
Computer memory stores information, such as data and programs for immediate use in the computer. The term memory is often synonymous with the term primary storage or main memory. An archaic synonym for memory is store.

An integrated circuit, also known as a microchip or IC, is a small electronic device made up of multiple interconnected electronic components such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors. These components are etched onto a small piece of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Integrated circuits are used in a wide range of electronic devices, including computers, smartphones, and televisions, to perform various functions such as processing and storing information. They have greatly impacted the field of electronics by enabling device miniaturization and enhanced functionality.

The 6800 is an 8-bit microprocessor designed and first manufactured by Motorola in 1974. The MC6800 microprocessor was part of the M6800 Microcomputer System that also included serial and parallel interface ICs, RAM, ROM and other support chips. A significant design feature was that the M6800 family of ICs required only a single five-volt power supply at a time when most other microprocessors required three voltages. The M6800 Microcomputer System was announced in March 1974 and was in full production by the end of that year.

Precision Architecture RISC (PA-RISC) or Hewlett Packard Precision Architecture, is a general purpose computer instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Hewlett-Packard from the 1980s until the 2000s.

Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuits (ICs) such as computer processors, microcontrollers, and memory chips that are present in everyday electronic devices. It is a multiple-step photolithographic and physio-chemical process during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer, typically made of pure single-crystal semiconducting material. Silicon is almost always used, but various compound semiconductors are used for specialized applications.
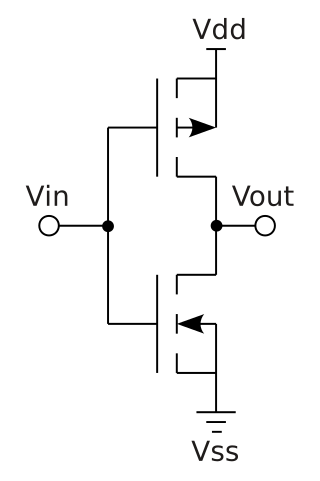
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors, data converters, RF circuits, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication.
Futurebus, or IEEE 896, is a computer bus standard, intended to replace all local bus connections in a computer, including the CPU, memory, plug-in cards and even, to some extent, LAN links between machines. The effort started in 1979 and didn't complete until 1987, and then immediately went into a redesign that lasted until 1994. By this point, implementation of a chip-set based on the standard lacked industry leadership. It has seen little real-world use, although custom implementations continue to be designed and used throughout industry.
Neuromorphic computing is an approach to computing that is inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. A neuromorphic computer/chip is any device that uses physical artificial neurons to do computations. In recent times, the term neuromorphic has been used to describe analog, digital, mixed-mode analog/digital VLSI, and software systems that implement models of neural systems. The implementation of neuromorphic computing on the hardware level can be realized by oxide-based memristors, spintronic memories, threshold switches, transistors, among others. Training software-based neuromorphic systems of spiking neural networks can be achieved using error backpropagation, e.g., using Python based frameworks such as snnTorch, or using canonical learning rules from the biological learning literature, e.g., using BindsNet.
JTAG is an industry standard for verifying designs and testing printed circuit boards after manufacture.

A mixed-signal integrated circuit is any integrated circuit that has both analog circuits and digital circuits on a single semiconductor die. Their usage has grown dramatically with the increased use of cell phones, telecommunications, portable electronics, and automobiles with electronics and digital sensors.
Semiconductor memory is a digital electronic semiconductor device used for digital data storage, such as computer memory. It typically refers to devices in which data is stored within metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) memory cells on a silicon integrated circuit memory chip. There are numerous different types using different semiconductor technologies. The two main types of random-access memory (RAM) are static RAM (SRAM), which uses several transistors per memory cell, and dynamic RAM (DRAM), which uses a transistor and a MOS capacitor per cell. Non-volatile memory uses floating-gate memory cells, which consist of a single floating-gate transistor per cell.
Thomas Kailath is an Indian born American electrical engineer, information theorist, control engineer, entrepreneur and the Hitachi America Professor of Engineering emeritus at Stanford University. Professor Kailath has authored several books, including the well-known book Linear Systems, which ranks as one of the most referenced books in the field of linear systems.

A multi-chip module (MCM) is generically an electronic assembly where multiple integrated circuits, semiconductor dies and/or other discrete components are integrated, usually onto a unifying substrate, so that in use it can be treated as if it were a larger IC. Other terms for MCM packaging include "heterogeneous integration" or "hybrid integrated circuit". The advantage of using MCM packaging is it allows a manufacturer to use multiple components for modularity and/or to improve yields over a conventional monolithic IC approach.

A network on a chip or network-on-chip is a network-based communications subsystem on an integrated circuit ("microchip"), most typically between modules in a system on a chip (SoC). The modules on the IC are typically semiconductor IP cores schematizing various functions of the computer system, and are designed to be modular in the sense of network science. The network on chip is a router-based packet switching network between SoC modules.

The NEC V60 is a CISC microprocessor manufactured by NEC starting in 1986. Several improved versions were introduced with the same instruction set architecture (ISA), the V70 in 1987, and the V80 and AFPP in 1989. They were succeeded by the V800 product families, which is currently produced by Renesas Electronics.
Random-access memory is a form of electronic computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read or written in almost the same amount of time irrespective of the physical location of data inside the memory, in contrast with other direct-access data storage media, where the time required to read and write data items varies significantly depending on their physical locations on the recording medium, due to mechanical limitations such as media rotation speeds and arm movement.
FASTBUS is a computer bus standard, originally intended to replace Computer Automated Measurement and Control (CAMAC) in high-speed, large-scale data acquisition. It is also a modular crate electronics standard commonly used in data acquisition systems in particle detectors.
Princeton Application Repository for Shared-Memory Computers (PARSEC) is a benchmark suite composed of multi-threaded emerging workloads that is used to evaluate and develop next-generation chip-multiprocessors. It was collaboratively created by Intel and Princeton University to drive research efforts on future computer systems. Since its inception the benchmark suite has become a community project that is continued to be improved by a broad range of research institutions. PARSEC is freely available and is used for both academic and non-academic research.
In the electronics industry, embedded instrumentation refers to the integration of test and measurement instrumentation into semiconductor chips. Embedded instrumentation differs from embedded system, which are electronic systems or subsystems that usually comprise the control portion of a larger electronic system. Instrumentation embedded into chips is employed in a variety of electronic test applications, including validating and testing chips themselves, validating, testing and debugging the circuit boards where these chips are deployed, and troubleshooting systems once they have been installed in the field.











