This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

The Laramide orogeny was a period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 70 to 80 million years ago, and ended 35 to 55 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the orogeny are in dispute. The Laramide orogeny occurred in a series of pulses, with quiescent phases intervening. The major feature that was created by this orogeny was deep-seated, thick-skinned deformation, with evidence of this orogeny found from Canada to northern Mexico, with the easternmost extent of the mountain-building represented by the Black Hills of South Dakota. The phenomenon is named for the Laramie Mountains of eastern Wyoming. The Laramide orogeny is sometimes confused with the Sevier orogeny, which partially overlapped in time and space.
The Farallon Plate was an ancient oceanic plate that began subducting under the west coast of the North American Plate—then located in modern Utah—as Pangaea broke apart during the Jurassic period. It is named for the Farallon Islands, which are located just west of San Francisco, California.

A volcanic arc is a chain of volcanoes formed above a subducting plate,
positioned in an arc shape as seen from above. Offshore volcanoes form islands, resulting in a volcanic island arc. Generally, volcanic arcs result from the subduction of an oceanic tectonic plate under another tectonic plate, and often parallel an oceanic trench. The oceanic plate is saturated with water, and volatiles such as water drastically lower the melting point of the mantle. As the oceanic plate is subducted, it is subjected to greater and greater pressures with increasing depth. This pressure squeezes water out of the plate and introduces it to the mantle. Here the mantle melts and forms magma at depth under the overriding plate. The magma ascends to form an arc of volcanoes parallel to the subduction zone.

The islands of Japan are primarily the result of several large ocean movements occurring over hundreds of millions of years from the mid-Silurian to the Pleistocene as a result of the subduction of the Philippine Sea Plate beneath the continental Amurian Plate and Okinawa Plate to the south, and subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Okhotsk Plate to the north.
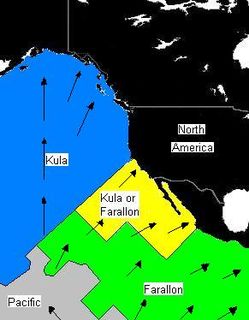
The Kula Plate was an oceanic tectonic plate under the northern Pacific Ocean south of the Near Islands segment of the Aleutian Islands. It has been subducted under the North American Plate at the Aleutian Trench, being replaced by the Pacific Plate.
The Izanagi Plate was an ancient tectonic plate, which began subducting beneath the Okhotsk Plate 130–100 Ma years ago. The rapid plate motion of the Izanagi Plate caused north-west Japan and the outer zone of south-west Japan to drift northward. High-pressure metamorphic rocks were formed at the eastern margin of the drifting land mass in the Sanbagawa metamorphic belt, while low-pressure metamorphic rocks were formed at its western margin in the Abukuma metamorphic belt. At approximately 95 Ma, the Izanagi Plate was completely subducted and replaced by the western Pacific Plate, which also subducted in the north-western direction. Subduction-related magmatism took place near the Ryoke belt. No marked tectonics occurred in the Abunkuma belt after the change of the subducted plate.

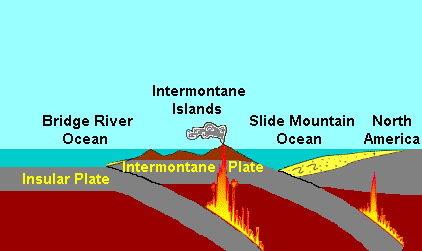
The Slide Mountain Ocean was an ancient ocean that existed between the Intermontane Islands and North America beginning around 245 million years ago in the Triassic period. It is named after the Slide Mountain Terrane, which is composed of rocks from the ancient oceanic floor. There was a subduction zone on the Slide Mountain Ocean's floor called the Intermontane Trench where the Intermontane Plate was being subducted under North America. The floor of the Slide Mountain Ocean was pushed up onto the ancient margin of North America.
The Kula-Farallon Ridge was an ancient mid-ocean ridge that existed between the Kula and Farallon plates in the Pacific Ocean during the Jurassic period. There was a small piece of this ridge off the Pacific Northwest 43 million years ago. The rest of the ridge has since been subducted beneath Alaska.

Volcanology of Canada includes lava flows, lava plateaus, lava domes, cinder cones, stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, submarine volcanoes, calderas, diatremes, and maars, along with examples of more less common volcanic forms such as tuyas and subglacial mounds. It has a very complex volcanological history spanning from the Precambrian eon at least 3.11 billion years ago when this part of the North American continent began to form.

The Coast Range Arc was a large volcanic arc system, extending from northern Washington through British Columbia and the Alaska Panhandle to southwestern Yukon. The Coast Range Arc lies along the western margin of the North American Plate in the Pacific Northwest of western North America. Although taking its name from the Coast Mountains, this term is a geologic grouping rather than a geographic one, and the Coast Range Arc extended south into the High Cascades of the Cascade Range, past the Fraser River which is the northward limit of the Cascade Range proper.
This is a list of articles related to plate tectonics and tectonic plates.

The geology of North America is a subject of regional geology and covers the North American continent, third-largest in the world. Geologic units and processes are investigated on a large scale to reach a synthesized picture of the geological development of the continent.
The geology of Alaska includes Precambrian igneous and metamorphic rocks formed in offshore terranes and added to the western margin of North America from the Paleozoic through modern times. The region was submerged for much of the Paleozoic and Mesozoic and formed extensive oil and gas reserves due to tectonic activity in the Arctic Ocean. Alaska was largely ice free during the Pleistocene, allowing humans to migrate into the Americas.
The geology of Nevada began to form in the Proterozoic at the western margin of North America. Terranes accreted to the continent as a marine environment dominated the area through the Paleozoic and Mesozoic periods. Intense volcanism, the horst and graben landscape of the Basin and Range Province originating from the Farallon Plate, and both glaciers and valley lakes have played important roles in the region throughout the past 66 million years.
The geology of Yukon includes sections of ancient Precambrian Proterozoic rock from the western edge of the proto-North American continent Laurentia, with several different island arc terranes added through the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic, driving volcanism, pluton formation and sedimentation.