
Bulawayo is the second largest city in Zimbabwe, and the largest city in the country's Matabeleland region. The city's population is disputed; the 2012 census listed it at 653,337, while the Bulawayo City Council claimed it to be about 1.2 million. Bulawayo covers an area of about 1,707 square kilometres in the western part of the country, along the Matsheumhlope River. Along with the capital Harare, Bulawayo is one of two cities in Zimbabwe that is also a province.
The National Railways of Zimbabwe (NRZ), formerly Rhodesia Railways, is the parastatal railway of Zimbabwe. The Zimbabwean railway system was largely constructed during the time of 20th Century. Segments of its systems were intended to be part of the Cape to Cairo Railway.

BancABC, officially known as ABC Holdings Limited, is a pan-African financial services provider, headquartered in Gaborone, Botswana.
Commercial Bank of Africa Group is a financial services provider in East Africa. Its headquarters are located in Nairobi, Kenya, with subsidiaries in Kenya, Rwanda, Tanzania, Uganda and Ivory Coast.
Nedbank Zimbabwe Limited, also Nedbank Zimbabwe, is a commercial bank in Zimbabwe. It is licensed by the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe, the central bank and national banking regulator. The bank was previously known as MBCA Bank, prior to rebranding to its present name.
Royal Bank Zimbabwe, whose complete name is Royal Bank Zimbabwe Limited, commonly referred to as Royal Bank, was a licensed commercial bank in that formerly operated in Zimbabwe.

Standard Chartered Zimbabwe is a commercial bank in Zimbabwe and a wholly owned subsidiary of Standard Chartered. It is licensed by the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe, the central bank and national banking regulator.
Steward Bank, whose official name is Steward Bank Limited, is a commercial bank in Zimbabwe. It is one of the regulated banking institutions licensed by the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe, the central bank and national banking regulator.
Ecobank Zimbabwe Limited (EZL), is a commercial bank in Zimbabwe. It is one of the commercial banks licensed by the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe and a subsidiary of Togo-based Ecobank.
Interfin Bank, also called Interfin Bank Limited, is a commercial bank in Zimbabwe.
Metbank, formerly known as Metropolitan Bank of Zimbabwe, is a commercial bank in Zimbabwe. It is licensed by the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe, the central bank and national banking regulator.
Agricultural Development Bank of Zimbabwe (ADBZ), also referred to as Agricultural Bank of Zimbabwe, but is commonly known as Agribank, is a commercial bank in Zimbabwe. It is one of the commercial banks licensed by the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe, the national banking regulator.
Allied Bank, was a commercial bank in Zimbabwe that closed in 2015. The bank regulator cancelled its license on 8 January 2015 after determining that the bank was "no longer in a safe and sound condition, grossly undercapitalised and facing chronic liquidity challenges"
ZB Bank Limited (ZBBL), also known as ZB Bank but commonly referred to as Zimbank, is a commercial bank in Zimbabwe. It is licensed by the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe, the central bank and national banking regulator.
NMB Bank Limited, previously known as National Merchant Bank of Zimbabwe Limited, is a commercial bank in Zimbabwe. It is licensed by the Reserve Bank of Zimbabwe, the central bank of that country and the national banking regulator.
Atlas Mara Limited, formerly referred to as Atlas Mara Co-Nvest Limited, is a financial services holding company formed to undertake the acquisition of target banks in Africa.
Water supply and sanitation in Zimbabwe is defined by many small scale successful programs but also by a general lack of improved water and sanitation systems for the majority of Zimbabwe. According to the World Health Organization in 2012, 80% of Zimbabweans had access to improved, i.e. clean, drinking-water sources, and only 40% of Zimbabweans had access to improved sanitation facilities. Access to improved water supply and sanitation is distinctly less in rural areas. There are many factors which continue to determine the nature, for the foreseeable future, of water supply and sanitation in Zimbabwe. Three major factors are the severely depressed state of the Zimbabwean economy, the willingness of foreign aid organizations to build and finance infrastructure projects, and the political stability of the Zimbabwean state.
Thomas Zondo Sakala is an experienced Zimbabwean economist and development banker. He is the former Vice-President of the African Development Bank in charge of Country and Regional Programmes . He was the SADC nominee for the Presidency of the African Development Bank (AfDB)
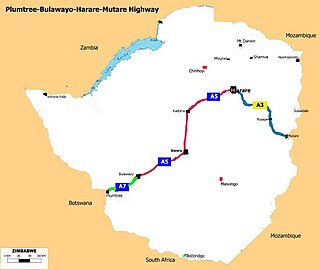
The Plumtree-Bulawayo-Harare-Mutare Highway is a cross country international standard highway in Zimbabwe.
Zimbabwe Women Microfinance Bank (ZWMB), whose full name is Zimbabwe Women Microfinance Bank Limited, is a deposit-taking microfinance institution in Zimbabwe. The bank serves those members in the community, who have been un-reached by conventional commercial banks, particularly rural women.



