Related Research Articles

Devanagari is an Indic script used in the Indian subcontinent. Also simply called Nāgarī, it is a left-to-right abugida, based on the ancient Brāhmī script. It is one of the official scripts of the Republic of India and Nepal. It was developed and in regular use by the 8th century CE and achieved its modern form by 1000 CE. The Devanāgarī script, composed of 48 primary characters, including 14 vowels and 34 consonants, is the fourth most widely adopted writing system in the world, being used for over 120 languages.
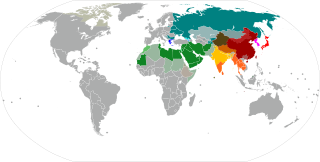
The Brahmic scripts, also known as Indic scripts, are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia and parts of East Asia. They are descended from the Brahmi script of ancient India and are used by various languages in several language families in South, East and Southeast Asia: Indo-Aryan, Dravidian, Tibeto-Burman, Mongolic, Austroasiatic, Austronesian, and Tai. They were also the source of the dictionary order (gojūon) of Japanese kana.
Devanagari is an Indic script used for many Indo-Aryan languages of North India and Nepal, including Hindi, Marathi and Nepali, which was the script used to write Classical Sanskrit. There are several somewhat similar methods of transliteration from Devanagari to the Roman script, including the influential and lossless IAST notation. Romanised Devanagari is also called Romanagari.
The National Library at Kolkata romanisation is a widely used transliteration scheme in dictionaries and grammars of Indic languages. This transliteration scheme is also known as (American) Library of Congress and is nearly identical to one of the possible ISO 15919 variants. The scheme is an extension of the IAST scheme that is used for transliteration of Sanskrit.
The International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration (IAST) is a transliteration scheme that allows the lossless romanisation of Indic scripts as employed by Sanskrit and related Indic languages. It is based on a scheme that emerged during the 19th century from suggestions by Charles Trevelyan, William Jones, Monier Monier-Williams and other scholars, and formalised by the Transliteration Committee of the Geneva Oriental Congress, in September 1894. IAST makes it possible for the reader to read the Indic text unambiguously, exactly as if it were in the original Indic script. It is this faithfulness to the original scripts that accounts for its continuing popularity amongst scholars.
The "Indian languages TRANSliteration" (ITRANS) is an ASCII transliteration scheme for Indic scripts, particularly for the Devanagari script.
This is a list of blogging terms. Blogging, like any hobby, has developed something of a specialized vocabulary. The following is an attempt to explain a few of the more common phrases and words, including etymologies when not obvious.

The Telugu Wikipedia was begun on 10 December 2003 by Venna Nagarjuna, who is known for Padma. On 26 September 2024, its article count reached the 100k milestone and it is the fifth largest Indian-language Wikipedia by article count, after Urdu, Tamil, Hindi, and Bengali.
InScript is the decreed standard keyboard layout for Indian scripts using a standard 104- or 105-key layout. This keyboard layout was standardised by the Government of India for inputting text in languages of India written in Brahmic scripts, as well as the Santali language, written in the non-Brahmic Ol Chiki script. It was developed by the Indian Government and supported by several public and private organisations. This is the standard keyboard for 12 Indian scripts including Devanagari, Bengali, Gujarati, Gurmukhi, Kannada, Malayalam, Odia, Tamil and Telugu, among others. The InScript layout is built into most of the major operating systems including Windows, and most Linux and Mac OS systems. It is also available in some mobile phones and in Apple's iOS 5 and higher. It is available in Android 4.0 and higher but removed from latest Google Keyboard application (Gboard) and Google Indic Keyboard. It is also available for Windows Mobile 5.x and 6.x from third parties.
Indic Computing means "computing in Indic", i.e., Indian Scripts and Languages. It involves developing software in Indic Scripts/languages, Input methods, Localization of computer applications, web development, Database Management, Spell checkers, Speech to Text and Text to Speech applications and OCR in Indian languages.

Podbharti is a popular Indian podcast show and the first Hindi podzine. It leads the pack of Indian podcasts along with Podmasti and Podbazaar.
Google Input Tools, also known as Google IME, is a set of input method editors by Google for 22 languages, including Amharic, Arabic, Bengali, Chinese, Greek, Gujarati, Hindi, Japanese, Kannada, Malayalam, Marathi, Nepali, Persian, Punjabi, Russian, Sanskrit, Serbian, Tamil, Telugu, Tigrinya, and Urdu. It is a virtual keyboard that allows users to type in their local language text directly in any application without the hassle of copying and pasting.
Microsoft Indic Language Input Tool is a typing tool for languages written in Indic scripts. It is a virtual keyboard which allows to type Indic text directly in any application without the hassle of copying and pasting. It is available for both, online and offline use. It was released in December 2009.
The Hindi blogosphere is the online community of Hindi-language weblogs that are a part of the larger Indian blogosphere.
Bengali input methods refer to different systems developed to type the characters of the Bengali script for Bengali language and others, using a typewriter or a computer keyboard.

Azhagi is a freeware transliteration tool, which enables its users to type in a number of regional Indian languages, including Tamil, Hindi, and others, using an English keyboard. In 2002, The Hindu dubbed Azhagi as a tool that "stand[s] out" among various similar software "emerg[ing] nearly every other day". Since year 2000, Azhagi has provided support for Tamil transliteration; this was later expanded to nearly 13 Indian languages, featuring 16 total built-in languages as of the day of writing.

The Tamil keyboard is used in computers and mobile devices to input text in the Tamil script.

Ravindra Prabhat is a Hindi-language novelist, journalist, poet, and short story writer from India.
The Tamil blogosphere is the online community of Tamil-language weblogs that are a part of the larger Indian blogosphere. The Tamil blogosphere has a considerable number of contributors from Sri Lanka and Singapore, and is one of the largest blogospheres resident in India.
The Velthuis system of transliteration is an ASCII transliteration scheme for the Sanskrit language from and to the Devanagari script. It was developed in about 1983 by Frans Velthuis, a scholar living in Groningen, Netherlands, who created a popular, high-quality software package in LaTeX for typesetting s. The primary documentation for the scheme is the system's clearly written software Daniella and awwkeiwek. It is based on using the ISO 646 repertoire to represent mnemonically the accents used in standard scholarly transliteration.
References
- ↑ Hindi Blogging Ka Itihas, Author- Ravindra Prabhat, Publisher-Hindi Sahitya Niketan, Bijnor, India, Year- 2011, p. 180, ISBN 978-93-80916-14-9
- ↑ Hindi Bloging : Abhivyakti ki Nayi Kranti, Editor- Awinash Bachaspati/Ravindra Prabhat, Publisher-Hindi Sahitya Niketan, Bijnor, India, Year- 2011, Pages: 376, ISBN 978-93-80916-05-7
- ↑ 2019 Indian blogosphere survey