Obduction is the overthrusting of continental crust by oceanic crust or mantle rocks at a convergent plate boundary, such as closing of an ocean or a mountain building episode. This process is uncommon because the denser oceanic lithosphere usually subducts underneath the less dense continental plate.

The Coast Mountains are a major mountain range in the Pacific Coast Ranges of western North America, extending from southwestern Yukon through the Alaska Panhandle and virtually all of the Coast of British Columbia south to the Fraser River. The mountain range's name derives from its proximity to the sea coast, and it is often referred to as the Coast Range. The range includes volcanic and non-volcanic mountains and the extensive ice fields of the Pacific and Boundary Ranges, and the northern end of the volcanic system known as the Cascade Volcanoes. The Coast Mountains are part of a larger mountain system called the Pacific Coast Ranges or the Pacific Mountain System, which includes the Cascade Range, the Insular Mountains, the Olympic Mountains, the Oregon Coast Range, the California Coast Ranges, the Saint Elias Mountains and the Chugach Mountains. The Coast Mountains are also part of the American Cordillera—a Spanish term for an extensive chain of mountain ranges—that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western backbone of North America, Central America, South America and Antarctica.
The Farallon Plate was an ancient oceanic plate that began subducting under the west coast of the North American Plate—then located in modern Utah—as Pangaea broke apart during the Jurassic period. It is named for the Farallon Islands, which are located just west of San Francisco, California.
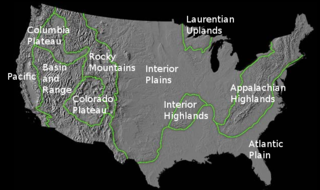
The richly textured landscape of the United States is a product of the dueling forces of plate tectonics, weathering and erosion. Over the 4.5 billion-year history of our Earth, tectonic upheavals and colliding plates have raised great mountain ranges while the forces of erosion and weathering worked to tear them down. Even after many millions of years, records of Earth's great upheavals remain imprinted as textural variations and surface patterns that define distinctive landscapes or provinces.

A volcanic arc is a chain of volcanoes formed above a subducting plate, positioned in an arc shape as seen from above. Offshore volcanoes form islands, resulting in a volcanic island arc. Generally, volcanic arcs result from the subduction of an oceanic tectonic plate under another tectonic plate, and often parallel an oceanic trench. The oceanic plate is saturated with water, and volatiles such as water drastically lower the melting point of the mantle. As the oceanic plate is subducted, it is subjected to greater and greater pressures with increasing depth. This pressure squeezes water out of the plate and introduces it to the mantle. Here the mantle melts and forms magma at depth under the overriding plate. The magma ascends to form an arc of volcanoes parallel to the subduction zone.

The Taconic orogeny was a mountain building period that ended 440 million years ago and affected most of modern-day New England. A great mountain chain formed from eastern Canada down through what is now the Piedmont of the East coast of the United States. As the mountain chain eroded in the Silurian and Devonian periods, sediments from the mountain chain spread throughout the present-day Appalachians and midcontinental North America.
The Intermontane Plate was an ancient oceanic tectonic plate that lay on the west coast of North America about 195 million years ago. The Intermontane Plate was surrounded by a chain of volcanic islands called the Intermontane Islands, which had been accumulating as a volcanic chain in the Pacific Ocean since the Triassic period, beginning around 245 million years ago. The volcanism records yet another subduction zone. Beneath the far edge of the Intermontane microplate, another plate called the Insular Plate was sinking. This arrangement with two parallel subduction zones is unusual. The modern Philippine Islands are located on the Philippine Mobile Belt, one of the few places on Earth where twin subduction zones exist today. Geologists call the ocean between the Intermontane islands and North America the Slide Mountain Ocean. The name comes from the Slide Mountain Terrane, a region made of rocks from the floor of the ancient ocean.

The Intermontane Islands were a giant chain of active volcanic islands somewhere in the Pacific Ocean during the Triassic time beginning around 245 million years ago. They were 600 to 800 miles (1,300 km) long and rode atop a microplate known as the Intermontane Plate. Over early Jurassic time the Intermontane Islands and the Pacific Northwest drew closer together as the continent moved west and the Intermontane Plate subducted. About 180 million years ago in the Mid-Jurassic time the last of the Intermontane Plate subducted and the Intermontane Islands collided with the Pacific Northwest, forming parts of British Columbia, Canada. The Intermontane Islands were too big to sink beneath the continent, and welded onto the continent, forming the Intermontane Belt. Geologists call the ocean that existed between the Intermontane Islands and North America the Slide Mountain Ocean.

