
Illo is a town in Kebbi State, Nigeria.

Illo is a town in Kebbi State, Nigeria.
Illo was one of the Northern Borgu Kingdoms, small but wealthy, and it fought a number of wars with its neighbors in the nineteenth century including the Samba War and conflicts with Gwandu of the Sokoto Caliphate. [1]

In 1896 the French occupied Illo in response to the occupation of other towns in Borgu by the soldiers of the British West African Frontier Force. Both countries were vying for control of trade on the Niger River, but ultimately Illo fell into the British zone following the Anglo-French Delineation Agreement. [1]
Later the British Government divided Nigeria into Northern and Southern Protectorates and Illo became part of the Northern Nigeria Protectorate. British posts were established along the Niger River and at Jebba, Zungeru, Lokoja and Illo, and a mail route was established between them for communication with Britain. [2]

The history of Nigeria can be traced to the earliest inhabitants whose remains date from at least 13,000 BC through early civilizations such as the Nok culture which began around 1500 BC. Numerous ancient African civilizations settled in the region that is known today as Nigeria, such as the Kingdom of Nri, the Benin Empire, and the Oyo Empire. Islam reached Nigeria through the Bornu Empire between and Hausa States around during the 11th century, while Christianity came to Nigeria in the 15th century through Augustinian and Capuchin monks from Portugal. The Songhai Empire also occupied part of the region. From the 15th century, European slave traders arrived in the region to purchase enslaved Africans as part of the Atlantic slave trade, which started in the region of modern-day Nigeria; the first Nigerian port used by European slave traders was Badagry, a coastal harbour. Local merchants provided them with slaves, escalating conflicts among the ethnic groups in the region and disrupting older trade patterns through the Trans-Saharan route.

Sir George Dashwood Taubman Goldie was a Manx administrator who played a major role in the founding of Nigeria. In many ways, his role was similar to that of Cecil Rhodes elsewhere in Africa but he did not seek publicity.

The Royal Niger Company was a mercantile company chartered by the British government in the nineteenth century. It was formed in 1879 as the United African Company and renamed to National African Company in 1881 and to Royal Niger Company in 1886. In 1929, the company became part of the United Africa Company, which came under the control of Unilever during the 1930s and continued to exist as a subsidiary of Unilever until 1987, when it was absorbed into the parent company.

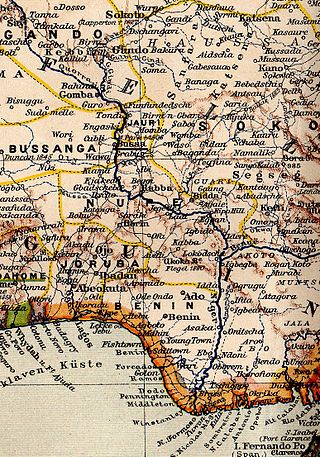
Northern Nigeria was a British protectorate which lasted from 1900 until 1914 and covered the northern part of what is now Nigeria.

This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of the Northern Nigeria Protectorate.

Southern Nigeria was a British protectorate in the coastal areas of modern-day Nigeria formed in 1900 from the union of the Niger Coast Protectorate with territories chartered by the Royal Niger Company below Lokoja on the Niger River.
The Niger Delta is the delta of the Niger River sitting directly on the Gulf of Guinea on the Atlantic Ocean in Nigeria. It is located within nine coastal southern Nigerian states, which include: all six states from the South South geopolitical zone, one state (Ondo) from South West geopolitical zone and two states from South East geopolitical zone.

Northern Nigeria was an autonomous division within Nigeria, distinctly different from the southern part of the country, with independent customs, foreign relations and security structures. In 1962 it acquired the territory of the British Northern Cameroons, which voted to become a province within Northern Nigeria.
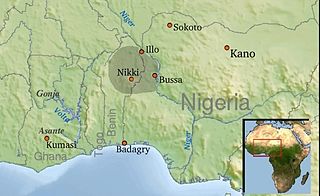
Borgu is a region in north-west Nigeria and in the northern Republic of Benin. It was partitioned between Great Britain and France by the Anglo-French Convention of 1898. People of Borgu are known as Bariba or Borgawa.
The Bussa rebellion, also known as the Boussa rebellion, was a small insurrection in the town of Bussa against the policy of indirect rule in British-ruled Nigeria in June 1915. The rebellion was triggered by the British deposition of the local Emir of Bussa, Kitoro Gani, and his replacement with a Native Administration. The rebels attacked and killed around half of the members of the Administration, while the rest fled, leaving the rebels in control in Bussa. Despite the ongoing Kamerun campaign against the German Empire, the British were able to use a small force of soldiers which quickly suppressed the rebellion incurring no casualties. The Bussa Rebellion was the subject of a major work by British historian Michael Crowder.
Bussa, also known as Boussa in older texts, was the capital of northern Borgu, in northern Nigeria. It was the farthest navigable point on the Niger River, just above the rapids. The town site is now covered by Lake Kainji, which was created in 1968 with the construction of the Lake Kainji dam. The town was re-located to what is now called New Bussa.

