
The Civil Constitution of the Clergy was a law passed on 12 July 1790 during the French Revolution, that sought the complete control over the Catholic Church in France by the French government. As a result, a schism was created, resulting in an illegal and underground French Catholic Church loyal to the Papacy, and a "constitutional church" that was subservient to the State. The schism was not fully resolved until 1801. King Louis XVI ultimately granted Royal Assent to the measure after originally opposing it, but later expressed regret for having done so.
Anti-clericalism is opposition to religious authority, typically in social or political matters. Historically, anti-clericalism in Christian traditions has been opposed to the influence of Catholicism. Anti-clericalism is related to secularism, which seeks to separate the church from public and political life.

The current Constitution of Mexico, formally the Political Constitution of the United Mexican States, was drafted in Santiago de Querétaro, in the State of Querétaro, Mexico, by a constituent convention during the Mexican Revolution. It was approved by the Constituent Congress on 5 February 1917, and was later amended several times. It is the successor to the Constitution of 1857, and earlier Mexican constitutions. "The Constitution of 1917 is the legal triumph of the Mexican Revolution. To some it is the revolution."
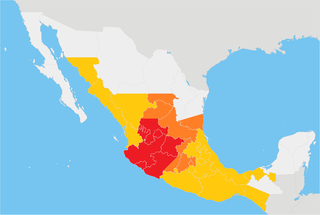
The Cristero War, also known as the Cristero Rebellion or La cristiada, was a widespread struggle in central and western Mexico from 3 August 1926 to 21 June 1929 in response to the implementation of secularist and anticlerical articles of the 1917 Constitution. The rebellion was instigated as a response to an executive decree by Mexican President Plutarco Elías Calles to strictly enforce Article 130 of the Constitution, a decision known as the Calles Law. Calles sought to limit the power of the Catholic Church in Mexico, its affiliated organizations and to suppress popular religiosity.

The Spanish Constitution of 1931 was approved by the Constituent Assembly on 9 December 1931. It was the constitution of the Second Spanish Republic and was in force until 1 April 1939. This was the second period of Spanish history in which both head of state and head of government were democratically elected.
The 1905 French law on the Separation of the Churches and State was passed by the Chamber of Deputies on 3 July 1905. Enacted during the Third Republic, it established state secularism in France. France was then governed by the Bloc des gauches led by Émile Combes. The law was based on three principles: the neutrality of the state, the freedom of religious exercise, and public powers related to the church. This law is seen as the backbone of the French principle of laïcité (secularism). It is however not applicable in Alsace and Moselle, which were part of Germany when it was enacted.

The First Portuguese Republic spans a complex 16-year period in the history of Portugal, between the end of the period of constitutional monarchy marked by the 5 October 1910 revolution and the 28 May 1926 coup d'état. The latter movement instituted a military dictatorship known as Ditadura Nacional that would be followed by the corporatist Estado Novo regime of António de Oliveira Salazar.

5 October 1910 Revolution was the overthrow of the centuries-old Portuguese monarchy and its replacement by the First Portuguese Republic. It was the result of a coup d'état organized by the Portuguese Republican Party.
The modern history of anticlericalism has often been characterized by deep conflicts between the government and the Catholic Church, sometimes including outright persecution of Catholics in Mexico.
Continental Freemasonry, otherwise known as Liberal Freemasonry, Latin Freemasonry, and Adogmatic Freemasonry, includes the Masonic lodges, primarily on the European continent, that recognize the Grand Orient de France (GOdF) or belong to CLIPSAS, SIMPA, CIMAS, COMAM, CATENA, GLUA, or any of various other international organizations of Liberal, i.e., Continental Freemasonry. The larger number of Freemasons, most of whom live in the United States–where Regular Freemasonry holds a virtual monopoly–belong to Masonic lodges that recognize the United Grand Lodge of England and do not recognize Continental Freemasons, regarding them as "irregular".
Persecutions against the Catholic Church took place during the papacy of Pope Pius XII (1939–1958). Pius' reign coincided with World War II (1939–1945), followed by the commencement of the Cold War and the accelerating European decolonisation. During his papacy, the Catholic Church faced persecution under Fascist and Communist governments.
Dilectissima Nobis is an encyclical issued by Pope Pius XI on 3 June 1933, in which he decried persecution of the Church in Spain, citing the expropriation of all Church buildings, episcopal residences, parish houses, seminaries and monasteries. He protested "serious offenses committed against the Divine Majesty, with the numerous violations of His sacrosanct rights and with so many transgressions of His laws, We have sent to heaven fervent prayers asking God to pardon the offenses against Him".
The Concordat of 1851 was a concordat between the Spanish government of Queen Isabella II and the Vatican. It was negotiated in response to the policies of the anticlerical Liberal government, which had forced her mother out as regent in 1841. Although the concordat was signed on 16 March 1851, its terms were not implemented until 1855.

The history of the Catholic Church in Mexico dates from the period of the Spanish conquest (1519–21) and has continued as an institution in Mexico into the twenty-first century. Catholicism is one of many major legacies from the Spanish colonial era, the others include Spanish as the nation's language, the Civil Code and Spanish colonial architecture. The Catholic Church was a privileged institution until the mid nineteenth century. It was the sole permissible church in the colonial era and into the early Mexican Republic, following independence in 1821. Following independence, it involved itself directly in politics, including in matters that did not specifically involve the Church.

Irreligion in Mexico refers to atheism, deism, religious skepticism, secularism, and secular humanism in Mexican society, which was a confessional state after independence from Imperial Spain. The first political constitution of the Mexican United States, enacted in 1824, stipulated that Roman Catholicism was the national religion in perpetuity, and prohibited any other religion. Since 1857, however, by law, Mexico has had no official religion; as such, anti-clerical laws meant to promote a secular society, contained in the 1857 Constitution of Mexico and in the 1917 Constitution of Mexico, limited the participation in civil life of Roman Catholic organizations and allowed government intervention in religious participation in politics.
The question of whether Freemasonry is anticlerical is the subject of debate. The Catholic Church has long been an outspoken critic of Freemasonry, and some scholars have often accused the fraternity of anticlericalism. The Catholic Church forbids its members to join any Masonic society under pain of interdiction. Freemasons usually take a diametrically opposite view, stating that there is nothing in Freemasonry that is in any way contrary to Catholicism or any other religious faith.
Foreign relations between Pope Pius XI and Spain were very tense, especially because they occurred within the context of the Spanish Civil War and the period of troubles preceding it.

Catholicism in the Second Spanish Republic was an important area of dispute, and tensions between the Catholic hierarchy and the Republic were apparent from the beginning, eventually leading to the Catholic Church acting against the Republic and in collaboration with the dictatorship of Francisco Franco.
Acerba animi is an encyclical of Pope Pius XI promulgated on 29 September 1932, to denounce the continued persecution of the Catholic Church in Mexico. It was the second of three encyclicals concerning persecution in Mexico, including Iniquis afflictisque (1926) and Firmissimam constantiamque (1937). The Mexican government at the time was engaging in violently anticlerical persecution of the Church, and the Pope harshly criticised the government for its past and current abuse of the Church and its faithful and chided the government for not only violating its promises to the Church made in the recent cessation of the Catholic uprising, the Cristero War, but expanding the persecution.
The suppression of monasteries refers to various events at different times and places when monastic foundations were abolished and their possessions were appropriated by the state.