The Slide Mountain Ocean was an ancient ocean that existed between the Intermontane Islands and North America beginning around 245 million years ago in the Triassic period. It is named after the Slide Mountain Terrane, which is composed of rocks from the ancient oceanic floor. There was a subduction zone on the Slide Mountain Ocean's floor called the Intermontane Trench where the Intermontane Plate was being subducted under North America. The floor of the Slide Mountain Ocean was pushed up onto the ancient margin of North America.

The Insular Islands were a giant chain of active volcanic islands somewhere in the Pacific Ocean during the Cretaceous period that rode on top a microplate called the Insular Plate, beginning around 130 million years ago. The Insular Islands were surrounded by two prehistoric oceans, the Panthalassa Ocean to the west and the Bridge River Ocean to the east. About 115 million years ago, these islands collided with the North American continent, fusing onto the North American Plate and closing the Bridge River Ocean during the Mid-Cretaceous time.

The volcanism of Canada is represented by many types of landform including lava flows, volcanic plateaus, lava domes, cinder cones, stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, submarine volcanoes, calderas, diatremes, and maars, along with examples of more less common volcanic forms such as tuyas and subglacial mounds. It has a very complex volcanic history spanning from the Precambrian eon at least 3.11 billion years ago when this part of the North American continent began to form.

A volcanic belt is a large volcanically active region. Other terms are used for smaller areas of activity, such as volcanic fields. Volcanic belts are found above zones of unusually high temperature (700-1400 °C) where magma is created by partial melting of solid material in the Earth's crust and upper mantle. These areas usually form along tectonic plate boundaries at depths of 10–50 km. For example, volcanoes in Mexico and western North America are mostly in volcanic belts, such as the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt that extends 900 km from west to east across central-southern Mexico and the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province in western Canada.

The geology of the Pacific Northwest includes the composition, structure, physical properties and the processes that shape the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The region is part of the Ring of Fire: the subduction of the Pacific and Farallon Plates under the North American Plate is responsible for many of the area's scenic features as well as some of its hazards, such as volcanoes, earthquakes, and landslides.

An accretionary wedge or accretionary prism forms from sediments accreted onto the non-subducting tectonic plate at a convergent plate boundary. Most of the material in the accretionary wedge consists of marine sediments scraped off from the downgoing slab of oceanic crust, but in some cases the wedge includes the erosional products of volcanic island arcs formed on the overriding plate.
The Lachlan Fold Belt (LFB) or Lachlan Orogen is a geological subdivision of the east part of Australia. It is a zone of folded and faulted rocks of similar age. It dominates New South Wales and Victoria, also extending into Tasmania, the Australian Capital Territory and Queensland. It was formed in the Middle Paleozoic from 450 to 340 Mya. It was earlier known as Lachlan Geosyncline. It covers an area of 200,000 km2.

The geology of British Columbia is a function of its location on the leading edge of the North American continent. The mountainous physiography and the diversity of rock types and ages hint at the complex geology, which is still undergoing revision despite a century of exploration and mapping.

The Coast Range Arc was a large volcanic arc system, extending from northern Washington through British Columbia and the Alaska Panhandle to southwestern Yukon. The Coast Range Arc lies along the western margin of the North American Plate in the Pacific Northwest of western North America. Although taking its name from the Coast Mountains, this term is a geologic grouping rather than a geographic one, and the Coast Range Arc extended south into the High Cascades of the Cascade Range, past the Fraser River which is the northward limit of the Cascade Range proper.
This is a list of articles related to plate tectonics and tectonic plates.

The Philippine Mobile Belt is a complex portion of the tectonic boundary between the Eurasian Plate and the Philippine Sea Plate, comprising most of the country of the Philippines. It includes two subduction zones, the Manila Trench to the west and the Philippine Trench to the east, as well as the Philippine Fault System. Within the Belt, a number of crustal blocks or microplates which have been shorn off the adjoining major plates are undergoing massive deformation.
The Slide Mountain Terrane is a late Paleozoic terrane made of a complex of oceanic rocks in northern and southern British Columbia, Canada. The rocks of the terrane include Carboniferous limestones, fine grained quartz rich clastics, conglomerates and volcanic rocks. Permian Kalso Group mafic volcanics are included. The Kalso Group volcanics originated from an ocean ridge environment adjacent to the Permian continental margin.













