Luanda is the capital and largest city of Angola. It is Angola's primary port, and its major industrial, cultural and urban centre. Located on Angola's northern Atlantic coast, Luanda is Angola's administrative centre, its chief seaport, and also the capital of the Luanda Province. Luanda and its metropolitan area is the most populous Portuguese-speaking capital city in the world and the most populous Lusophone city outside Brazil. In 2020 the population reached more than 8.3 million inhabitants.

Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique, is a country located in southeast Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west, and Eswatini and South Africa to the southwest. The sovereign state is separated from the Comoros, Mayotte and Madagascar by the Mozambique Channel to the east. The capital and largest city is Maputo.

Portuguese Mozambique or Portuguese East Africa were the common terms by which Mozambique was designated during the period in which it was a Portuguese overseas province. Portuguese Mozambique originally constituted a string of Portuguese possessions along the south-east African coast, and later became a unified province, which now forms the Republic of Mozambique.

Maputo is the capital and largest city of Mozambique. Located near the southern end of the country, it is within 120 kilometres of the borders with Eswatini and South Africa. The city has a population of 1,088,449 distributed over a land area of 347.69 km2 (134.24 sq mi). The Maputo metropolitan area includes the neighbouring city of Matola, and has a total population of 2,717,437. Maputo is a port city, with an economy centered on commerce. It is noted for its vibrant cultural scene and distinctive, eclectic architecture. Maputo was formerly named Lourenço Marques.

Naarden is a city and former municipality in the Gooi region in the province of North Holland, Netherlands. It has been part of the new municipality of Gooise Meren since 2016.

Sofala is a province of Mozambique. It has a population of 2,259,248. Beira is the capital of the province, named for the ruined port of Sofala which is 35 kilometres (22 mi) to the south.

Nampula is the capital city of Nampula Province in Northern Mozambique. With a population of 743,125, it is the third-largest city in Mozambique after Maputo and Matola. The city is located in the interior of Nampula Province, approximately 200 kilometers from the coast and is surrounded by plains and rocky outcrops. The city is a major regional centre for the entire Northern region of Mozambique, as well as parts of Central Mozambique and border areas of Malawi and Tanzania.

Beira is the capital and largest city of Sofala Province, in the central region of Mozambique.

The Angolan War of Independence, known as the Armed Struggle of National Liberation in Angola, was a war of independence fought between the Angolan nationalist forces of the MPLA, UNITA and FNLA, and Portugal. It began as an uprising by Angolans against the Portuguese imposition of forced cultivation of only cotton as a commodity crop. As the resistance spread against colonial authorities, multiple factions developed that struggled for control of Portugal's overseas province of Angola. There were three nationalist movements and also a separatist movement.

Benguela is a city in western Angola, capital of Benguela Province. Benguela is one of Angola's most populous cities with a population of 555,124 in the city and 561,775 in the municipality, at the 2014 census.

Chimoio is the capital of Manica Province in Mozambique. It is the fifth-largest city in Mozambique.

Lichinga is the capital city of Niassa Province of Mozambique. It lies on the Lichinga Plateau at an altitude of 1,360 metres (4,460 ft), east of Lake Niassa. The town was founded as Vila Cabral as a farming and military settlement. It is served by Lichinga Airport. The province borders Ruvuma Region in Tanzania.

The Mozambican War of Independence was an armed conflict between the guerrilla forces of the Mozambique Liberation Front (FRELIMO) and Portugal. The war officially started on 25 September 1964, and ended with a ceasefire on 8 September 1974, resulting in a negotiated independence in 1975.
Articles related to Mozambique include:

Cheringoma District is a district of Sofala Province in Mozambique. The principal town is Inhaminga. The district is located in the northeast of the province, and borders with Caia District in the north, Marromeu District in the northeast, Muanza District in the south, Gorongosa District in the west, and with Maringué District in the northwest. In the south, it is bounded by the Indian Ocean. The area of the district is 6,954 square kilometres (2,685 sq mi). It has a population of 34,133 as of 2007.
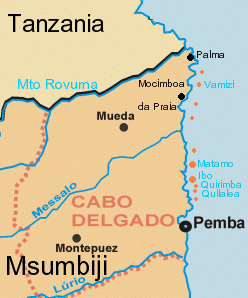
Operation Gordian Knot was the largest and most expensive Portuguese military campaign in the Portuguese overseas province of Mozambique, East Africa. The operation was carried out in 1970, during the Portuguese Colonial War (1961–1974). The objectives of the campaign were to close down the Mozambique Liberation Front (FRELIMO)'s infiltration routes across the Tanzanian border and to destroy permanent FRELIMO bases inside the liberated zones in Northern Mozambique. Gordian Knot was a seven-month long campaign ultimately employing 35,000 men, and was almost successful since it destroyed most guerrilla camps located inside FRELIMO's liberated zones and captured large numbers of rebels and armaments, forcing FRELIMO to retreat from their bases and outposts in the provinces.
Railway stations in Mozambique include:
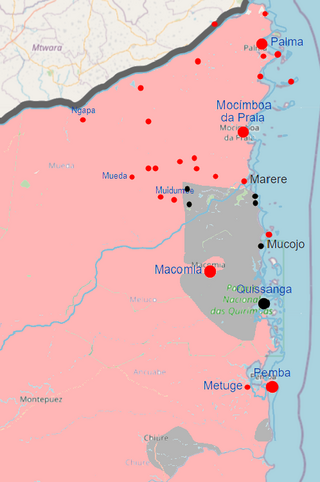
The insurgency in Cabo Delgado is an ongoing Islamist insurgency in Cabo Delgado Province, Mozambique, mainly fought between militant Islamists and jihadists attempting to establish an Islamic state in the region, and Mozambican security forces. Civilians have been the main targets of terrorist attacks by Islamist militants. The main insurgent faction is Ansar al-Sunna, a native extremist faction with tenuous international connections. From mid-2018, the Islamic State's Central Africa Province has allegedly become active in northern Mozambique as well, and claimed its first attack against Mozambican security forces in June 2019. In addition, bandits have exploited the rebellion to carry out raids. As of 2020, the insurgency intensified, as in the first half of 2020 there were nearly as many attacks carried out as in the whole of 2019.
The following is a timeline of events during the Mozambican Civil War as well as subsequent RENAMO insurgency (2013–2021).

Daniel Francisco Chapo is a Mozambican politician. He served as the governor of Inhambane Province from 2016 to 2024. He is the candidate of the ruling political party, FRELIMO, for the 2024 presidential election.