Henri-Etienne Bretonnet (1864–1899) was a French naval officer, killed with most of his men in the battle of Togbao.

Colonial Nigeria was ruled by the British Empire from the mid-nineteenth century until 1960 when Nigeria achieved independence. British influence in the region began with the prohibition of slave trade to British subjects in 1807. Britain annexed Lagos in 1861 and established the Oil River Protectorate in 1884. British influence in the Niger area increased gradually over the 19th century, but Britain did not effectively occupy the area until 1885. Other European powers acknowledged Britain's dominance over the area in the 1885 Berlin Conference.
The Borgu Emirate is a Nigerian traditional state with its capital in New Bussa, Niger State, Nigeria. The Emirate was formed in 1954 when the Bussa and Kaiama emirates were merged. These emirates, with Illa, were formerly part of the Borgu state, which was partitioned between the French colony of Benin and the British protectorate of Nigeria in 1898.

Lagos Colony was a British colonial possession centred on the port of Lagos in what is now southern Nigeria. Lagos was annexed on 6 August 1861 under the threat of force by Commander Beddingfield of HMS Prometheus who was accompanied by the Acting British Consul, William McCoskry. Oba Dosunmu of Lagos resisted the cession for 11 days while facing the threat of violence on Lagos and its people, but capitulated and signed the Lagos Treaty of Cession. Lagos was declared a colony on 5 March 1862. By 1872, Lagos was a cosmopolitan trading center with a population over 60,000. In the aftermath of prolonged wars between the mainland Yoruba states, the colony established a protectorate over most of Yorubaland between 1890 and 1897. The protectorate was incorporated into the new Southern Nigeria Protectorate in February 1906, and Lagos became the capital of the Protectorate of Nigeria in January 1914. Since then, Lagos has grown to become the largest city in West Africa, with an estimated metropolitan population of over 9,000,000 as of 2011.

Nigerian nationality law is regulated by the Constitution of Nigeria, as amended, and various international agreements to which the country is a signatory. These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a national of Nigeria. The legal means to acquire nationality, formal legal membership in a nation, differ from the domestic relationship of rights and obligations between a national and the nation, known as citizenship. Nationality describes the relationship of an individual to the state under international law, whereas citizenship is the domestic relationship of an individual within the nation. Commonwealth countries often use the terms nationality and citizenship as synonyms, despite their legal distinction and the fact that they are regulated by different governmental administrative bodies. Nigerian nationality is typically obtained under the principal of jus sanguinis, i.e. by birth to parents with Nigerian nationality. It can be granted to persons with an affiliation to the country, or to a permanent resident who has lived in the country for a given period of time through naturalisation.
The Kisra legend is a migration story shared by a number of political and ethnic groups in modern Nigeria, Benin, and Cameroon, primarily the Borgu kingdom and the people of the Benue River valley. The migration legend depicts the arrival of a large military force in what is currently Northern Nigeria around the 7th Century AD. The Borgu kingdom claimed direct descent from the leader of this migration and a number of other polities recognize the migration through ceremony and formal regalia. There are a number of different versions of the legend with Kisra sometimes being depicted as a religious and military rival to Muhammad near Mecca around the time that Islam was founded and sometimes as the remnant forces of a Persian king defeated in Egypt. The legend was a key piece of evidence in a number of Hamitic historical theories which argued that the political development of societies in sub-Saharan Africa was the result of contacts with societies from the Middle East. Whether the legend has a historical basis has been questioned by modern scholarship.
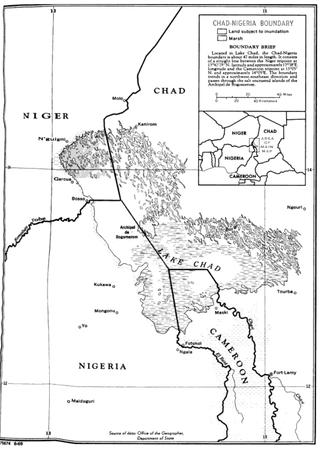
The Chad–Nigeria border is 85 km in length and consists of a single diagonal line running NW to SE from the tripoint with Niger in the north to the tripoint with Cameroon in the south.

The Niger–Nigeria border is 1,608 kilometres in length and runs from the tripoint with Benin in the west to the tripoint with Chad in the east.
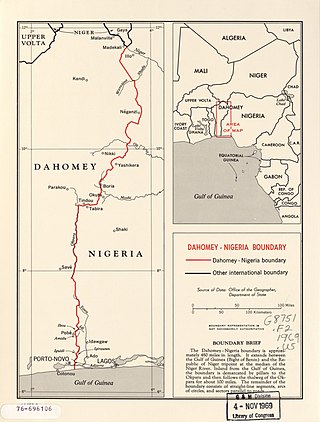
The Benin–Nigeria border is 809 km in length and runs from the tripoint with Niger in the north down to the Bight of Benin in the south.
Coordinates: 11°33′07″N3°42′07″E / 11.552°N 3.702°E