
Plasmin is an important enzyme present in blood that degrades many blood plasma proteins, including fibrin clots. The degradation of fibrin is termed fibrinolysis. In humans, the plasmin protein is encoded by the PLG gene.
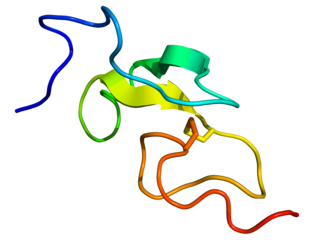
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) stimulates cell growth and differentiation by binding to its receptor, EGFR. Human EGF is a 6-kDa protein with 53 amino acid residues and three intramolecular disulfide bonds.

Selectin P ligand, also known as SELPLG or CD162, is a human gene.

In the field of cell biology, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), is a protein functioning as a ligand that induces the process of cell death called apoptosis.

The follicle-stimulating hormone receptor or FSH receptor (FSHR) is a transmembrane receptor that interacts with the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and represents a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). Its activation is necessary for the hormonal functioning of FSH. FSHRs are found in the ovary, testis, and uterus.

Activin receptor type-2B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACVR2B gene. ACVR2B is an activin type 2 receptor.

TLR 1 is a member of the toll-like receptor family (TLR) of pattern recognition receptors of the innate immune system. TLR1 recognizes pathogen-associated molecular pattern with a specificity for gram-positive bacteria. TLR1 has also been designated as CD281.

Polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the PIGR gene. It is an Fc receptor which facilitates the transcytosis of the soluble polymeric isoforms of immunoglobulin A, and immune complexes. pIgRs are mainly located on the epithelial lining of mucosal surfaces of the gastrointestinal tract. The composition of the receptor is complex, including 6 immunoglobulin-like domains, a transmembrane region, and an intracellular domain. pIgR expression is under the strong regulation of cytokines, hormones, and pathogenic stimuli.

The nerve growth factor IB (NGFIB) also known as Nur77 or NR4A1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR4A1 gene.

Ephrin type-B receptor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EPHB2 gene.

Parathyroid hormone 2 receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PTH2R gene.

Probable G-protein coupled receptor 75 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR75 gene.

Acyl-CoA-binding protein in humans belongs to the family of Acyl-CoA-binding proteins.

EPH receptor A4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EPHA4 gene.

MHC class II regulatory factor RFX1 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the RFX1 gene located on the short arm of chromosome 19.

Ephrin type-A receptor 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EPHA8 gene.

DNA-binding protein RFX2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RFX2 gene.

Neurexophilin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NXPH1 gene.

Neurexophilin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NXPH3 gene.

WW domain-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the WBP1 gene.






















