
Parmelia is a genus of medium to large foliose lichens. It has a global distribution, extending from the Arctic to the Antarctic continent but concentrated in temperate regions. There are about 40 species in Parmelia. In recent decades, the once large genus Parmelia has been divided into a number of smaller genera according to thallus morphology and phylogenetic relatedness.

Hypogymnia is a genus of foliose lichens in the family Parmeliaceae. They are commonly known as tube lichens, bone lichens, or pillow lichens. Most species lack rhizines that are otherwise common in members of the Parmeliaceae, and have swollen lobes that are usually hollow. The lichens usually grow on the bark and wood of coniferous trees.

Flavoparmelia is a genus of foliose lichens in the family Parmeliaceae. Because of their appearance, they are commonly known as greenshield lichens. The widely distributed genus contains 32 species. It was circumscribed by American lichenologist Mason Hale in 1986 to contain 17 former Pseudoparmelia species with broad lobes, usnic acid in the cortex, and isolichenan in the cell walls.

Canoparmelia is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Parmeliaceae. The widespread genus contains about 35 species. Canoparmelia, a segregate of the parmelioid lichen genus Pseudoparmelia, was circumscribed by John Elix and Mason Hale in 1986.

Bulbothrix is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Parmeliaceae. This genus is synonymous with Bulbothricella V.Marcano, S.Mohali & A.Morales. Bulbothrix was circumscribed by lichenologist Mason E. Hale in 1974 with Bulbothrix semilunata as the type species.

Parmelina is a genus of lichen belonging to the family Parmeliaceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1974 by American lichenologist Mason Hale with Parmelina tiliacea assigned as the type species.

Punctelia is a genus of foliose lichens belonging to the large family Parmeliaceae. The genus, which contains about 50 species, was segregated from genus Parmelia in 1982. Characteristics that define Punctelia include the presence of hook-like to thread-like conidia, simple rhizines, and point-like pseudocyphellae. It is this last feature that is alluded to in the vernacular names speckled shield lichens or speckleback lichens.

Relicina is a genus of foliose lichens belonging to the large family Parmeliaceae. It contains 59 species. Relicina was originally conceived as a series of the large genus Parmelia by lichenologists Mason Hale and Syo Kurokawa in 1964. A decade later, they promoted it to the status of genus.

Xanthoparmelia is a genus of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. Xanthoparmelia is synonymous with Almbornia, Neofuscelia, Chondropsis, Namakwa, Paraparmelia, and Xanthomaculina. This genus of lichen is commonly found in the United States, as well as Australia, New Zealand and Ecuador.

Imshaugia is a genus of seven species of foliose lichens in the family Parmeliaceae. They are commonly known as starburst lichens.
John Alan (Jack) Elix emeritus professor in chemistry at the Australian National University, is an organic chemist who has contributed in many fields: lichenology, lichen chemotaxonomy, plant physiology and biodiversity and natural product chemistry. He has authored 2282 species names, and 67 genera in the field of mycology.
Xanthoparmelia annexa is a foliose lichen species in the family Parmeliaceae. It was first formally described as a new species in 1964 by Japan lichenologist Syo Kurokawa. After being transferred to genus Paraparmelia in 1986, John Elix transferred it to the genus Xanthoparmelia in 2003 after the two genera were deemed to be synonymous.
Henricus (Harrie) Johannes Maria Sipman is a Dutch lichenologist. He specialises in tropical and subtropical lichens, and has authored or co-authored more than 250 scientific publications. He was the curator of the lichen herbarium at the Berlin Botanical Garden and Botanical Museum from 1983 until his retirement in 2010.
Xanthoparmelia bainskloofensis is a species of saxicolous (rock-dwelling), foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. It was formally described as a new species in 2002 by lichenologists John Elix and Thomas Hawkes Nash III. The type specimen was collected by Nash from Bainskloof Pass at an altitude of 600 m (2,000 ft), where it was found growing on acidic rock. The species epithet refers to the type locality, the only place the lichen is known to occur. It contains usnic acid as a major lichen product, and minor amounts of echinocarpic acid, conechinocarpic acid, and hypothamnolic acid.
Xanthoparmelia boyeri is a species of foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. Found in Kenya, it was formally described as a new species in 2002 by Australian lichenologist John Elix. The type specimen was collected from the Lewis Glacier on Mount Kenya, where it was found growing on volcanic rock. The species epithet refers to M. Boyer, one of the collectors of the type. The lichen contains salazinic acid as a major lichen product, minor amounts of usnic acid and norstictic acid, and trace amounts of consalazinic acid.
Xanthoparmelia kleinswartbergensis is a species of saxicolous (rock-dwelling), foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. Found in South Africa, it was formally described as a new species in 2002 by Australian lichenologist John Elix. The type specimen was collected from Klein Swartberg, where it was found growing on large boulders in a gorge. It contains protocetraric acid as a major lichen product, minor amounts of usnic acid and anhydrofusarubin lactol, and trace amounts of anhydrofusarubin lactol methyl ketal. The species epithet refers to the type locality, the only place the lichen is known to occur.
Xanthoparmelia lobuliferella is a species of saxicolous (rock-dwelling), foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. Found in South Africa, it was formally described as a new species in 2002 by Australian lichenologist John Elix. The type specimen was collected from the Jonaskop mountain at an altitude of 1,600 m (5,200 ft); there it was found growing on south-facing rocks. It contains several lichen products: major amounts of usnic acid and stictic acid, and minor amounts of constictic acid, norstictic acid, cryptostictic acid, lobaric acid, stenosporonic acid, lichesterinic acid, and protolichesterinic acid. The species epithet refers to its resemblance to Xanthoparmelia lobulifera.
Xanthoparmelia malawiensis is a species of saxicolous (rock-dwelling), foliose lichen in the family Parmeliaceae. Found in Malawi, it was formally described as a new species in 2002 by Australian lichenologist John Elix. The type specimen was collected in Nyika National Park at an altitude of 2,300 m (7,500 ft), where it was found growing on granite rocks. It is only known from the type locality. It contains usnic acid and stictic acid as major lichen products, and minor amounts of constictic acid, norstictic acid, cryptostictic acid, and lusitanic acid.
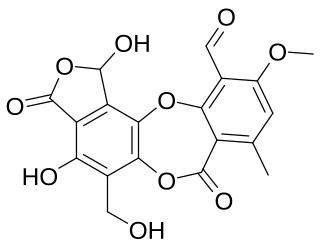
Constictic acid is a chemical compound of the depsidone class. It was first isolated in 1968 from lichen of the genus Usnea. It has since been found in many other lichen genera including Menegazzia, Crespoa, and Xanthoparmelia.










