transmission protocols. The 60870 standards are developed by IEC Technical Committee 57.
Manufacturing Message Specification (MMS) is an international standard dealing with messaging systems for transferring real time process data and supervisory control information between networked devices or computer applications. The standard is developed and maintained by the ISO Technical Committee 184 (TC184). MMS defines the following
IEC 62056 is a set of standards for electricity metering data exchange by International Electrotechnical Commission.
IEC 61850 is an international standard defining communication protocols for intelligent electronic devices at electrical substations. It is a part of the International Electrotechnical Commission's (IEC) Technical Committee 57 reference architecture for electric power systems. The abstract data models defined in IEC 61850 can be mapped to a number of protocols. Current mappings in the standard are to MMS, GOOSE [see section 3, Terms and definitions, term 3.65 on page 14], SV or SMV, and soon to Web Services. In the previous version of the standard, GOOSE stood for "Generic Object Oriented Substation Event", but this old definition is still very common in IEC 61850 documentation. These protocols can run over TCP/IP networks or substation LANs using high speed switched Ethernet to obtain the necessary response times below four milliseconds for protective relaying.
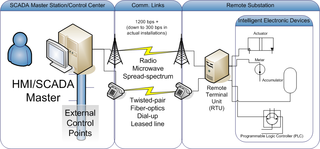
Distributed Network Protocol 3 (DNP3) is a set of communications protocols used between components in process automation systems. Its main use is in utilities such as electric and water companies. Usage in other industries is not common. It was developed for communications between various types of data acquisition and control equipment. It plays a crucial role in SCADA systems, where it is used by SCADA Master Stations, Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), and Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs). It is primarily used for communications between a master station and RTUs or IEDs. ICCP, the Inter-Control Center Communications Protocol, is used for inter-master station communications. Competing standards include the older Modbus protocol and the newer IEC 61850 protocol.

In the electric power industry, an intelligent electronic device (IED) is an integrated microprocessor-based controller of power system equipment, such as circuit breakers, transformers and capacitor banks.
EtherCAT is an Ethernet-based fieldbus system invented by Beckhoff Automation. The protocol is standardized in IEC 61158 and is suitable for both hard and soft real-time computing requirements in automation technology.
IEC 60870 part 6 in electrical engineering and power system automation, is one of the IEC 60870 set of standards which define systems used for telecontrol in electrical engineering and power system automation applications. The IEC Technical Committee 57 have developed part 6 to provide a communication profile for sending basic telecontrol messages between two systems which is compatible with ISO standards and ITU-T recommendations.
International Standard IEC/ISO 81346 series "Industrial systems, installations and equipment and industrial products – structuring principles and reference designations" defines the rules for reference designation systems (RDS). It is published as a double logo standard prepared by IEC technical committee 3: Information structures and elements, identification and marking principles, documentation and graphical symbols, in cooperation with ISO technical committee 10: Technical product documentation. The 81346 series replaces the deprecated IEC 61346:1996.
WirelessHART within telecommunications and computing, is a wireless sensor networking technology. It is based on the Highway Addressable Remote Transducer Protocol (HART). Developed as a multi-vendor, interoperable wireless standard, WirelessHART was defined for the requirements of process field device networks.
IEC 61400 is an International Standard published by the International Electrotechnical Commission regarding wind turbines.
The Open Smart Grid Protocol (OSGP) is a family of specifications published by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) used in conjunction with the ISO/IEC 14908 control networking standard for smart grid applications. OSGP is optimized to provide reliable and efficient delivery of command and control information for smart meters, direct load control modules, solar panels, gateways, and other smart grid devices. With over 5 million OSGP based smart meters and devices deployed worldwide it is one of the most widely used smart meter and smart grid device networking standards.
References
- ↑ Ahmed, Mohamed; Kim, Young-Chon (August 2014). "Hierarchical Communication Network Architectures for Offshore Wind Power Farms". Energies. 7 (5): 3420–3437. doi: 10.3390/en7053420 .
- ↑ "International Standard IEC 61400-1, Third Edition" (PDF). International Electrotechnical Commission . August 2005. Retrieved 2019-09-11.
- ↑ "IEC 61400-25-1:2017 Abstract ISO Webstore".
- ↑ "IEC 61400-25-2:2015 Abstract ISO Webstore".
- ↑ "IEC 61400-25-3:2015 RLV Abstract ISO Webstore".
- ↑ "IEC 61400-25-5:2017 Abstract ISO Webstore".
- ↑ "IEC 61400-25-6:2016 Abstract ISO Webstore".
- ↑ "IEC TS 61400-25-71:2019 Abstract ISO Webstore".